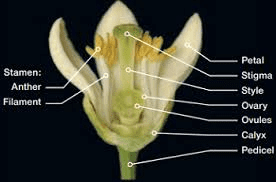
Lemon stamens are key components of the lemon flower’s reproductive system, crucial for the production of pollen and ultimately, seeds. Positioned within the flower’s central region, the stamens consist of slender filaments topped with pollen-bearing anthers.
Botanically, stamens are part of the androecium, the male reproductive organ of the flower. In lemon flowers, they typically surround the central female reproductive organ, the pistil, which comprises the stigma, style, and ovary. The arrangement of stamens and pistils within the flower facilitates efficient pollination, a vital step in lemon fruit formation.
Each lemon stamen consists of two main parts: the filament and the anther. The filament is a thin, elongated structure that supports the anther, positioning it at a suitable height within the flower for pollen dispersal. The anther, located at the top of the filament, contains pollen sacs where pollen grains are produced through meiosis.
Pollen grains are the male gametophytes of flowering plants and carry the genetic material necessary for fertilization. In lemon stamens, pollen grains develop within the anthers and are released when the flower reaches maturity. Pollination occurs when these pollen grains are transferred to the stigma, either by wind, insects, or other pollinators.
The reproductive success of lemon plants relies significantly on effective pollination. Once pollen grains land on the stigma, they germinate and grow pollen tubes that extend down the style to reach the ovules contained within the ovary. Fertilization occurs when sperm cells within the pollen grains unite with egg cells in the ovule, leading to seed formation.
Lemon stamens, like those of other citrus plants, are essential not only for sexual reproduction but also for maintaining genetic diversity within the species. Cross-pollination, facilitated by insects such as bees, enhances genetic variability and can lead to more robust fruit production and improved resilience to environmental stressors.
From a horticultural perspective, understanding the anatomy and function of lemon stamens is crucial for optimizing fruit yields and quality. Growers may manipulate pollination practices to increase fruit set, particularly in regions with limited insect activity or during adverse weather conditions.
Lemon stamens are integral to the reproductive success of lemon trees, facilitating the transfer of pollen and subsequent fertilization of ovules. Their intricate structure and function highlight the complexity of plant reproduction and underscore their importance in ensuring the continuation of the lemon species.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Lemon Stamens
1. Pollination: Lemon stamens are essential for the pollination process, leading to fruit production and ensuring a good yield for farmers.
2. Beekeeping: Lemon stamens attract bees, which collect pollen and help in pollination, crucial for honey production and ecosystem health.
3. Crop Yield Improvement: Proper pollination involving stamens can increase the quantity and quality of lemon fruit, benefiting agricultural output.
4. Genetic Research: Lemon stamens are used in genetic studies to understand plant reproduction and improve crop varieties.
5. Breeding Programs: Stamens are crucial in hybridization and breeding programs to develop new lemon varieties with desirable traits.
6. Medicinal Uses: Pollen from lemon stamens has been studied for its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
7. Nutritional Supplements: Lemon pollen can be processed into supplements for its nutritional and health benefits.
8. Aromatherapy: Essential oils derived from lemon flowers, including stamens, are used in aromatherapy to promote relaxation and well-being.
9. Culinary Uses: Pollen can be used as a garnish or ingredient in culinary dishes, adding a unique flavor and nutritional value.
10. Cosmetic Products: Extracts from lemon stamens are used in skincare products for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
11. Fertilizer Production: Decomposed lemon stamens can be used as an organic fertilizer, enriching the soil with nutrients.
12. Pest Control: Natural compounds in stamens can be used in eco-friendly pest control solutions.
13. Crafting: Dried lemon stamens can be used in arts and crafts projects, adding a natural element to decorations.
14. Perfume Industry: Aromatic compounds from lemon stamens are used to enhance the fragrance of perfumes.
15. Environmental Monitoring: Pollen analysis from stamens helps in studying environmental changes and plant health.
16. Educational Tools: Lemon stamens are used in educational settings to teach about plant biology and reproduction.
17. Natural Dyes: Lemon pollen can be used to create natural dyes for textiles and other materials.
18. Phytotherapy: Stamens are used in traditional herbal remedies for their potential therapeutic benefits.
Read Also: Steps On How Bees Make Honey
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Lemon Stamens

1. Essential Oils: Lemon stamens are steam distilled to extract essential oils used in aromatherapy, perfumes, and cleaning products.
2. Nutritional Supplements: Pollen from lemon stamens is processed into dietary supplements for its nutritional benefits.
3. Herbal Teas: Lemon stamen extracts are used to make herbal teas with potential health benefits.
4. Natural Dye: Pollen from stamens can be used to create natural dyes for textiles and crafts.
5. Cosmetic Extracts: Extracts from lemon stamens are used in creams, lotions, and serums for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
6. Fertilizers: Decomposed stamens are used as organic fertilizers, enriching the soil with essential nutrients.
7. Pest Control Products: Natural compounds in lemon stamens are used to create eco-friendly pest control solutions.
8. Perfumes: Aromatic compounds from stamens are used in the production of high-quality perfumes.
9. Culinary Garnishes: Lemon pollen can be used as a garnish or ingredient in various dishes for added flavor and nutrition.
10. Craft Materials: Dried stamens are used in crafting projects like making scented sachets and decorative items.
11. Health Drinks: Lemon stamen extracts are added to health drinks and smoothies for their nutritional value.
12. Phytotherapy Products: Stamens are used in traditional herbal remedies for their potential therapeutic benefits.
13. Beekeeping Products: Lemon pollen is collected by bees and used in the production of honey and other bee products.
14. Environmental Studies: Pollen from stamens is used in environmental monitoring and research.
15. Educational Kits: Lemon stamens are included in educational kits for teaching about plant biology and reproduction.
16. Air Fresheners: Extracts from lemon stamens are used to create natural air fresheners.
17. Bath Products: Lemon stamen extracts are used in bath salts, bath bombs, and soaps for their soothing properties.
Read Also: How to Establish and Maintain a Beekeeping Operation
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Lemon Stamens

1. What are lemon stamens?
Lemon stamens are the pollen-producing part of the lemon flower, consisting of anthers and filaments.
2. How do lemon stamens contribute to pollination?
Stamens produce pollen, which is transferred to the pistil of flowers, enabling fertilization and fruit development.
3. Can lemon pollen be used in cooking?
Yes, lemon pollen can be used as a garnish or ingredient in culinary dishes for added flavor and nutritional value.
4. Are there health benefits to lemon pollen?
Lemon pollen has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, making it potentially beneficial for health when used in supplements.
5. How are lemon stamens used in skincare?
Extracts from lemon stamens are used in skincare products for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits, helping to protect and rejuvenate the skin.
6. Can lemon stamens be used to make tea?
Yes, lemon stamen extracts can be used to make herbal teas with potential health benefits.
7. What role do lemon stamens play in beekeeping?
Lemon stamens attract bees, which collect pollen and help with pollination, essential for honey production and ecosystem health.
8. Are lemon stamens used in perfumes?
Yes, aromatic compounds from lemon stamens are used to enhance the fragrance of perfumes.
9. How are lemon stamens processed into essential oils?
Lemon stamens are steam distilled to extract essential oils, which are then used in various aromatherapy and cosmetic products.
10. Are there any traditional medicinal uses for lemon stamens?
Yes, lemon stamens are used in traditional herbal remedies for their potential therapeutic benefits, such as reducing inflammation and promoting overall health.
