The Cowpea Stamens: Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products
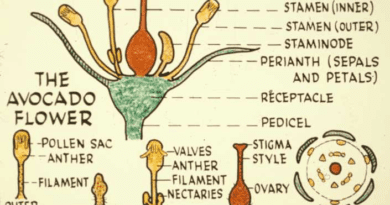
The cowpea stamen is a compact structure typically composed of two key parts: the anther and the filament. The anther, located at the tip of the stamen, is a sac-like structure where pollen grains are produced. It houses the pollen sacs, or microsporangia, where meiosis, a cell division process, occurs, giving rise to haploid pollen grains. The filament, a slender stalk-like structure, acts as a support system, elevating the anther and positioning it strategically for efficient pollen dispersal.
The anther, the heart of the cowpea stamen, is a marvel of cellular organization. Within the anther lie the microsporangia, each housing diploid microspore mother cells. Through the process of meiosis, these mother cells undergo cell division, giving rise to four haploid microspores. These microspores then mature into individual pollen grains, each containing the male gametes (sperm cells) essential for fertilization.
The filament, often thread-like or filamentous, serves as a crucial support system for the anther. It elevates the pollen-laden anther away from the other floral structures, promoting effective pollen dispersal. Additionally, the filament may exhibit specific characteristics, such as bending or twisting movements, that further enhance pollen release and distribution within the flower or to visiting pollinators.
The journey of a pollen grain begins within the microsporangia of the anther. The diploid microspore mother cells undergo meiosis, resulting in four haploid microspores. These microspores then embark on a process of development, undergoing cell wall formation and differentiation to become mature pollen grains. The mature pollen grain contains the male gametes (sperm cells) packaged within a tough outer wall that protects them during dispersal.
Once mature pollen grains are formed within the anthers, the crucial task of dispersal comes into play. Cowpeas primarily rely on biotic (animal) pollination. The vibrant colors and fragrant scents of the flower attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, or insects. As these pollinators forage for nectar, their bodies become dusted with pollen grains. They then inadvertently transfer these pollen grains to the stigmas (female receptive surfaces) of other cowpea flowers, facilitating the potential for fertilization.
The cowpea stamen’s effectiveness can be significantly influenced by environmental factors. Extreme temperatures or nutrient deficiencies can disrupt meiosis within the anther, leading to the formation of non-viable pollen grains. Similarly, adverse weather conditions like heavy rain or strong winds can hinder pollen dispersal and reduce the chances of successful fertilization.
The cowpea stamen plays a vital role in ensuring the plant’s reproductive success. By producing viable pollen grains and facilitating their dispersal, the stamen paves the way for fertilization and ultimately, seed set. Understanding the stamen’s structure, function, and response to environmental cues is crucial for breeders and researchers. By optimizing pollen production and dispersal strategies, they can contribute to improved cowpea seed yields and overall crop productivity.
In conclusion, the cowpea stamen, often overlooked amidst the beauty of the flower, plays a vital role in the intricate dance of plant reproduction. From acting as a factory for pollen production to facilitating its dispersal, this tiny organ exemplifies the wonders of plant biology. By understanding the stamen’s intricate workings, we can contribute to advancements in cowpea cultivation, ultimately ensuring a more reliable and sustainable source of this valuable legume crop.
The cowpea stamen, a seemingly simple structure nestled within the vibrant flower of the cowpea plant, serves as a cornerstone of legume reproduction. These tiny organs act as powerhouses for pollen production, the lifeblood of fertilization and seed development. This article delves into the intricate world of cowpea stamens, exploring their economic importance, the products derived from their successful functioning, and addressing frequently asked questions.
Economic Importance and Uses of Cowpea Stamens

1. Seed Production: Stamens are essential for seed production. They produce viable pollen grains that fertilize the ovules within the female pistil, leading to seed development. Cowpea seeds are a vital source of protein, dietary fiber, essential vitamins, and minerals for millions, particularly in developing countries.
2. Food Security: By enabling seed production, cowpea stamens contribute to food security. Cowpeas’ ability to thrive in diverse environments and their relatively short growing season make them a reliable source of food, especially in regions facing food insecurity challenges.
3. Nutritional Security: Successful pollen transfer and fertilization, facilitated by the stamen, lead to cowpea seeds rich in protein, dietary fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals. This enhances dietary diversity and nutritional security for populations reliant on cowpeas.
4. Improved Diets: Cowpea consumption offers a readily available source of essential nutrients. The stamen’s role in pollen production ensures the presence of cowpeas in diets, contributing to improved overall nutrition.
5. Livestock Feed: Cowpea plants, including leaves, stems, and pods, are a valuable source of animal feed. Stamens play a crucial indirect role by enabling seed production and plant establishment, leading to the availability of cowpea forage for livestock.
6. Income Generation: Cowpea production can be a source of income for smallholder farmers. Healthy and functional stamens translate to increased cowpea yields, allowing farmers to sell their produce and improve their livelihoods.
7. Sustainable Agriculture: Cowpeas promote sustainable agricultural practices due to their nitrogen-fixing capabilities and ability to thrive in low-input conditions. Stamens contribute by enabling seed production and plant establishment for these benefits to be realized.
8. Multiple Cropping Systems: Cowpeas can be effectively integrated into multiple cropping systems due to their short growing season. Stamens play a role by facilitating seed production, allowing cowpeas to be used as a cover crop or intercrop, improving soil fertility and overall agricultural productivity.
9. Soil Fertility Enhancement: Cowpeas are nitrogen-fixing legumes, meaning they harbor beneficial bacteria that convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plants. Successful pollen transfer and seed set, enabled by stamens, lead to the establishment of cowpea plants that enrich the soil with nitrogen, benefiting subsequent crops. 10. Green Manure:** Cowpea residues left after harvest can be incorporated back into the soil as green manure. Stamens play an indirect role in this process by facilitating seed production and plant growth. Cowpea residues enrich the soil with organic matter, improve soil structure, and suppress weeds.
11. Drought Tolerance: Cowpeas are known for their drought tolerance. The stamen’s ability to function effectively even under dry conditions is crucial for seed production in arid and semi-arid regions, where reliable rainfall can be scarce.
12. Pest and Disease Resistance: Certain cowpea varieties exhibit resistance to pests and diseases. Functional stamens ensure the continuation of these resistant lines through pollen production, contributing to reduced crop losses and improved yields.
13. Climate Change Adaptation: Cowpeas are relatively resilient to climate change impacts like drought and heat stress. Stamens play a role by facilitating seed production, allowing cowpeas to contribute to food security even under changing climatic conditions.
14. Food Diversification: Cowpeas offer culinary diversity, being consumed fresh, dried, or processed into various products. Stamens, although not directly consumed, play a vital role in ensuring cowpea availability for diverse food applications.
15. Research and Development: Cowpea research plays a crucial role in developing improved varieties and cultivation practices. Stamens are a key area of study for understanding pollen production, dispersal, and fertilization processes, ultimately leading to breeding for enhanced yields.
16. Educational Tool: Studying cowpea stamens can be a valuable educational tool in plant biology and agriculture. The stamen’s intricate structure and function provide a tangible example of plant reproduction and pollen’s role in seed development.
17. Alleviation of Malnutrition: Cowpeas are a rich source of plant-based protein, particularly valuable in regions facing malnutrition. Stamens contribute by enabling seed production, leading to increased cowpea availability, offering a readily accessible source of essential nutrients.
Read Also Scrapie in Sheep and Goats: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
Products and By-products Derived from Cowpea Stamens

1. Cowpea Seeds: The primary product derived from cowpea reproduction is the seed itself. These seeds develop within the ovary, fertilized by pollen produced by the stamen. Cowpea seeds are a rich source of protein, dietary fiber, essential vitamins, and minerals. They can be consumed directly (fresh or dried), processed into various food products (flour, snacks), or used as planting material for the next generation of cowpeas.
2. Cowpea Fodder: Cowpea plants, including leaves, stems, and pods, can be used as a valuable source of animal feed, particularly for ruminants like cattle, sheep, and goats. Stamens play an indirect role here by facilitating seed production and plant growth, leading to the availability of cowpea forage for livestock.
3. Cowpea Hay: Cowpea plants can be harvested and dried to produce hay, a form of dry fodder for livestock. Stamens play an indirect role by facilitating seed production and plant growth, leading to the biomass used for hay production.
4. Green Manure: Cowpea residues left after harvest can be incorporated back into the soil as green manure. This practice enriches the soil with organic matter, improves soil structure, and suppresses weeds. While the stamen itself isn’t directly utilized, it plays a crucial role by facilitating seed production and plant growth, leading to the biomass used for green manure.
5. Cover Crops: Cowpeas can be planted as cover crops to suppress weeds, improve soil moisture retention, and prevent soil erosion. Stamens, by enabling seed production, allow cowpeas to establish themselves effectively as a cover crop, offering various soil health benefits.
6. Improved Varieties: Research on cowpea stamens can lead to the development of improved cowpea varieties with enhanced pollen production and viability. Understanding factors affecting pollen development and dispersal can inform breeding strategies for higher yields and improved stress tolerance.
7. Hybrid Seed Production: Stamens play a vital role in sexual reproduction, allowing for the exchange of genetic material between different cowpea varieties through controlled crosses. Breeders can leverage this by selecting parental lines with desired traits and utilizing these crosses to create offspring with beneficial characteristics.
8. In Vitro Pollen Germination Studies: Understanding pollen viability and germination is crucial for various applications. Techniques like in vitro pollen germination studies involve isolating pollen grains from the stamen and culturing them in a controlled environment. This can be used to assess pollen viability for breeding programs or germplasm conservation efforts.
9. Pollination Efficiency Studies: Optimizing pollination efficiency is critical for maximizing seed set. Research on stamen structure, pollen production, and attractiveness to pollinators can inform strategies to improve pollination efficiency, leading to increased cowpea yields.
10. Synthetic Seed Production: Synthetic seed production involves developing artificial seeds containing embryos or other plant propagules encapsulated in a protective coating. Research on stamen function and pollen characteristics can inform the creation of synthetic seeds for cowpeas, potentially offering advantages like extended storage life and disease-free propagation.
11. Doubled Haploid Production: Doubled haploid (DH) production is a technique for creating plants with completely homozygous genomes. This can be achieved through various methods, some of which utilize pollen derived from the stamen. DH lines can be valuable for breeding programs due to their genetic uniformity and faster breeding cycles.
12. Male Sterility and Hybrid Seed Production: Male sterility mechanisms can be induced in cowpea plants, rendering them incapable of producing functional pollen from their stamens. This facilitates the production of hybrid seeds by controlling unwanted self-pollination and allowing for controlled crosses with other desired varieties.
13. Pollen Banking: Pollen banking involves collecting, storing, and preserving pollen grains for future use. Pollen derived from cowpea stamens can be cryopreserved for various purposes, such as breeding programs, germplasm conservation efforts, or reintroduction of rare cowpea varieties.
14. Food Processing Industries: Cowpea seeds are used in various food processing industries. Stamens play an indirect role by facilitating seed production, which is then processed into diverse products like flour, grits, and snacks.
15. Biofuel Production: Research is exploring the potential of using cowpea biomass for biofuel production. The stamen, although not directly involved, plays a role in facilitating plant growth and seed production, contributing to the overall biomass available for biofuel exploration.
16. Model Systems for Pollen Development: Cowpea stamens can serve as model systems for studying pollen development and physiology. Research on stamen function can provide insights into pollen wall formation, gene expression during pollen development, and the interaction between pollen and pollinators.
Read Also Management of Breeding Stock in Sheep and Goats
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cowpea Styles

1. What are cowpea styles?
Cowpea styles are the female reproductive organs found within the flowers of cowpea plants. They play a crucial role in the pollination and fertilization process, ultimately leading to the development of pods and seeds.
2. How do cowpea styles contribute to crop production?
Cowpea styles facilitate pollination and fertilization, leading to the formation of pods containing seeds. These seeds can be harvested for consumption or planting, contributing to crop production in agricultural systems.
3. Can cowpea styles be consumed as food?
No, cowpea styles themselves are not typically consumed as food. However, the pods that develop from fertilized styles are harvested when young and tender, then cooked and eaten as a nutritious vegetable in various cuisines.
4. What is the economic importance of cowpea styles?
Cowpea styles are economically important as they contribute to seed production, food security, and agricultural livelihoods. Successful pollination and fertilization lead to the formation of seeds that can be sold or used for planting in commercial and subsistence farming systems.
5. How are cowpea styles used in traditional medicine?
While cowpea styles are not commonly used in traditional medicine, extracts from other parts of the cowpea plant may be used for their purported medicinal properties. However, scientific research on the medicinal benefits of cowpea is limited, and more studies are needed to validate traditional uses.
6. Can cowpea styles be composted?
Yes, cowpea styles, along with other plant residues, can be composted to produce nutrient-rich compost for soil amendment. Composting cowpea residues helps improve soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity, promoting healthy plant growth in agricultural and gardening applications.
7. How do cowpea styles contribute to soil health?
Cowpea styles, along with the entire plant, contribute to soil health by adding organic matter to the soil through decomposition. Organic matter improves soil structure, water retention, nutrient cycling, and microbial activity, creating a conducive environment for plant growth and productivity.
8. Are cowpea styles beneficial for livestock feed?
While cowpea styles themselves are not used as livestock feed, the seeds that develop from fertilized styles are valuable sources of nutrition for grazing animals. Cowpea seeds are high in protein and can be fed to livestock such as cattle, goats, and sheep as a supplemental feed source.
9. How can cowpea styles be used in sustainable agriculture?
Cowpea styles can be used in sustainable agriculture practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and agroforestry. Including cowpea in agricultural systems helps improve soil health, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity while reducing the reliance on synthetic inputs and minimizing environmental impacts.
10. Are there any environmental benefits associated with cowpea styles?
Yes, cowpea styles contribute to various environmental benefits, including soil conservation, carbon sequestration, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Incorporating cowpea into agroecosystems helps mitigate soil erosion, enhance soil fertility, and promote sustainable land management practices.
Read Also How to Make an Avocado Tree Bear Fruit