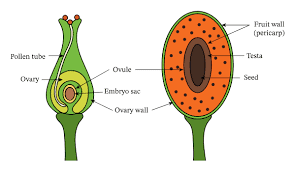
The breadfruit ovary is a crucial part of the female reproductive structure within the flower. It is a swollen, typically rounded structure located at the base of the pistil, below the style and stigma. The ovary contains one or more ovules, which are the potential seeds or future offspring of the plant.
The primary function of the ovary is to house and protect the ovules, which are the female reproductive cells. Each ovule has the potential to develop into a seed upon successful fertilization. The ovary provides a nourishing environment for the ovules to develop, supplying them with nutrients and support as they mature.
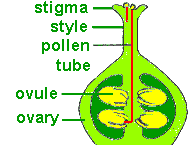
During pollination, pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of the pistil and may germinate to form pollen tubes, which grow through the style and reach the ovules within the ovary. Fertilization occurs when sperm cells from the pollen grains fuse with egg cells within the ovules, initiating seed development.
After fertilization, the ovary undergoes changes and matures into a fruit, enclosing the seeds within its protective tissues. In the case of breadfruit, the mature fruit contains numerous seeds embedded within its fleshy interior.
Overall, the breadfruit ovary plays a vital role in the reproductive process, facilitating the development of seeds and ultimately the production of fruit. It is a critical component of the flower’s female reproductive structure and is essential for the propagation and continuation of the species.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Breadfruit Ovary
1. Fruit Formation: The breadfruit ovary is essential for fruit formation, as it houses the ovules that, once fertilized, develop into seeds within the fruit.
2. Agricultural Production: Healthy ovaries ensure successful fruit development, contributing to agricultural production and providing a valuable food source for local consumption and commercial markets.
3. Culinary Applications: Breadfruit ovaries are not consumed directly, but the fruits produced from successful pollination are widely used in culinary dishes, offering versatility in cooking methods and culinary creativity.
4. Food Security: Breadfruit ovaries support food security by enabling the production of a nutritious and abundant food source that can be processed into various culinary products, helping to alleviate hunger and malnutrition.
5. Horticulture: Understanding breadfruit ovary development and morphology guides horticultural practices such as pollination management, fruit thinning, and irrigation scheduling, optimizing fruit production and tree health in orchards and gardens.
6. Genetic Studies: Breadfruit ovaries are studied by botanists and geneticists to understand their reproductive biology, genetic diversity, and breeding patterns, facilitating crop improvement efforts and conservation strategies.
7. Sustainable Agriculture: Breadfruit ovaries contribute to sustainable agriculture by supporting natural pollination processes, reducing the need for chemical inputs, and promoting ecosystem health and biodiversity in agroecosystems.
8. Cultural Significance: In some cultures, breadfruit trees and their reproductive parts, including the ovaries, hold cultural or symbolic significance, associated with traditional beliefs, rituals, or folklore, contributing to cultural heritage and identity.
9. Ecotourism: Breadfruit ovaries and their role in fruit production may be showcased in ecotourism destinations such as fruit orchards or agricultural farms, where visitors can learn about breadfruit cultivation, flowering cycles, and pollination processes firsthand.
10. Food Sovereignty: Breadfruit ovaries support food sovereignty by providing communities with the means to cultivate and harvest their own food resources, reducing dependence on imported goods and strengthening local food systems.
11. Botanical Illustrations: Breadfruit ovaries are depicted in botanical illustrations, paintings, and scientific diagrams, documenting their structure and function for educational and scientific purposes, aiding in plant identification and classification.
12. Plant Reproduction Studies: Breadfruit ovaries are utilized in plant reproduction studies investigating aspects of plant physiology, reproductive ecology, or molecular biology, advancing scientific knowledge and understanding of plant systems.
13. Environmental Conservation: Breadfruit ovaries and their role in fruit production contribute to ecosystem health and biodiversity conservation by supporting plant reproduction and maintaining plant-pollinator interactions in natural habitats.
14. Landscape Design: Breadfruit ovaries contribute to the aesthetic appeal of landscapes when trees are in bloom, attracting pollinators and adding color, texture, and visual interest to outdoor environments such as parks, gardens, or urban spaces.
15. Floriculture: Breadfruit ovaries may be utilized in floriculture practices such as flower arrangement, bouquet design, or landscaping, providing unique and exotic floral elements for decorative purposes.
16. Genetic Resources: Breadfruit ovaries represent valuable genetic resources for breeding programs aimed at developing new cultivars with improved traits such as disease resistance, yield potential, or fruit quality, contributing to crop improvement efforts.
17. Medicinal Research: Compounds extracted from breadfruit ovaries may have potential pharmaceutical properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, or antimicrobial effects, which can be utilized in medicinal research and drug discovery efforts.
Read Also: 10 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Banisteriopsis caapi (Ayahuasca)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Breadfruit Ovary
1. Fruits: The primary product derived from the breadfruit ovary is the breadfruit itself, which serves as a valuable food source in many tropical regions, providing nutrition and sustenance to millions of people worldwide.
2. Food Products: Breadfruit fruits produced as a result of successful pollination can be processed into various food products such as breadfruit flour, chips, crisps, snacks, or canned goods, offering diverse culinary options and extending the shelf life of the fruit.
3. Culinary Ingredients: Breadfruit fruits can be cooked, roasted, boiled, mashed, or incorporated into a wide range of culinary dishes, including soups, stews, curries, stir-fries, salads, desserts, and beverages, providing flavor, texture, and nutrition to meals.
4. Nutritional Supplements: Breadfruit fruits are rich in carbohydrates, dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients, making them a nutritious and wholesome dietary supplement for addressing nutrient deficiencies and promoting overall health and well-being.
5. Animal Feed: Breadfruit fruits not suitable for human consumption or processing can be utilized as animal feed for livestock, poultry, or aquaculture, providing a valuable source of energy, protein, and nutrients in animal diets.
6. Industrial Applications: Breadfruit fruits contain starches, sugars, and fibers that can be extracted and utilized in various industrial applications such as biofuel production, biodegradable packaging, or textile manufacturing, contributing to sustainable and eco-friendly industries.
7. Medicinal Extracts: Compounds extracted from breadfruit fruits may have potential pharmaceutical properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, or antimicrobial effects, which can be utilized in the development of herbal remedies, dietary supplements, or medicinal drugs.
8. Cosmetic Ingredients: Extracts or distillates obtained from breadfruit fruits may be used as cosmetic ingredients in skincare, haircare, or personal care products, offering moisturizing, nourishing, or rejuvenating properties to enhance the beauty and well-being of consumers.
9. Horticultural Uses: Breadfruit fruits can be used as horticultural resources for planting, propagation, or landscaping purposes, providing shade, shelter, or orn
amental value in gardens, parks, or urban green spaces.
10. Environmental Benefits: Breadfruit trees, including their ovaries and fruits, provide various environmental benefits such as carbon sequestration, soil conservation, erosion control, and habitat restoration, contributing to ecosystem health and resilience.
Read Also: The Curry Inflorescence: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Breadfruit Ovary
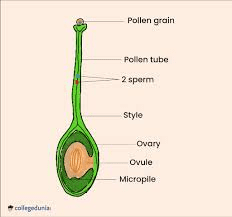
1. How does the breadfruit ovary contribute to fruit production?
The breadfruit ovary houses the ovules, which, once fertilized, develop into seeds within the fruit, essential for fruit formation and agricultural production.
2. Are breadfruit ovaries important for agricultural production?
Yes, healthy ovaries ensure successful fruit development, contributing to agricultural production and providing a valuable food source for local consumption and commercial markets.
3. Can compounds extracted from the breadfruit ovary be used in medicine?
Compounds extracted from the breadfruit ovary may have potential pharmaceutical properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, or antimicrobial effects, which can be utilized in medicinal research and drug discovery efforts.
4. How are breadfruit ovaries utilized in horticulture?
Understanding breadfruit ovary development and morphology guides horticultural practices such as pollination management, fruit thinning, and irrigation scheduling, optimizing fruit production and tree health in orchards and gardens.
5. Are breadfruit ovaries important for food security?
Yes, breadfruit ovaries support food security by enabling the production of a nutritious and abundant food source that can be processed into various culinary products, helping to alleviate hunger and malnutrition.
6. Can breadfruit ovaries attract pollinators?
Breadfruit ovaries produce nectar and are visited by pollinators such as bees, butterflies, or birds, which facilitate pollination and fruit production in breadfruit trees.
7. What are the cultural significances associated with breadfruit ovaries?
In some cultures, breadfruit trees and their reproductive parts, including the ovaries, hold cultural or symbolic significance, associated with traditional beliefs, rituals, or folklore, contributing to cultural heritage and identity.
8. Do breadfruit ovaries benefit the environment?
Yes, breadfruit ovaries, along with the fruits they produce, provide various environmental benefits such as carbon sequestration, soil conservation, erosion control, and habitat restoration, contributing to ecosystem health and resilience.
9. How can breadfruit ovaries support sustainable agriculture?
Breadfruit ovaries contribute to sustainable agriculture by supporting natural pollination processes, reducing the need for chemical inputs, and promoting ecosystem health and biodiversity in agroecosystems.
10. Are breadfruit ovaries utilized in industrial applications?
Compounds extracted from breadfruit ovaries may have potential industrial applications in sectors such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, or biotechnology, contributing to sustainable and eco-friendly industries.
Read Also: Hydroponics Guide 101: All You Need to Know About it






