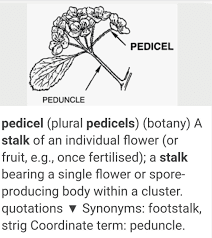
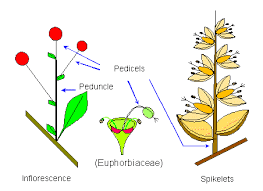
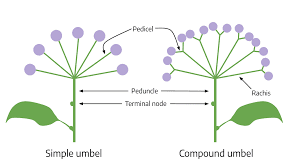
The carrot pedicels are essential botanical structure, is part of the Daucus carota plant, commonly known as the carrot. In botanical terms, a pedicel is the stalk that attaches a single flower to the main inflorescence stem, known as the peduncle. In the carrot plant, the pedicels are integral components of the umbel, which is the characteristic flower cluster.
Each umbel consists of numerous small flowers, each connected to the peduncle via its own pedicel. This arrangement is critical for both the plant’s reproductive success and its ecological interactions.
The development of carrot pedicels occurs in the second year of the plant’s biennial life cycle, when it shifts focus from vegetative growth to reproduction.
This transition is driven by hormonal changes, particularly an increase in gibberellins and cytokinins. The pedicels grow from the peduncle, which itself elongates to support the umbel. Each pedicel ensures that individual flowers are spaced appropriately, facilitating optimal access for pollinators and maximizing the exposure of flowers to sunlight.
Structurally, carrot pedicels are slender but strong, capable of supporting the small, delicate flowers they hold. They are composed of several layers, including an outer epidermis, a supportive cortex, and a central vascular bundle. The vascular bundle, which includes xylem and phloem tissues, is vital for transporting water, nutrients, and photosynthetic products from the plant’s roots to the flowers. This transportation system supports the metabolic needs of the flowers, ensuring their growth and the development of seeds.
The primary function of carrot pedicels is to present the flowers in a manner that maximizes reproductive success. By spacing the flowers out from the central peduncle, the pedicels ensure that each flower is accessible to pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other insects.
This arrangement not only facilitates effective pollination but also reduces competition among flowers for pollinator visits. The accessibility and visibility of the flowers are crucial for cross-pollination, which enhances genetic diversity and leads to the production of viable seeds.
Environmental factors such as light, temperature, and soil nutrients significantly influence the growth and development of carrot pedicels. Adequate sunlight and favorable temperatures stimulate their elongation, while sufficient soil nutrients support their structural integrity and function. Stress factors like drought or nutrient deficiencies can hinder pedicel development, adversely affecting the plant’s reproductive success.
After pollination, the flowers develop into small, dry fruits called schizocarps, each containing two seeds. The pedicels continue to play a role in supporting these developing fruits until they are mature and ready for dispersal. The structural design of the pedicels aids in the effective distribution of seeds, which can be dispersed by wind or through animal interactions.
Understanding the role of carrot pedicels extends beyond basic botanical knowledge; it has practical implications in agriculture and horticulture. Efficient pollination facilitated by well-developed pedicels leads to higher seed production, which is crucial for the propagation of carrot crops. Furthermore, insights into pedicel development and function can inform breeding programs aimed at improving crop yield and quality.
In summary, carrot pedicels are vital structures that support the flowers of the carrot plant, playing a crucial role in its reproductive process. They ensure optimal flower presentation for pollination, facilitate nutrient transport, and support seed development and dispersal. The study and understanding of pedicel biology are essential for enhancing agricultural practices and ensuring the sustainability of carrot cultivation.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Carrot Pedicels
1. Seed Production: Carrot pedicels support flowers, facilitating efficient pollination and the production of viable seeds essential for future carrot crops.
2. Pollinator Attraction: By properly spacing flowers, pedicels make them more accessible to pollinators, ensuring effective pollination and improving crop yields.
3. Genetic Diversity: Effective pollination supported by pedicels leads to cross-pollination, enhancing genetic diversity and crop resilience.
4. Agricultural Research: Understanding pedicel development aids in breeding programs aimed at improving carrot yield and quality.
5. Botanical Education: Pedicels serve as excellent examples in educational settings for teaching plant anatomy and reproductive biology.
6. Organic Farming: Pedicels, when decomposed, contribute to organic matter in soil, enhancing soil fertility and structure.
7. Livestock Feed: Residual pedicels can be processed into feed for livestock, providing an economical and nutritious resource.
8. Compost Production: Pedicels are composted to produce nutrient-rich organic fertilizer, promoting sustainable agriculture.
9. Mulch Material: Shredded pedicels can be used as mulch to suppress weeds, retain soil moisture, and regulate soil temperature.
10. Companion Planting: Carrot pedicels in companion planting systems attract beneficial insects, enhancing overall garden health.
11. Pest Management: The presence of pedicels attracts beneficial insects that prey on pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
12. Soil Erosion Control: Pedicels contribute to mulch that prevents soil erosion and maintains soil integrity.
13. Craft Materials: Dried pedicels can be used in various crafts, adding a natural element to decorative projects.
14. Garden Supports: The sturdy nature of pedicels makes them useful as natural supports for climbing plants in gardens.
15. Environmental Conservation: Using pedicels in sustainable practices like composting and mulching aids in environmental conservation efforts.
16. Carbon Sequestration: Composting pedicels helps sequester carbon, reducing the carbon footprint of agricultural activities.
17. Biodiversity Support: Pedicels help maintain biodiversity by supporting a variety of pollinators and beneficial insects.
18. Educational Programs: Pedicels are used in programs that teach sustainable farming practices and environmental stewardship.
Read Also Scrapie in Sheep and Goats: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Carrot Pedicels
1. Compost: Decomposed pedicels enrich soil with organic matter, enhancing soil fertility and structure.
2. Mulch: Shredded pedicels are used as mulch to improve soil moisture retention and weed suppression.
3. Livestock Feed: Residual pedicels are processed and added to livestock feed for a nutritious supplement.
4. Organic Fertilizer: Pedicels are composted to create organic fertilizer, providing essential nutrients to crops.
5. Craft Materials: Dried pedicels are used in making natural decorations and craft projects.
6. Natural Pesticide: Extracts from pedicels can be used in formulations to repel pests and protect crops.
7. Soil Conditioner: Decomposed pedicels are used to improve soil health and fertility.
8. Plant Supports: The robust nature of dried pedicels can be used as natural supports for garden plants.
9. Companion Planting: Pedicels are utilized in companion planting to attract beneficial insects and improve crop yields.
10. Educational Tools: Pedicels are used in educational settings to demonstrate plant growth and reproductive processes.
11. Environmental Conservation: Pedicels contribute to conservation efforts by promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
12. Erosion Control: Decomposed pedicels create mulch that helps control soil erosion in agricultural fields.
13. Carbon Sequestration: Using pedicels in composting helps sequester carbon, reducing the environmental impact.
14. Garden Aesthetics: Pedicels enhance the visual appeal of gardens by adding natural elements.
15. Natural Dye: Extracts from pedicels can be used to create natural dyes for textiles and other materials.
16. Pest Management: Pedicels attract beneficial insects that help manage pest populations naturally.
17. Biochar: Pedicels can be processed into biochar, which is used to improve soil health and increase agricultural productivity.
Read Also Management of Breeding Stock in Sheep and Goats
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Carrot Pedicels
1. What is a carrot pedicel?
A carrot pedicel is the stalk that connects an individual flower to the main inflorescence stem (peduncle) of the carrot plant.
2. How do carrot pedicels benefit pollination?
Pedicels space the flowers out from the central stem, making them more accessible to pollinators, thus enhancing pollination efficiency.
3. Can carrot pedicels be used as livestock feed?
Yes, residual pedicels can be processed into a nutritious feed for livestock.
4. What products can be made from carrot pedicels?
Products include compost, mulch, organic fertilizer, craft materials, and natural pesticides.
5. How do carrot pedicels contribute to organic farming?
They decompose into organic matter that improves soil health and fertility, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
6. Are carrot pedicels useful in pest management?
Yes, the presence of pedicels attracts beneficial insects that help control pest populations.
7. What role do carrot pedicels play in environmental conservation?
They promote sustainable agricultural practices, reduce waste, and help in carbon sequestration.
8. Can carrot pedicels be used in garden aesthetics?
Yes, they add visual appeal and provide natural support structures in gardens.
9. How do carrot pedicels help in soil erosion control?
Decomposed pedicels create mulch that prevents soil erosion and maintains soil integrity.
10. Are carrot pedicels used in educational programs?
Yes, they are used to teach about plant anatomy, growth, and sustainable farming practices.
Read Also How to Make an Avocado Tree Bear Fruit






