The Cowpea Pedicels: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
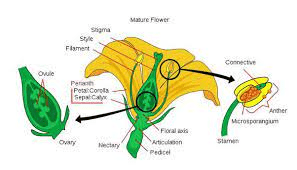
Cowpea pedicels are slender structures that serve as the connection between the flowers or pods and the main stem of cowpea plants (Vigna unguiculata). These pedicels play a crucial role in supporting and positioning the reproductive structures of the plant, facilitating processes such as pollination, fertilization, and seed development.
Found at the base of each flower or pod, cowpea pedicels are typically thin and elongated, allowing for flexibility and movement. They emerge from the main stem of the plant and extend outward to support the reproductive structures. The length of the pedicel may vary depending on the specific variety of cowpea and the stage of development of the flower or pod.
One of the primary functions of cowpea pedicels is to position the flowers or pods in a way that maximizes exposure to sunlight and facilitates pollination. By holding the reproductive structures away from the main stem of the plant, pedicels help to ensure that they are easily accessible to pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other insects. This positioning is essential for promoting successful pollination and fertilization.
In addition to their role in pollination, cowpea pedicels also play a crucial role in supporting developing pods and seeds. As pods mature and fill with seeds, the weight can put stress on the pedicels. However, the pedicels are strong and flexible enough to withstand this weight, ensuring that the pods remain attached to the plant until they are fully mature and ready for harvest.
Cowpea pedicels may also facilitate the dispersal of seeds once the pods have matured and dried. As the pods dry out, they may split open along the seams, releasing the seeds inside. The pedicels help to position the pods in a way that allows the seeds to be dispersed by wind, animals, or human activities, facilitating the spread of the plant and the establishment of new populations.
Overall, cowpea pedicels are essential structures that support and position the reproductive structures of the plant, facilitating processes such as pollination, fertilization, and seed development. Their role in promoting successful reproduction and dispersal is vital for the continued propagation and cultivation of cowpea crops for food and agricultural purposes.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Cowpea Pedicels
1. Fruit Attachment: Cowpea pedicels serve as the structural support that attaches the cowpea pods (fruits) to the main stem or branches of the plant. This attachment ensures proper positioning of the developing pods for optimal exposure to sunlight and airflow, contributing to fruit development and seed production.
2. Seed Distribution: After harvest, cowpea pedicels facilitate the distribution and dispersal of cowpea seeds. The attachment of mature pods to the plant via pedicels allows seeds to remain in place until they are ready for harvest, preventing premature seed loss and ensuring efficient seed collection.
3. Crop Yield: Healthy cowpea pedicels contribute to higher crop yields by supporting the development and maturation of cowpea pods. Adequate pedicel strength and structure prevent pod detachment or premature pod drop, maximizing seed set and overall crop productivity.
4. Marketability: The presence of intact pedicels on harvested cowpea pods enhances their marketability and commercial value. Pods with attached pedicels are perceived as fresher and more visually appealing, increasing consumer confidence and demand in agricultural markets.
5. Culinary Applications: Cowpea pedicels are edible and can be consumed along with the tender pods in various culinary dishes. In some cuisines, cowpea pods with attached pedicels are prized for their crunchy texture and nutty flavor, adding both visual appeal and nutritional value to recipes.
6. Livestock Feed: Cowpea pedicels, along with other plant parts, may be used as feed for livestock such as cattle, sheep, and goats. Harvested cowpea residues, including pods and pedicels, provide valuable fodder for grazing animals, supporting their nutritional needs and overall health.
7. Organic Mulch: After harvest, cowpea pedicels can be incorporated into the soil as organic mulch or green manure. Mulching with cowpea residues helps conserve soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and improve soil fertility, promoting sustainable agricultural practices and crop production.
8. Soil Health: Decomposing cowpea pedicels contribute organic matter to the soil, enhancing soil structure, nutrient cycling, and microbial activity. Their incorporation into the soil improves soil health and fertility, supporting healthy plant growth and crop yield in agricultural systems.
9. Companion Planting: Cowpea pedicels, along with the entire plant, can be utilized in companion planting schemes to enhance soil fertility and pest management. Intercropping cowpeas with other crops benefits soil health and biodiversity while reducing the need for synthetic inputs.
10. Cover Cropping: In cover cropping systems, cowpea pedicels and residues provide ground cover and organic matter to protect and improve soil quality during fallow periods. Cover crops such as cowpeas contribute to erosion control, weed suppression, and soil conservation in agricultural landscapes.
11. Nutrient Cycling: Cowpea pedicels play a role in nutrient cycling within agroecosystems by returning organic matter and nutrients to the soil upon decomposition. Their incorporation into the soil helps replenish soil nutrients, supporting sustainable nutrient management practices in agriculture.
12. Soil Erosion Control: By improving soil structure and stability, cowpea pedicels contribute to soil erosion control in agricultural fields and landscapes. Their extensive root systems and organic residues help bind soil particles together, reducing the risk of erosion by water or wind.
13. Water Infiltration: Cowpea pedicels and residues enhance water infiltration and retention in the soil, improving soil moisture levels and drought resilience in agricultural systems. Their presence improves soil structure and porosity, allowing water to penetrate deeper into the soil profile.
14. Organic Weed Control: Cowpea pedicels, when used as mulch or green manure, suppress weed growth by shading the soil surface and inhibiting weed seed germination. This natural weed control method reduces the need for synthetic herbicides, promoting organic farming practices and environmental sustainability.
15. Soil Carbon Sequestration: Decomposing cowpea pedicels contribute to soil carbon sequestration, storing carbon in the soil as organic matter. This process helps mitigate climate change by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in stable soil organic pools.
16. Biodiversity Conservation: By promoting soil health and ecosystem resilience, cowpea pedicels contribute to biodiversity conservation in agricultural landscapes. Healthy soils support diverse microbial communities, beneficial insects, and plant species, enhancing ecosystem services and ecological balance.
17. Agroforestry Integration: Cowpea pedicels and residues can be integrated into agroforestry systems to enhance soil fertility, biodiversity, and crop productivity. In agroforestry settings, cowpeas serve as companion plants or understory crops, providing multiple benefits to tree crops and the surrounding environment.
Read Also: 3 Health Benefits of Slippery Elm (Ulmus fulva)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Cowpea Pedicels

1. Organic Fertilizer: Cowpea pedicels, along with other plant residues, can be composted to produce nutrient-rich organic fertilizer for soil enrichment. Compost made from cowpea residues improves soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity, promoting healthy plant growth and crop yield.
2. Livestock Feed: Cowpea pedicels and other plant parts may be utilized as fodder for livestock such as cattle, sheep, and poultry. Dried or ensiled cowpea residues provide supplemental nutrition to grazing animals, supporting their growth, reproduction, and overall health.
3. Soil Amendment: Decomposing cowpea pedicels contribute organic matter to the soil, enhancing soil structure, nutrient availability, and water retention. Their incorporation into the soil improves soil health and fertility, supporting sustainable agriculture and crop production.
4. Vermicompost Substrate: Cowpea pedicels can be used as a substrate for vermicomposting, where earthworms decompose organic matter to produce nutrient-rich worm castings. Vermicompost enhances soil fertility and microbial activity, benefiting plant growth and crop yield in organic farming systems.
5. Green Manure: Cowpea pedicels and residues can be incorporated into the soil as green manure to improve soil fertility and structure. Green manuring with cowpea residues enhances soil organic matter content, nitrogen fixation, and microbial diversity, promoting sustainable crop production.
6. Soil Conservation: By improving soil structure and stability, cowpea pedicels contribute to soil conservation efforts in agricultural fields and landscapes. Their incorporation into the soil helps prevent erosion, nutrient runoff, and soil degradation, protecting valuable land resources.
7. Organic Mulch: Cowpea pedicels can be used as organic mulch to cover the soil surface and suppress weed growth. Mulching with cowpea residues conserves soil moisture, moderates soil temperature, and enhances nutrient cycling, supporting healthy plant growth and crop yield.
8. Plant Nutrition: Decomposing cowpea pedicels release nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium into the soil, providing essential nutrition for plant growth. Their incorporation into the soil improves soil fertility and nutrient availability, supporting vigorous plant growth and high crop yields.
9. Soil Microbial Activity: Cowpea pedicels promote soil microbial activity by providing organic matter and habitat for beneficial soil organisms. Microbes such as bacteria, fungi, and earthworms decompose pedicel residues, releasing nutrients and enzymes that enhance soil health and plant productivity.
10. Sustainable Agriculture: By enhancing soil fertility, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience, cowpea pedicels support sustainable agriculture practices that conserve natural resources and protect the environment. Their integration into agroecosystems promotes soil conservation, water management, and climate resilience in farming systems.
Read Also: 6 Health Benefits of Oregano (Origanum vulgare)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cowpea Pedicels

1. What are cowpea pedicels?
Cowpea pedicels are the slender stalks that attach the cowpea pods (fruits) to the main stem or branches of the cowpea plant. They serve as the structural support that holds the pods in place during development and maturation.
2. How do cowpea pedicels contribute to crop yield?
Cowpea pedicels play a crucial role in crop yield by supporting the growth and development of cowpea pods. Intact pedicels prevent premature pod detachment, ensuring that seeds reach full maturity and contribute to overall seed yield in cowpea cultivation.
3. Can cowpea pedicels be consumed as food?
While cowpea pedicels are not commonly consumed as food, the tender pods attached to the pedicels are edible and prized for their nutritional value. Cowpea pods, along with attached pedicels, are cooked and consumed in various culinary dishes in many cultures.
4. Do cowpea pedicels have any economic value?
Cowpea pedicels indirectly contribute to the economic value of cowpea cultivation by supporting higher crop yields and quality. Intact pedicels on harvested cowpea pods enhance their marketability and commercial appeal, influencing consumer preferences and market demand.
5. How do cowpea pedicels benefit soil health?
After harvest, cowpea pedicels and residues can be incorporated into the soil as organic matter, improving soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity. Their decomposition releases nutrients and organic carbon into the soil, supporting healthy soil ecosystems and sustainable crop production.
6. Are cowpea pedicels used in any agricultural practices?
Yes, cowpea pedicels are utilized in various agricultural practices such as cover cropping, green manuring, and organic mulching. Their incorporation into agricultural systems enhances soil fertility, moisture retention, and weed suppression, promoting sustainable farming practices.
7. Do cowpea pedicels contribute to environmental sustainability?
Yes, cowpea pedicels contribute to environmental sustainability by promoting soil conservation, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience in agricultural landscapes. Their integration into agroecosystems supports sustainable farming practices that conserve natural resources and protect the environment.
8. Can cowpea pedicels be composted for soil improvement?
Yes, cowpea pedicels can be composted along with other plant residues to produce nutrient-rich organic fertilizer for soil enrichment. Composting cowpea residues improves soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity, supporting healthy plant growth and crop yield.
9. How do cowpea pedicels compare to other plant parts in terms of nutritional value?
Cowpea pedicels may contain some nutrients and organic compounds similar to other plant parts such as leaves, stems, and pods. While not commonly consumed directly, cowpea pedicels contribute to overall soil fertility and plant nutrition through decomposition and nutrient cycling.
10. Are there any research studies focused on cowpea pedicels?
Research studies on cowpea pedicels may focus on their role in crop physiology, seed development, and soil ecology in agricultural systems. Scientists investigate pedicel anatomy, function, and ecological interactions to improve crop management practices and enhance agricultural sustainability.
Read Also: Practical Steps to Covert Paper Wastes into New Paper Products









