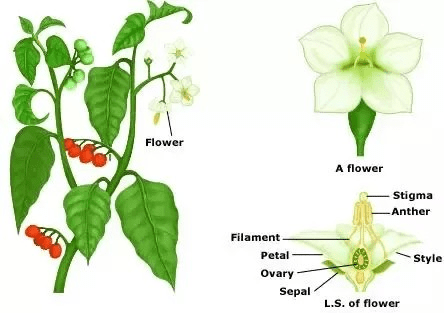
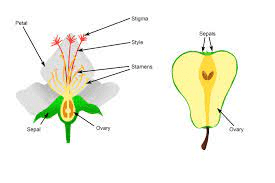
The Breadfruit styles of breadfruit flowers typically have a slender and elongated shape. They extend upward from the ovary, often appearing as fine filaments or tubes. These styles serve as conduits for pollen to reach the ovules during the process of pollination, which is crucial for fertilization and subsequent seed development.
The surface of the styles may have specialized structures to facilitate pollen adhesion and germination, ensuring successful reproduction.
Breadfruit flowers usually possess multiple styles, each connected to an individual ovule within the ovary. This arrangement allows for efficient pollination and fertilization, increasing the chances of successful seed formation.
After fertilization, the styles may undergo various changes as the ovules develop into seeds within the ovary. Eventually, the mature seeds may be dispersed, contributing to the plant’s reproductive success and propagation.
Understanding the structure and function of breadfruit flower styles provides valuable insights into the reproductive biology of this plant species. By studying these botanical features, researchers gain knowledge essential for breeding programs, conservation efforts, and understanding the ecological roles of breadfruit in its native habitats.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Breadfruit Styles
1. Food Security: Breadfruit styles play a crucial role in food security, particularly in tropical regions where they are abundant. They serve as a staple food source for many communities, providing a reliable source of carbohydrates.
2. Dietary Diversity: Incorporating breadfruit styles into diets enhances dietary diversity, offering essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
3. Culinary Delicacies: Breadfruit styles are versatile ingredients in various culinary dishes, ranging from savory stews to sweet desserts. For instance, they can be fried, roasted, mashed, or baked to create flavorful meals.
4. Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, breadfruit styles are used in traditional medicine for their potential health benefits. They are believed to possess medicinal properties that can alleviate certain ailments.
5. Livelihood Opportunities: The cultivation and sale of breadfruit styles provide livelihood opportunities for farmers and entrepreneurs, contributing to economic development in rural areas.
6. Export Industry: In regions where breadfruit styles are abundant, they can be exported to international markets, generating revenue and foreign exchange.
7. Sustainable Agriculture: Breadfruit styles are a sustainable crop option due to their ability to thrive in diverse climates and soils, requiring minimal inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides.
8. Agroforestry: Breadfruit trees, which produce breadfruit styles, contribute to agroforestry systems by providing shade, improving soil fertility, and supporting biodiversity.
9. Food Preservation: Breadfruit styles can be preserved through various methods such as drying, canning, and freezing, ensuring year-round availability even during off-seasons.
10. Culinary Tourism: Regions known for their breadfruit styles attract culinary tourists seeking authentic food experiences, thereby boosting local economies through tourism revenue.
11. Climate Resilience: Breadfruit trees are resilient to climate change, making them valuable assets in climate adaptation strategies for vulnerable communities.
12. Community Resilience: In times of natural disasters or food shortages, breadfruit styles serve as a reliable food source, contributing to community resilience and food security.
13. Livestock Feed: Breadfruit styles can be used as feed for livestock, providing a nutritious supplement to their diets and reducing the dependency on conventional feed sources.
14. Bioenergy Production: Breadfruit styles can be utilized in bioenergy production through processes such as fermentation and anaerobic digestion, contributing to renewable energy initiatives.
15. Soil Improvement: The leaves and other organic matter from breadfruit trees contribute to soil improvement, enhancing fertility and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
16. Culinary Innovation: Chefs and food enthusiasts continually explore new ways to incorporate breadfruit styles into innovative dishes, contributing to culinary diversity and creativity.
17. Cultural Significance: Breadfruit styles hold cultural significance in many societies, featuring prominently in rituals, ceremonies, and traditional cuisines, preserving cultural heritage and identity.
18. Nutritional Security: Including breadfruit styles in diets enhances nutritional security by providing a source of essential nutrients, especially in regions where access to diverse foods is limited.
Read Also: Soybean Hypocotyl: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Breadfruit Styles
1. Breadfruit Flour: Breadfruit styles can be dried and milled into flour, which can be used as a gluten-free alternative in baking and cooking.
2. Breadfruit Chips: Sliced breadfruit styles can be fried or baked to make crispy chips, offering a nutritious snack option.
3. Breadfruit Puree: Cooked and mashed breadfruit styles can be processed into a smooth puree, suitable for various culinary applications such as soups, sauces, and baby food.
4. Breadfruit Jam: Breadfruit styles can be cooked down with sugar and flavorings to make delicious jams and preserves, perfect for spreading on toast or pastries.
5. Breadfruit Juice: Fresh breadfruit styles can be juiced to make a refreshing beverage, rich in vitamins and minerals.
6. Breadfruit Wine: Fermented breadfruit juice can be transformed into wine, offering a unique and flavorful alcoholic beverage.
7. Breadfruit Peel Powder: Dried breadfruit peels can be ground into a powder, which can be used in cosmetics, skincare products, or as a natural dye.
8. Breadfruit Leaf Tea: Dried breadfruit leaves can be brewed into a fragrant tea, known for its potential health benefits and soothing properties.
9. Breadfruit Seed Oil: The seeds of breadfruit styles can be pressed to extract oil, which can be used for cooking, skincare, and industrial purposes.
10. Animal Feed Supplements: Residues from processing breadfruit styles, such as peels and seeds, can be utilized as feed supplements for livestock, enriching their diets with essential nutrients.
11. Biofuel Production: Breadfruit styles can be converted into biofuels such as ethanol or biodiesel, offering a renewable energy source for transportation and power generation.
12. Biodegradable Packaging: Bioplastics derived from breadfruit styles offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic packaging, reducing environmental impact.
13. Medicinal Extracts: Active compounds extracted from breadfruit styles have potential medicinal properties and can be used in pharmaceuticals or herbal remedies.
14. Organic Fertilizers: Compost made from breadfruit styles and other organic materials serves as a natural fertilizer, enriching soil fertility and promoting sustainable agriculture.
15. Textile Dyes: Extracts from breadfruit styles can be used as natural dyes for textiles, offering a sustainable alternative to synthetic dyes.
16. Flavor Enhancers: Extracts and essences from breadfruit styles can be used as natural flavor enhancers in food and beverage products, adding depth and complexity to culinary creations.
17. Cosmetic Ingredients: Bioactive compounds from breadfruit styles can be incorporated into cosmetics and skincare products for their moisturizing, antioxidant, and anti-aging properties.
Read Also: Soybean Lateral roots: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Breadfruit Styles
1. What nutritional benefits do breadfruit styles offer?
Breadfruit styles are rich in carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, providing essential nutrients for a balanced diet.
2. How can breadfruit styles be incorporated into everyday meals?
Breadfruit styles can be boiled, roasted, fried, or mashed and used in various dishes such as soups, stews, salads, and desserts.
3. Are breadfruit styles suitable for people with gluten intolerance?
Yes, breadfruit styles are naturally gluten-free, making them a suitable alternative for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
4. Can breadfruit styles be grown in temperate climates?
While breadfruit trees thrive in tropical regions, some varieties can be grown in subtropical or temperate climates with proper care and protection from frost.
5. Are there any health risks associated with consuming breadfruit styles?
When cooked properly, breadfruit styles are generally safe to consume. However, consuming raw or undercooked breadfruit styles may cause digestive discomfort.
6. How can I store breadfruit styles for long-term use?
Breadfruit styles can be stored in a cool, dry place for short-term use or preserved through methods such as drying, freezing, or canning for long-term storage.
7. Can breadfruit styles be used in vegan and vegetarian diets?
Yes, breadfruit styles are plant-based and can be incorporated into vegan and vegetarian diets as a nutritious option.
Read Also: Wool Production: Complete Production Guide