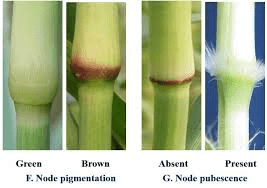
Millet nodes are a critical part of the millet plant’s structure. These nodes, also known as joints, are points along the stem where leaves, branches, and roots can grow. They are crucial for the plant’s growth, stability, and reproduction. Millet is a group of small-seeded grasses that includes various types such as pearl millet, foxtail millet, proso millet, and finger millet. The nodes of these plants, while similar in function, can vary slightly in their specific characteristics.
The primary function of millet nodes is to serve as growth points. From these nodes, new leaves and branches emerge, allowing the plant to expand and capture more sunlight for photosynthesis. This process is essential for the plant’s energy production and overall growth. Nodes are also where roots can sprout if they come into contact with the soil, providing additional stability and nutrient uptake for the plant. This ability to produce roots from nodes is particularly beneficial for millet, as it can help the plant survive in challenging environments with poor soil quality and limited water.
Another important aspect of millet nodes is their role in the plant’s reproductive process. The nodes are the sites where flowers and subsequently seeds develop. These flowers are often located on the upper nodes of the plant and, once pollinated, will produce millet seeds. The efficient functioning of these nodes is crucial for a successful harvest, as they directly impact the number and quality of seeds produced.
In agricultural practices, the health and development of millet nodes are closely monitored. Farmers often check the nodes for signs of disease or pest infestation, as these can severely affect the plant’s growth and yield. For instance, certain fungal infections can target the nodes, weakening the plant and reducing seed production. Integrated pest management and proper crop rotation are some strategies used to protect millet nodes and ensure healthy plant development.
The structure and flexibility of millet nodes also play a role in the plant’s ability to withstand environmental stress. Millet plants are known for their resilience to drought and poor soil conditions, and the nodes contribute to this by enabling the plant to grow new roots and shoots even under adverse conditions. This adaptability makes millet a valuable crop in regions prone to harsh climates and erratic rainfall patterns.
Millet nodes can also be studied to understand the plant’s growth patterns and improve cultivation techniques. For example, research on the genetic regulation of node development can lead to the breeding of millet varieties with enhanced growth characteristics, such as increased height, more robust stems, or greater seed production. Such advancements can significantly boost agricultural productivity and food security in regions where millet is a staple crop.
In addition to their agricultural importance, millet nodes have potential uses in environmental sustainability. The plant material, including nodes, can be utilized in various eco-friendly applications. For example, the fibers from millet nodes can be processed into biodegradable materials, offering an alternative to traditional plastics. This use of agricultural residues not only provides an additional revenue stream for farmers but also contributes to reducing environmental pollution.
Millet nodes are an essential part of the millet plant, playing a crucial role in its growth, stability, and reproduction. They serve as points of new leaf, branch, and root development, contributing to the plant’s ability to capture sunlight and absorb nutrients. The health and functionality of these nodes directly impact the plant’s yield and resilience to environmental stress.
Additionally, millet nodes offer potential applications in sustainable practices and eco-friendly products. Understanding and optimizing the role of nodes in millet cultivation can lead to improved agricultural outcomes and environmental benefits.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Millet Nodes

1. Plant Growth Indicator: Millet nodes indicate the growth stage and health of the millet plant, helping farmers make informed decisions about irrigation and fertilization.
2. Propagation: Nodes are crucial for vegetative propagation. New plants can be grown from cut sections of the stem that include nodes.
3. Structural Support: Nodes provide structural strength to millet plants, ensuring they stand upright and support grain production.
4. Nutrient Transport: Nodes are involved in the transport of nutrients and water throughout the plant, contributing to overall plant health and productivity.
5. Disease Resistance: Healthy nodes are less susceptible to disease, helping to maintain the health of the entire plant and reducing crop losses.
6. Livestock Feed: Nodes, along with other parts of the millet plant, are used as livestock feed, providing essential nutrients for animals.
7. Craft Material: Millet nodes are sometimes used in crafting, particularly in making natural decorations and ornaments.
8. Soil Enrichment: When millet plants decompose, nodes contribute organic matter to the soil, enhancing soil fertility and structure.
9. Biofuel Production: Millet nodes can be processed into biofuel, similar to other plant parts, contributing to renewable energy sources.
10. Composting: Millet nodes decompose well in compost piles, adding valuable nutrients to compost used for gardening and farming.
11. Carbon Sequestration: Millet nodes, as part of the plant biomass, contribute to carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change.
12. Biomass Energy: Nodes are used in biomass energy production, providing a renewable source of energy when burned or processed.
13. Mulching: Crushed or chopped millet nodes can be used as mulch to help retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil health.
14. Erosion Control: Nodes and other plant residues are used in erosion control practices to stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
15. Handicrafts: Millet nodes are sometimes used in creating handicrafts and natural decor items, adding a rustic touch to various projects.
16. Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, millet nodes are used in traditional medicine practices to treat certain ailments.
17. Soil Amendment: Decomposed millet nodes act as a soil amendment, improving soil quality and promoting healthy plant growth.
18. Animal Bedding: Crushed millet nodes can be used as bedding material for livestock, providing a comfortable and absorbent surface.
Read Also: Definition of Water and Wind Erosion
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Millet Nodes

1. Livestock Feed: Millet nodes are included in chopped forage or silage, providing essential nutrients and roughage for animals.
2. Biofuel: Millet nodes can be processed into biofuel. The biomass is fermented to produce ethanol or other biofuels.
3. Compost: Nodes are added to compost piles where they decompose and contribute to nutrient-rich compost used in gardening and farming.
4. Mulch: Crushed or chopped millet nodes are spread over soil as mulch, helping to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
5. Handicrafts: Millet nodes are used to make natural crafts and decorations. They can be incorporated into various art projects for a rustic look.
6. Soil Amendment: Decomposed millet nodes are used as a soil amendment, adding organic matter and improving soil structure and fertility.
7. Biomass Energy: Millet nodes are used as a source of biomass energy. They are burned or gasified to produce heat and electricity.
8. Traditional Medicine: Nodes are sometimes used in traditional medicine preparations, believed to have various health benefits.
9. Carbon Sequestration: When used in agricultural practices, millet nodes help sequester carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation.
10. Erosion Control: Millet nodes are used in erosion control measures. They help stabilize soil and prevent it from being washed away by water.
11. Animal Bedding: Dried and crushed millet nodes are used as bedding material for livestock, providing a soft and absorbent surface.
12. Craft Materials: Millet nodes are used in various craft projects. They can be woven, shaped, or used as decorative elements.
13. Biogas Production: Nodes can be anaerobically digested to produce biogas, a renewable energy source composed primarily of methane.
14. Soil Health: Incorporating millet nodes into the soil improves its health by adding organic matter and nutrients.
15. Plant Support: Nodes provide structural support to millet plants, helping them stand upright and support grain production.
16. Nutrient Transport: Nodes play a crucial role in the transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant, contributing to overall plant health.
17. Disease Resistance: Healthy nodes help the plant resist diseases, ensuring better crop yields and reducing losses.
Read Also: Winter Aconite Flowers (Eranthis hyemalis) – All you need to know
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Millet Nodes

1. What are millet nodes?
Millet nodes are the joints on the millet plant’s stem where leaves and branches emerge.
2. What is the function of nodes in millet plants?
Nodes provide structural support, facilitate nutrient transport, and enable the growth of leaves and branches.
3. Can millet nodes be used for propagation?
Yes, millet nodes are essential for vegetative propagation. New plants can grow from stem sections that include nodes.
4. How do millet nodes contribute to plant health?
Nodes help transport nutrients and water, support the plant structure, and can contribute to disease resistance.
5. Are millet nodes used in animal feed?
Yes, millet nodes are included in forage and silage, providing essential nutrients and roughage for livestock.
6. Can millet nodes be used as biofuel?
Yes, millet nodes can be processed into biofuel, contributing to renewable energy sources.
7. What role do millet nodes play in soil health?
When decomposed, millet nodes add organic matter and nutrients to the soil, improving its fertility and structure.
8. How are millet nodes used in erosion control?
Millet nodes help stabilize soil in erosion control practices, preventing soil from being washed away by water.
9. Are millet nodes used in handicrafts?
Yes, millet nodes are used to make natural crafts and decorations, adding a rustic touch to various projects.
10. Can millet nodes be used for composting?
Yes, millet nodes decompose well in compost piles, contributing valuable nutrients to the compost used for gardening and farming.
Read Also: A Comprehensive Guide to Jeff Belzer Fresh Start Financing