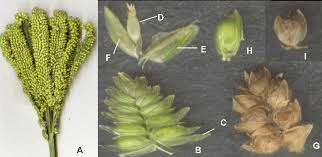
Millet stamens are the male reproductive organs within the flowers of millet plants. These structures play a critical role in the process of pollination and seed formation, which are essential for the plant’s reproduction and the production of millet grain.
Each millet flower typically contains three stamens, although this number can vary slightly among different millet species. The stamen consists of two main parts: the filament and the anther. The filament is a slender stalk that supports the anther, positioning it effectively within the flower to maximize the chances of successful pollination. The anther is the part of the stamen where pollen is produced and stored.
Pollen grains are the carriers of the male genetic material necessary for fertilization. When the anthers mature, they release the pollen, which is then transported to the female reproductive organs (the pistils) of the same or another flower. In millet plants, pollination is primarily facilitated by wind, although insects can also play a role in some species.
The release of pollen from the anthers is a critical step in the reproductive process. In many millet species, the anthers are exposed when the flowers open, allowing the wind to carry the pollen to the pistils. The lightweight and powdery nature of the pollen makes it easily airborne, increasing the likelihood of successful cross-pollination. This process is essential for genetic diversity and the production of viable seeds.
The structure and development of the stamens can be influenced by various factors, including genetics, environmental conditions, and agricultural practices. For instance, adequate sunlight, temperature, and nutrient availability are vital for the healthy development of stamens. Any stress or deficiency in these factors can adversely affect pollen production and viability, leading to reduced seed set and yield.
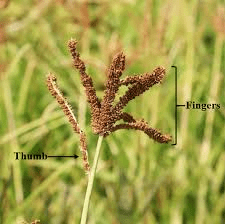
In different millet species, the characteristics of the stamens can vary. For example, in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum), the stamens are typically well-developed and prominently displayed when the flowers open, facilitating efficient wind pollination. In finger millet (Eleusine coracana), the stamens are also well-adapted for wind pollination, with anthers positioned to maximize pollen dispersal.
The timing of stamen development and pollen release is crucial for synchronization with the pistils’ receptivity to ensure successful fertilization. This synchronization, often regulated by environmental cues such as light and temperature, helps in maximizing the chances of seed development.
Understanding the role and structure of millet stamens is important for breeding and agricultural practices. Breeders often select for traits that enhance stamen development and pollen viability to improve yield and resilience. For instance, selecting for plants with robust stamens that produce abundant, viable pollen can lead to better seed set and higher grain production.
Millet stamens are the male reproductive organs that consist of filaments and anthers, which produce and release pollen. Their structure and function are critical for the process of pollination and subsequent seed formation. Understanding the factors that influence stamen development and pollen viability can help improve millet cultivation practices and enhance crop yield.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Millet Stamens
1. Pollination: Millet stamens are crucial for the pollination process, which is necessary for seed production and overall crop yield.
2. Seed Development: Healthy stamens ensure effective pollination and fertilization, leading to the development of viable millet seeds.
3. Genetic Diversity: Stamens contribute to genetic diversity by facilitating cross-pollination, which can improve crop resilience and adaptability.
4. Crop Improvement: By studying the stamens and their role in pollination, agricultural scientists can develop better millet varieties with higher yields and improved traits.
5. Research and Education: Stamens are studied in botanical research and education to understand plant reproductive biology and the pollination process.
6. Breeding Programs: Millet breeding programs utilize stamens for controlled pollination to develop new hybrids with desired characteristics.
7. Biodiversity: Stamens play a role in maintaining biodiversity by supporting the reproduction of various millet species.
8. Ecosystem Services: Stamens support ecosystems by providing pollen for pollinators, contributing to ecological balance and biodiversity.
9. Food Security: Effective pollination by stamens ensures a stable production of millet, which is a staple food in many regions, thus contributing to food security.
10. Agricultural Sustainability: Understanding the role of stamens in millet production helps develop sustainable farming practices that optimize pollination and yield.
11. Cultural Practices: In some cultures, millet stamens may be used in traditional rituals and practices, highlighting their cultural significance.
12. Nutritional Studies: Research on stamens can lead to discoveries about the nutritional components of millet, enhancing its value as a food source.
13. Herbal Medicine: In some traditional medicine systems, parts of millet plants, including stamens, may be used for their purported health benefits.
14. Horticultural Practices: Knowledge of stamens and their function can improve horticultural practices, leading to better crop management and yield.
15. Climate Resilience: Understanding how stamens contribute to pollination can help develop millet varieties that are more resilient to climate change.
16. Pest Management: Studies on stamens can provide insights into pest interactions, leading to better pest management strategies.
17. Seed Industry: The seed industry relies on healthy stamens for producing high-quality millet seeds for commercial distribution.
18. Conservation Efforts: Stamens are important for conserving millet varieties and ensuring their continued availability for future generations.
Read Also: 25 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Astragalus amphioxys (Crescent milkvetch)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Millet Stamens
1. Pollen: Millet stamens produce pollen, which is essential for the pollination and fertilization process in plants.
2. Hybrid Seeds: Controlled pollination using stamens can produce hybrid millet seeds with desired traits, enhancing crop yield and quality.
3. Research Material: Stamens can be used as research material in studies on plant reproduction, genetics, and crop improvement.
4. Educational Tools: Millet stamens can be used as teaching aids in educational settings to demonstrate plant anatomy and reproductive processes.
5. Herbal Extracts: In traditional medicine, stamens or their extracts might be used for their purported health benefits.
6. Biotechnological Applications: Stamens can be used in biotechnological research to develop new plant varieties and improve crop production.
7. Genetic Studies: Stamens provide material for genetic studies, helping understand the inheritance of traits and improving breeding programs.
8. Pollinator Support: The pollen from millet stamens supports pollinators like bees, contributing to the health of local ecosystems.
9. Seed Production: Stamens are integral in producing seeds, which are then used for food, feed, and other applications.
10. Nutritional Supplements: Research on stamens might lead to the development of nutritional supplements derived from their components.
11. Eco-friendly Practices: Using stamens in research and agriculture promotes eco-friendly practices by enhancing understanding of natural pollination processes.
12. Cultural Products: In some cultures, millet stamens may be used in traditional crafts, rituals, or decorations.
13. Botanical Collections: Stamens are included in botanical collections for study and preservation of plant diversity.
14. Agricultural Training: Stamens can be used in training programs for farmers to improve their understanding of millet cultivation and pollination.
15. Conservation Programs: Stamens are essential for conservation programs aimed at preserving millet biodiversity and ensuring sustainable crop production.
16. Food Product Development: Understanding the role of stamens can contribute to the development of new food products derived from millet.
17. Climate Adaptation: Research on stamens helps develop millet varieties that are better adapted to changing climate conditions.
Read Also: 25 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Gentianella alborosea (Hercampuri)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Millet Stamens
1. What are millet stamens?
Millet stamens are the male reproductive parts of the plant that produce pollen necessary for pollination and seed development.
2. How do stamens contribute to pollination?
Stamens produce pollen, which is transferred to the pistil of flowers, leading to fertilization and seed development.
3. Can millet stamens be used in research?
Yes, millet stamens are used in botanical and agricultural research to study plant reproduction and improve crop varieties.
4. What role do stamens play in crop yield?
Healthy stamens ensure effective pollination, leading to higher seed production and better crop yields.
5. Are millet stamens important for biodiversity?
Yes, stamens support genetic diversity through cross-pollination, which helps maintain and improve crop resilience.
6. How are stamens used in breeding programs?
Stamens are used for controlled pollination in breeding programs to develop new hybrids with desired traits.
7. Can millet stamens be used in traditional medicine?
In some cultures, parts of millet plants, including stamens, are used in traditional medicine for their potential health benefits.
8. What is the significance of stamens in ecosystem services?
Stamens provide pollen for pollinators like bees, supporting biodiversity and ecological balance.
9. How do stamens affect food security?
Effective pollination by stamens ensures stable millet production, which is crucial for food security in many regions.
10. Are millet stamens studied for nutritional purposes?
Yes, research on stamens can reveal nutritional components of millet, enhancing its value as a food source.
Read Also: Business Planning Process and Importance of Business Plan

