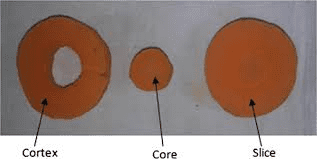
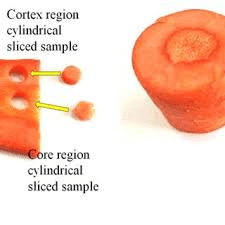
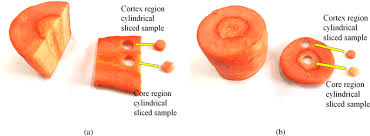
The carrot core is composed primarily of xylem tissues, which are specialized for the conduction of water and dissolved nutrients from the soil to the rest of the plant. This central vascular system is essential for the carrot’s overall health and development.
Surrounding the core is the phloem, which transports the sugars produced by photosynthesis from the leaves to the root, where they are stored. The distinction between the xylem and phloem can often be seen in the different coloration and texture of the carrot, with the core typically being denser and sometimes differing slightly in color from the surrounding cortex.
Anatomically, the carrot core consists of several concentric layers of xylem cells. These cells are primarily responsible for water conduction and are arranged in a way that maximizes the efficiency of nutrient transport.
The xylem vessels are strengthened by lignin, a complex organic polymer that provides rigidity and helps maintain the structural integrity of the core under various soil conditions. This structural support is crucial for the carrot as it grows downward into the soil, often encountering varying degrees of resistance and pressure.
The development of the carrot core begins early in the growth cycle of the plant. During the seedling stage, the primary root begins to differentiate into the xylem and phloem tissues.
As the carrot matures, secondary growth occurs, and the xylem expands, forming the characteristic core. This growth process is regulated by a combination of genetic factors and environmental conditions, including soil quality, water availability, and temperature.
The carrot core is not only vital for the plant’s physiological functions but also impacts its culinary properties. The texture and flavor of the carrot can vary between the core and the outer cortex. The core tends to be firmer and less sweet than the surrounding tissue, which can influence how the carrot is used in cooking.
In some varieties, the core may be more pronounced and woody, while in others, it may be tender and barely distinguishable from the rest of the root.
Nutritionally, the carrot core contributes to the overall value of the carrot. It contains significant amounts of water, fiber, and essential nutrients such as vitamins A, C, K, and various B vitamins, as well as minerals like potassium, calcium, and magnesium. The fibrous nature of the core aids in digestive health, providing bulk that helps regulate bowel movements and supports a healthy digestive system.
Carrot breeding programs often focus on the characteristics of the core to enhance the vegetable’s desirability and nutritional profile. Breeders aim to produce carrots with tender, less woody cores to improve their texture and taste. They also select for cores with higher nutrient densities, ensuring that the health benefits of consuming carrots are maximized.
The carrot core is a central component of the root, essential for water and nutrient transport, structural support, and overall plant health. Its development and characteristics are influenced by genetic and environmental factors, impacting both the agricultural and culinary value of the carrot. Understanding the scientific aspects of the carrot core allows for better cultivation practices and the continued enhancement of this valuable vegetable.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Carrot Core
1. Nutritional Value: Carrot cores are rich in vitamins A, C, K, and potassium, making them a vital component in diets for maintaining good health.
2. Food Industry: Carrot cores are used in various processed food products such as juices, baby foods, and snacks, contributing to the food industry.
3. Animal Feed: Carrot cores are often included in animal feed, providing essential nutrients to livestock, particularly rabbits and horses.
4. Health Supplements: Extracts from carrot cores are used in health supplements for their high beta-carotene content, which is essential for vision and immune health.
5. Cosmetic Industry: Carrot core extracts are used in cosmetic products like creams and lotions for their skin-enhancing properties.
6. Natural Coloring: The natural pigments in carrot cores are used as colorants in the food and cosmetic industries, offering a healthy alternative to synthetic dyes.
7. Culinary Uses: Carrot cores are used in cooking and baking, adding flavor, texture, and nutrition to dishes such as soups, salads, and cakes.
8. Agricultural Benefits: The by-products of carrot core processing are used as organic fertilizers, enriching the soil and promoting sustainable farming practices.
9. Beverages: Carrot core juice is a popular health drink, rich in nutrients and antioxidants, promoting overall health and wellness.
10. Food Fortification: Carrot core powder is used to fortify foods with essential nutrients, enhancing their nutritional profile.
11. Pet Food: Carrot cores are included in pet food formulations, providing essential vitamins and minerals to pets.
12. Traditional Medicine: Carrot cores have been used in traditional medicine for their healing properties, including digestive aid and anti-inflammatory benefits.
13. Baking Industry: Carrot core extracts are used in the baking industry to enhance the flavor and nutritional content of baked goods.
14. Food Preservation: Carrot cores are used in food preservation techniques, such as pickling, to extend the shelf life of vegetables.
15. Dairy Products: Carrot core extracts are used in dairy products like yogurt and cheese for added flavor and nutrition.
16. Biotechnology: Carrot cores are used in biotechnological research for developing new food products and improving crop varieties.
17. Culinary Arts: Chefs use carrot cores creatively in gourmet dishes for their vibrant color and sweet flavor.
18. Export Commodity: Carrot cores are part of the export market for fresh and processed carrots, contributing to international trade.
Read Also Scrapie in Sheep and Goats: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Carrot Core
1. Carrot Juice: Made by extracting the liquid from carrot cores, this beverage is rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
2. Carrot Powder: Produced by drying and grinding carrot cores, used for fortifying foods with nutrients.
3. Carrot Oil: Extracted from carrot cores, used in cosmetics and skincare products for its moisturizing properties.
4. Carrot Puree: Made by blending carrot cores, used in baby foods and as a base for soups and sauces.
5. Carrot Extract: Concentrated carrot core extract used in health supplements and food flavoring.
6. Animal Feed Pellets: Carrot cores are processed into pellets, providing a nutritious feed option for livestock.
7. Organic Fertilizer: By-products of carrot core processing are composted into organic fertilizers, enriching the soil.
8. Carrot Chips: Sliced and dehydrated carrot cores, used as a healthy snack option.
9. Carrot Syrup: Made from carrot core extract, used as a natural sweetener in foods and beverages.
10. Carrot Infused Water: Water infused with carrot cores, providing a nutritious and refreshing drink.
11. Carrot Soups: Pureed carrot cores used as a base for nutritious soups.
12. Carrot Tea: Dried carrot cores used to make a herbal tea rich in vitamins.
13. Carrot Flour: Made by grinding dried carrot cores, used in baking and cooking.
14. Cosmetic Creams: Carrot core extracts incorporated into skincare creams for their nourishing properties.
15. Carrot Smoothies: Blended carrot cores used in smoothies for a nutrient-packed beverage.
16. Carrot Supplements: Capsules containing carrot core extract, used as dietary supplements.
17. Carrot Bread: Bread made with carrot core flour, adding nutrition and flavor.
Read Also Management of Breeding Stock in Sheep and Goats
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Carrot Core
1. What is the carrot core?
The carrot core is the central part of the carrot, often firmer and more fibrous than the outer parts.
2. Are carrot cores nutritious?
Yes, carrot cores are rich in vitamins A, C, K, and potassium, contributing to a healthy diet.
3. Can carrot cores be used in cooking?
Absolutely, carrot cores can be used in various dishes such as soups, salads, and baked goods.
4. Are carrot cores used in animal feed?
Yes, carrot cores are commonly included in animal feed, providing essential nutrients for livestock.
5. How is carrot core extract used in cosmetics?
Carrot core extract is used in creams and lotions for its skin-enhancing and moisturizing properties.
6. Can carrot cores be juiced?
Yes, carrot cores can be juiced, providing a nutritious beverage rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
7. What products can be made from carrot core powder?
Carrot core powder can be used in food fortification, baking, and as a natural colorant.
8. Are there any traditional medicinal uses for carrot cores?
Yes, carrot cores have been used in traditional medicine for their digestive and anti-inflammatory benefits.
9. How do carrot cores benefit agriculture?
Carrot core by-products are used as organic fertilizers, improving soil health and promoting sustainable farming.
10. Can carrot cores be used in pet food?
Yes, carrot cores are included in pet food formulations, providing essential nutrients for pets.
Read Also How to Make an Avocado Tree Bear Fruit






