Cowpea roots are essential components of the cowpea plant (Vigna unguiculata), playing a vital role in anchoring the plant in the soil and absorbing water and nutrients from the surrounding environment. As part of the root system, cowpea roots contribute to the overall health and vigor of the plant, supporting its growth and development throughout its lifecycle.
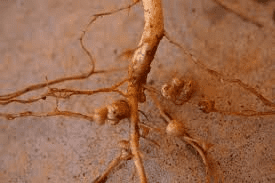
Cowpea roots typically consist of a primary root, known as the taproot, which extends vertically into the soil from the base of the plant. From the taproot, smaller secondary roots, known as lateral roots, branch out horizontally, spreading through the soil in search of water and nutrients. These lateral roots may further divide into smaller root hairs, which increase the surface area available for absorption.
One of the primary functions of cowpea roots is to anchor the plant securely in the soil, providing stability and support against wind, rain, and other environmental factors. The taproot penetrates deep into the soil, anchoring the plant and providing a firm foundation for the aboveground portions of the plant to grow and develop.
In addition to anchoring the plant, cowpea roots also play a crucial role in absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. Water is essential for plant growth and is absorbed by the roots through a process known as osmosis. The roots also absorb essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are necessary for plant health and development.
Cowpea roots have adapted to efficiently extract water and nutrients from the soil, with their fine root hairs increasing the surface area available for absorption. This allows the roots to absorb water and nutrients more effectively, ensuring that the plant receives the resources it needs for optimal growth and development.
In addition to their role in water and nutrient absorption, cowpea roots also play a role in soil health and fertility. As the roots grow and spread through the soil, they help to improve soil structure and aeration, allowing air and water to penetrate more easily. They also release organic compounds into the soil, which can improve soil fertility and promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
Cowpea roots are essential for the growth and development of cowpea plants, providing anchorage, absorbing water and nutrients, and contributing to soil health and fertility. Their role in supporting the plant’s overall health and vigor underscores the importance of maintaining healthy root systems for successful cowpea cultivation.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Cowpea Roots

1. Nutrient Uptake: Cowpea roots play a vital role in absorbing essential nutrients, water, and minerals from the soil. This nutrient uptake supports the growth and development of the cowpea plant, contributing to crop productivity.
2. Soil Structure Improvement: The growth of cowpea roots helps to improve soil structure by breaking up compacted soil and creating channels for air and water infiltration. Enhanced soil structure promotes better root penetration and nutrient availability for plants.
3. Nitrogen Fixation: Cowpea roots have nodules that contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enabling the plant to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by the plant. This biological nitrogen fixation reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, thus lowering production costs for farmers.
4. Erosion Control: The extensive root system of cowpea plants helps to stabilize soil, reducing the risk of erosion caused by water or wind. This erosion control is particularly beneficial in areas prone to soil degradation and loss.
5. Weed Suppression: Dense root growth of cowpea plants competes with weeds for water, nutrients, and space, thereby suppressing weed growth in agricultural fields. Reduced weed pressure can lead to higher crop yields and lower weed management costs.
6. Soil Carbon Sequestration: Cowpea roots contribute to soil carbon sequestration by storing carbon in the soil organic matter. This helps mitigate climate change by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
7. Green Manure: Cowpea roots, along with above-ground biomass, can be incorporated into the soil as green manure. Decomposing roots enrich the soil with organic matter, nutrients, and beneficial microorganisms, improving soil fertility and structure.
8. Soil Health Improvement: The presence of cowpea roots in the soil promotes microbial activity and diversity, enhancing soil health. Healthy soils support better plant growth, nutrient cycling, and ecosystem resilience.
9. Crop Rotation: Cowpea roots are integral to crop rotation systems, where they are used as a break crop to disrupt pest and disease cycles, improve soil health, and enhance overall crop productivity in rotation with other crops.
10. Livestock Forage: While less common, cowpea roots can serve as forage for livestock such as cattle, goats, and sheep. They provide a source of nutrition and can be grazed or harvested for feeding animals.
11. Soil Moisture Regulation: Cowpea roots help regulate soil moisture by absorbing excess water during periods of high rainfall and releasing stored water during dry spells. This moisture regulation contributes to drought resilience and crop survival.
12. Soil pH Modification: Cowpea roots can influence soil pH through the release of organic acids and other compounds. This pH modification can create more favorable soil conditions for plant growth and nutrient availability.
13. Rhizosphere Enhancement: The rhizosphere, the soil region influenced by root activity, benefits from the presence of cowpea roots through increased microbial diversity, nutrient cycling, and soil aggregation.
14. Soil Aeration: As cowpea roots penetrate the soil, they create air channels and promote soil aeration, which is essential for root respiration and nutrient uptake. Well-aerated soils support healthy root growth and overall plant vigor.
15. Phytoremediation: Cowpea roots have been studied for their ability to uptake and accumulate heavy metals and other contaminants from soil, a process known as phytoremediation. This can help remediate polluted soils and improve environmental quality.
16. Land Reclamation: In degraded or marginal lands, cowpea roots can play a role in land reclamation efforts by stabilizing soils, enhancing fertility, and restoring ecosystem functions.
17. Bioremediation: Cowpea roots can contribute to bioremediation processes by enhancing microbial activity and degradation of organic pollutants in soil, water, or sediment.
Read Also: The Benefits of Beekeeping and Honey Production
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Cowpea Roots

1. Biomass Fuel: Cowpea roots, along with above-ground biomass, can be used as a source of biomass fuel for cooking and heating purposes. This can reduce reliance on traditional biomass fuels and alleviate pressure on natural resources.
2. Compost Material: Decomposing cowpea roots contribute to the formation of compost, a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer. Cowpea root residues can be composted with other organic materials to produce high-quality compost for soil amendment.
3. Mulch Material: Cowpea roots, when left in the soil or surface-applied as mulch, can act as organic mulch to suppress weed growth, conserve soil moisture, and improve soil health. Mulching with cowpea residues enhances soil fertility and reduces erosion.
4. Livestock Feed Additive: Cowpea roots, particularly root nodules, contain proteins and carbohydrates that can serve as feed additives for livestock. Processed cowpea roots can be incorporated into animal feed formulations to enhance nutritional value.
5. Soil Amendments: Cowpea roots can be processed into soil amendments such as root meal or root extracts, which are applied to soils to improve soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity. These amendments enhance plant growth and yield.
6. Biofertilizers: Cowpea roots, specifically root nodules containing nitrogen-fixing bacteria, can be processed into biofertilizers for use in organic and sustainable agriculture. Biofertilizers inoculated with cowpea root bacteria contribute to nitrogen
fixation and enhance soil fertility.
7. Plant Growth Promoters: Extracts or compounds derived from cowpea roots may exhibit plant growth-promoting properties, stimulating root development, nutrient uptake, and stress tolerance in crop plants.
8. Soil Conditioners: Cowpea roots can be processed into soil conditioners, which are applied to soils to improve their physical, chemical, and biological properties. Soil conditioners derived from cowpea roots enhance soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability.
9. Biostimulants: Cowpea root extracts or compounds may have biostimulant effects on plants, promoting growth, flowering, and fruiting. Biostimulants derived from cowpea roots can enhance crop productivity and stress tolerance.
10. Microbial Inoculants: Cowpea roots can serve as carriers for beneficial microbial inoculants, such as mycorrhizal fungi or plant growth-promoting bacteria. These inoculants enhance plant-microbe interactions and nutrient cycling in the rhizosphere.
Read Also: How to Establish an Apiary and Produce Honey
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cowpea Roots
1. How do cowpea roots contribute to crop production?
Cowpea roots play a crucial role in nutrient uptake, soil structure improvement, nitrogen fixation, and water regulation, supporting overall crop growth and productivity.
2. Can cowpea roots be used for soil improvement?
Yes, cowpea roots improve soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity through their extensive root system and symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
3. Are cowpea roots beneficial for erosion control?
Cowpea roots help stabilize soil and reduce erosion by binding soil particles together and creating a protective cover on the soil surface.
4. Can cowpea roots be used as livestock feed?
While less common, cowpea roots can be used as forage or feed additives for livestock, providing nutrition and dietary diversity.
5. Do cowpea roots contribute to environmental sustainability?
Yes, cowpea roots support sustainable agriculture practices by enhancing soil health, reducing reliance on synthetic inputs, and promoting ecosystem resilience.
6. How can cowpea roots be utilized after harvest?
Cowpea roots can be left in the soil as organic matter, incorporated into compost or mulch, processed into soil amendments or biostimulants, or used as feed additives or biomass fuel.
7. Do cowpea roots attract pests or diseases?
Cowpea roots are generally not attractive to pests or diseases; however, they may be susceptible to certain soil-borne pathogens or nematodes.
8. Can cowpea roots improve soil fertility?
Yes, cowpea roots enhance soil fertility by increasing nutrient availability, promoting nitrogen fixation, and supporting beneficial microbial activity in the soil.
9. Are there any specific management practices for optimizing cowpea root growth?
Optimal soil moisture, pH, and nutrient levels, along with proper crop rotation and weed management, can promote healthy cowpea root development and maximize crop productivity.
10. Are there ongoing research efforts focused on cowpea roots?
Research studies on cowpea roots may explore their role in soil ecology, rhizosphere interactions, nutrient dynamics, and plant-microbe associations to enhance sustainable agriculture practices and crop productivity.
Read Also: Guide to Waste Management Industry Trends
