Cocoa or cacao pistils refer to the reproductive structures found within the flowers of the cocoa tree, scientifically known as Theobroma cacao. These pistils play a crucial role in the pollination process, ultimately leading to the formation of cocoa pods, which contain the seeds used to produce cocoa and chocolate products.
The cocoa or cacao flower typically consists of several components, including the pistil, stamen, petals, and sepals. The pistil, often referred to as the female reproductive organ, is composed of three main parts: the stigma, style, and ovary.
The stigma serves as the receptive surface for pollen grains, while the style provides support and connects the stigma to the ovary. Within the ovary, ovules develop, eventually maturing into seeds upon successful fertilization.
Pollination is essential for the reproduction of cocoa trees and the subsequent production of cocoa beans. Cocoa trees are primarily pollinated by tiny insects such as midges, which are attracted to the flowers’ sweet scent and nectar.
As the insects move from flower to flower in search of food, they inadvertently transfer pollen grains from the stamens (male reproductive organs) to the stigmas (female reproductive organs) of neighboring flowers, facilitating fertilization.
Once fertilization occurs, the ovules within the ovary develop into seeds, while the surrounding tissues swell and mature into a pod-like structure known as a cocoa pod.
These pods vary in size, shape, and color depending on the cocoa variety and environmental conditions. Within each pod, numerous cocoa beans are embedded in a pulp-like substance. The pistils, having fulfilled their reproductive function, eventually wither and fall off as the pods mature.
Cocoa pistils are critical for ensuring successful pollination and the subsequent development of cocoa pods. A healthy population of cocoa pistils is essential for maximizing cocoa yields and maintaining the genetic diversity of cocoa trees. Factors such as climate change, habitat loss, and pesticide use can adversely affect pollinator populations, potentially leading to reduced cocoa production and quality.
Cocoa or cacao pistils are integral components of the cocoa tree’s reproductive anatomy, playing a vital role in pollination and the production of cocoa pods. Understanding the structure and function of these pistils is crucial for sustainable cocoa cultivation and ensuring the continued availability of cocoa beans for chocolate production.
By safeguarding pollinator populations and promoting biodiversity, farmers can enhance cocoa yields and maintain the long-term viability of the cocoa industry.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Cocoa/Cacao Pistils
1. Cocoa Bean Production: The primary economic importance of cocoa pistils lies in their contribution to cocoa bean production. Through the process of pollination, pistils facilitate the formation of cocoa pods, which contain the seeds used to produce cocoa powder, cocoa butter, and chocolate products. A healthy population of pistils is crucial for ensuring adequate pollination and maximizing cocoa yields, thereby supporting the multi-billion dollar global cocoa industry.
2. Chocolate Industry: Cocoa pistils indirectly support the chocolate industry by enabling the production of cocoa beans, which are the main ingredient in chocolate manufacturing. High-quality cocoa beans, produced through efficient pollination facilitated by pistils, are essential for producing premium chocolate products prized by consumers worldwide.
3. Agricultural Economy: Cocoa cultivation, driven in part by the economic value of cocoa pistils, contributes significantly to the agricultural economy of cocoa-producing regions. Farmers rely on cocoa cultivation as a source of income and livelihood, with the sale of cocoa beans providing essential revenue for rural communities in countries such as Ivory Coast, Ghana, and Indonesia.
4. Pollination Services: In addition to their direct role in cocoa production, cocoa pistils provide valuable pollination services that benefit other crops and ecosystems. Cocoa trees attract pollinators such as midges, bees, and butterflies, which also contribute to the pollination of nearby plants and agricultural crops. This ecosystem service supports biodiversity and enhances agricultural productivity in cocoa-growing regions.
5. Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, cocoa pistils are used in traditional medicine for their purported health benefits. While scientific evidence supporting the medicinal properties of cocoa pistils is limited, they are believed to possess antioxidant properties and may be used in herbal remedies or dietary supplements.
6. Research and Development: Cocoa pistils serve as subjects of scientific research aimed at improving cocoa cultivation practices, enhancing pollination efficiency, and developing new cocoa varieties with desirable traits such as disease resistance and high yield potential. Research findings contribute to the advancement of sustainable cocoa production methods and the resilience of cocoa farming systems in the face of climate change and other challenges.
7. Culinary Applications: While not as widely recognized as other parts of the cocoa plant, cocoa pistils may have potential culinary applications in certain cuisines or as flavoring agents in food and beverage products. Creative chefs and food artisans may explore innovative ways to incorporate cocoa pistils into recipes, leveraging their unique flavor profile and nutritional attributes.
Read Also: 10 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Convolvulus prostratus (Bindweed)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Cocoa/Cacao Pistils
Cocoa or cacao pistils offer various products and by-products that contribute to diverse industries. Below are some examples and explanations of the products and by-products derived from cocoa pistils:
1. Cocoa Beans: The primary product derived from cocoa pistils is cocoa beans. After successful pollination and fertilization, the ovules within the cocoa pistils develop into seeds, which are harvested and processed to produce cocoa beans. These beans serve as the raw material for manufacturing cocoa powder, cocoa butter, and chocolate products.

2. Cocoa Powder: Cocoa beans obtained from cocoa pistils undergo processing to extract cocoa solids, which are then finely ground to produce cocoa powder. Cocoa powder is widely used in baking, confectionery, and beverage industries to impart chocolate flavor and color to various products such as cakes, cookies, hot chocolate, and desserts.

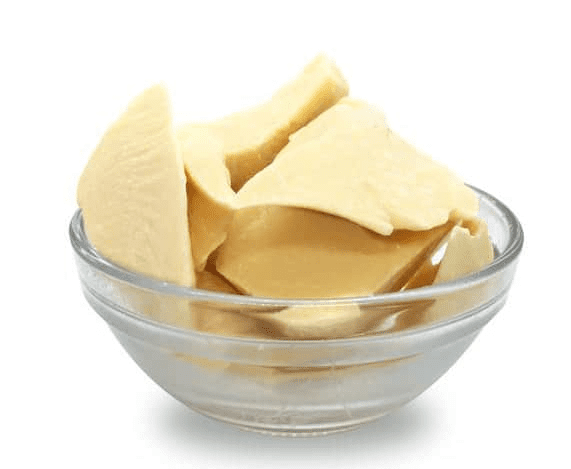
3. Cocoa Butter: Another valuable product derived from cocoa beans is cocoa butter. During cocoa bean processing, the fat content of the beans is extracted to obtain cocoa butter. This creamy, aromatic fat is used in chocolate manufacturing, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products due to its moisturizing properties and smooth texture.

4. Chocolate Products: Cocoa beans sourced from cocoa pistils are the key ingredient in the production of chocolate products such as chocolate bars, truffles, and candies. Chocolate manufacturers combine cocoa solids, cocoa butter, sugar, and other ingredients to create a wide range of chocolate confections enjoyed by consumers worldwide.
5. Cocoa Husks and Shells: After cocoa beans are processed, the outer husks and shells are left behind as by-products. These cocoa husks and shells can be utilized in various ways, including as mulch for gardening, animal feed additives, or biomass fuel for energy generation. Some companies also use cocoa husks to produce cocoa tea or infusions.
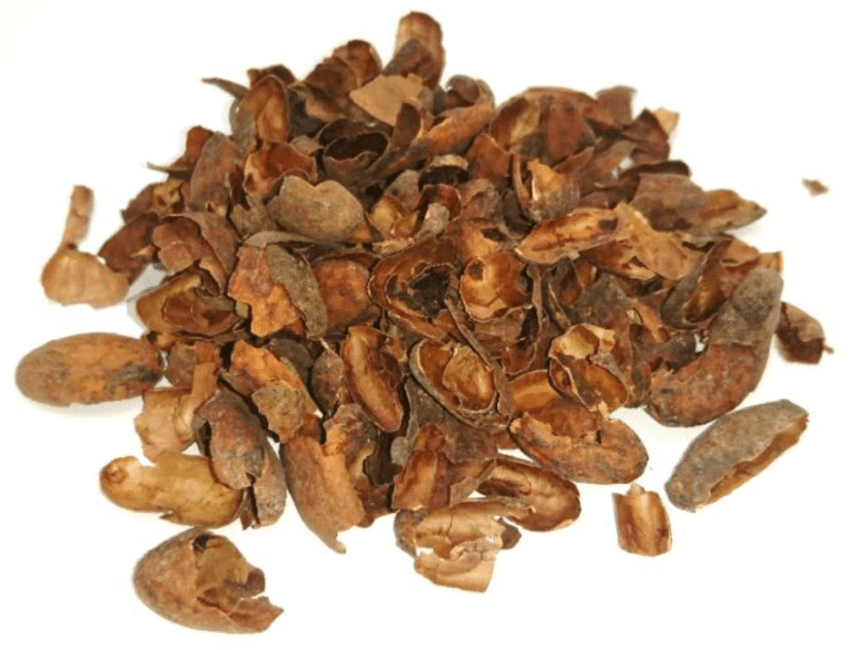

6. Fertilizer: Cocoa husks and shells can be composted and converted into organic fertilizer, enriching the soil with essential nutrients and improving soil structure. Farmers in cocoa-growing regions often utilize cocoa by-products as natural fertilizers to enhance soil fertility and promote healthy crop growth.
7. Phytochemical Extracts: Research has shown that cocoa pistils contain phytochemical compounds with potential health benefits, including antioxidants and flavonoids. Phytochemical extracts derived from cocoa pistils may be used in dietary supplements, functional foods, and nutraceuticals aimed at promoting health and well-being.
8. Bioplastics and Biofuels: Scientists are exploring the potential use of cocoa by-products, including husks and shells, as feedstock for producing bioplastics and biofuels. By converting cocoa waste into renewable materials, such as biodegradable plastics or bioethanol, researchers aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and minimize environmental impacts associated with traditional plastic production.
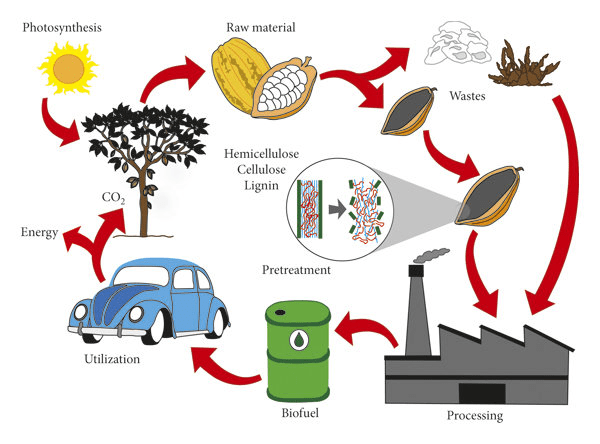
Cocoa or cacao pistils yield various valuable products and by-products that contribute to the food, beverage, cosmetics, pharmaceutical, and agricultural industries. From cocoa beans and chocolate products to fertilizer and biofuels, the utilization of cocoa pistils supports economic sustainability and promotes resource efficiency in cocoa-producing regions.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Artemisia Yam Sepals (Big Sagebrush)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cocoa/Cacao Pistils
1. What are cocoa pistils?
Cocoa pistils refer to the reproductive structures found within the flowers of the cocoa tree (Theobroma cacao). They consist of the female reproductive organs responsible for receiving pollen grains during pollination.
2. What is the role of cocoa pistils in cocoa production?
Cocoa pistils play a crucial role in pollination, facilitating the fertilization of cocoa flowers and the subsequent formation of cocoa pods. These pods contain the seeds used to produce cocoa beans, the primary ingredient in chocolate production.
3. How do cocoa pistils contribute to the chocolate industry?
Cocoa pistils indirectly support the chocolate industry by enabling the production of high-quality cocoa beans. These beans are processed to create cocoa powder, cocoa butter, and chocolate products consumed worldwide.
4. Are cocoa pistils edible?
While cocoa pistils themselves are not typically consumed, the seeds they produce (cocoa beans) are used to make various cocoa and chocolate products. However, some cultures may use cocoa pistils in traditional medicine or herbal remedies.
5. Can cocoa pistils be used for anything besides cocoa production?
Yes, cocoa pistils have potential uses in other industries and applications. For example, cocoa husks and shells, by-products of cocoa bean processing, can be utilized as fertilizer, animal feed additives, or biomass fuel. Additionally, cocoa phytochemical extracts may have health benefits and be used in dietary supplements.
6. How do cocoa pistils contribute to environmental sustainability?
Cocoa pistils support biodiversity and ecosystem health by attracting pollinators such as midges, bees, and butterflies. These pollinators not only facilitate cocoa production but also contribute to the pollination of other plants and crops in cocoa-growing regions.
7. Are there any challenges or threats to cocoa pistils and cocoa production?
Yes, cocoa production faces various challenges, including climate change, pests and diseases, and socioeconomic issues. Climate change can affect pollinator populations and alter growing conditions for cocoa trees, while pests and diseases such as cocoa swollen shoot virus can devastate cocoa crops.
8. How can farmers ensure the health and productivity of cocoa pistils?
Farmers can implement sustainable agricultural practices such as agroforestry, soil conservation, and integrated pest management to support the health and productivity of cocoa pistils and cocoa trees. Additionally, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience can enhance pollination services and mitigate risks to cocoa production.
9. Are there any ongoing research or innovations related to cocoa pistils?
Yes, researchers are continually studying cocoa pistils and exploring ways to improve cocoa cultivation practices, enhance pollination efficiency, and develop new cocoa varieties with desirable traits such as disease resistance and high yield potential. These research efforts contribute to the sustainability and resilience of the cocoa industry.
Read Also: Practical Steps to Convert Concrete Wastes into Road Base
