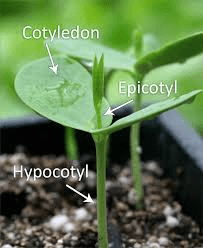
The mustard hypocotyl is a crucial part of the mustard plant’s early development, serving as the link between the root system and the cotyledons, or seed leaves. It plays a significant role in seed germination, seedling emergence, and initial plant growth.
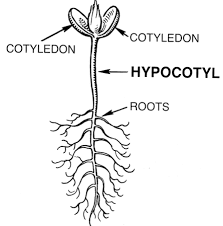
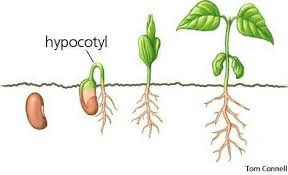
The hypocotyl is the stem-like part of the seedling that lies below the cotyledons and above the root system. When a mustard seed germinates, the hypocotyl elongates, pushing the cotyledons above the soil surface. This elongation process is driven by cell division and enlargement, primarily influenced by environmental factors like light and temperature, as well as hormonal signals within the plant.
During germination, the hypocotyl’s primary function is to lift the cotyledons out of the soil to expose them to light, allowing them to perform photosynthesis. This initial photosynthetic activity is crucial for the seedling’s survival and growth, providing the energy necessary for further development until true leaves form.
The mustard hypocotyl also serves as a conduit for transporting water, nutrients, and hormones between the roots and the cotyledons. The vascular tissues within the hypocotyl, comprising xylem and phloem, facilitate this transport. The xylem moves water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the cotyledons, while the phloem distributes sugars and other organic compounds produced by the cotyledons during photosynthesis.
Another important function of the mustard hypocotyl is to store energy reserves that support the early growth of the seedling. These energy reserves, primarily in the form of starches, are metabolized to provide the energy needed for cell division and elongation during the initial stages of growth.
The hypocotyl is also critical in determining the growth direction of the seedling. It exhibits a phenomenon known as phototropism, where it grows towards the light source. This directional growth ensures that the cotyledons are optimally positioned to capture sunlight for photosynthesis. Additionally, the hypocotyl shows geotropism, responding to gravity by growing upwards, while the roots grow downwards, establishing the correct orientation for the plant.
In mustard plants, the length and robustness of the hypocotyl can be influenced by various environmental conditions. For instance, seedlings grown in low light conditions may develop longer hypocotyls as they stretch towards the light. Conversely, seedlings exposed to sufficient light typically have shorter, sturdier hypocotyls.
The mustard hypocotyl also has significance in scientific research and agricultural practices. Researchers often study hypocotyl elongation as a model for understanding plant growth responses to environmental stimuli and hormonal regulation. Insights gained from these studies can inform breeding programs aimed at developing mustard varieties with improved growth characteristics and stress tolerance.
In agricultural contexts, understanding the development and function of the hypocotyl can help optimize planting techniques. For example, ensuring proper soil depth and moisture conditions can promote healthy hypocotyl elongation and seedling emergence, leading to better crop establishment and yields.
The mustard hypocotyl is a vital part of the plant’s early development, facilitating the emergence of the seedling, supporting initial growth through nutrient transport and energy storage, and ensuring proper orientation towards light and gravity.
Its growth and development are influenced by environmental conditions and internal hormonal signals, making it a key focus in both scientific research and agricultural practices. Understanding the role and function of the mustard hypocotyl enhances our ability to cultivate healthy mustard plants and improve crop productivity.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Mustard Hypocotyl
1. Plant Development: The mustard hypocotyl is crucial in the early development of mustard seedlings, aiding in the transition from seed to mature plant. Example: Healthy mustard seedlings with strong hypocotyls grow into robust plants.
2. Soil Stabilization: The hypocotyl helps anchor mustard plants, stabilizing soil and preventing erosion. Example: Mustard plants in erosion-prone areas help maintain soil integrity.
3. Organic Fertilizers: Mustard hypocotyls can be composted to create organic fertilizers. Example: Compost made from mustard plant residues, including hypocotyls, enhances soil fertility.
4. Animal Feed: Hypocotyls are used in animal feed due to their nutritional value. Example: Livestock feed formulations incorporating mustard hypocotyls.
5. Green Manure: Mustard hypocotyls can be used as green manure to improve soil structure and fertility. Example: Incorporating mustard hypocotyls into the soil to enrich it.
6. Medicinal Uses: Mustard hypocotyls have applications in traditional medicine. Example: Herbal remedies using mustard hypocotyl extracts.
7. Bioremediation: Hypocotyls contribute to bioremediation efforts by aiding in the absorption of soil contaminants. Example: Mustard plants with strong hypocotyls used in phytoremediation projects.
8. Soil Amendment: Mustard hypocotyls can be added to soil to improve its texture and nutrient content. Example: Soil amendment practices using mustard hypocotyls.
9. Nutrient Cycling: The decomposition of mustard hypocotyls contributes to nutrient cycling in agricultural systems. Example: Enhanced nutrient availability in soil through hypocotyl decomposition.
10. Research and Education: Mustard hypocotyls are used in botanical research and education to study plant development. Example: Research on hypocotyl growth patterns in mustard plants.
11. Sustainable Agriculture: Using mustard hypocotyls in farming supports sustainable practices by reducing the need for chemical inputs. Example: Sustainable agriculture techniques utilizing mustard hypocotyls.
12. Erosion Control: Hypocotyls help stabilize soil and prevent erosion in agricultural fields. Example: Erosion control measures involving mustard plants with strong hypocotyls.
13. Organic Mulch: Mustard hypocotyls can be used as organic mulch to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds. Example: Mulch made from mustard plant parts, including hypocotyls.
14. Plant Breeding: Hypocotyl characteristics are studied in plant breeding to select for desirable traits. Example: Breeding programs focusing on robust hypocotyl development.
15. Water Management: Hypocotyls aid in water management by improving soil water retention. Example: Enhanced soil moisture levels due to mustard hypocotyl growth.
16. Bioenergy Production: Mustard hypocotyls can be used in the production of bioenergy. Example: Biofuel production from mustard plant biomass, including hypocotyls.
17. Composting: Hypocotyls contribute to the composting process, creating nutrient-rich compost. Example: Compost piles containing mustard hypocotyls and other plant residues.
18. Functional Foods: Hypocotyls are used in functional foods for their potential health benefits. Example: Nutritional supplements and health products containing mustard hypocotyl extracts.
Read Also: 18 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Pomaria jamesii (James’ Skullcap)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Mustard Hypocotyl
1. Organic Fertilizers: Hypocotyls are composted to produce organic fertilizers that enrich soil. Example: Fertilizer products derived from mustard hypocotyl compost.
2. Animal Feed: Hypocotyls are processed into animal feed for their nutritional benefits. Example: Livestock feed incorporating mustard hypocotyls.
3. Bioenergy: Mustard hypocotyls are used in bioenergy production processes like biomass conversion. Example: Biofuels made from mustard hypocotyl biomass.
4. Green Manure: Hypocotyls are used as green manure to improve soil fertility. Example: Green manure applications using mustard hypocotyls.
5. Medicinal Products: Hypocotyl extracts are used in traditional and modern medicinal products. Example: Herbal remedies and supplements containing mustard hypocotyl extracts.
6. Compost: Mustard hypocotyls are composted to create nutrient-rich compost for gardening. Example: Compost piles enriched with mustard hypocotyls.
7. Soil Amendments: Hypocotyls are added to soil to enhance its structure and nutrient content. Example: Soil amendments made from mustard hypocotyl residues.
8. Functional Foods: Hypocotyls are used in the production of functional foods and supplements. Example: Health products containing mustard hypocotyl extracts.
9. Erosion Control Products: Mustard hypocotyls are used in products designed to prevent soil erosion. Example: Erosion control materials incorporating mustard hypocotyls.
10. Research Samples: Hypocotyls are used in botanical research to study plant development. Example: Research studies on mustard hypocotyl growth.
11. Organic Mulch: Hypocotyls are processed into organic mulch to retain soil moisture. Example: Mulch products made from mustard hypocotyls.
12. Sustainable Farming Inputs: Hypocotyls support sustainable agriculture by improving soil health. Example: Sustainable farming practices using mustard hypocotyls.
13. Craft Materials: Dried hypocotyls are used in crafting and decorative projects. Example: Craft projects using dried mustard hypocotyls.
14. Biodegradable Products: Hypocotyls are processed into biodegradable materials. Example: Biodegradable packaging made from mustard hypocotyl fibers.
15. Water Management Tools: Hypocotyls help improve soil water retention. Example: Water retention materials using mustard hypocotyls.
16. Educational Resources: Hypocotyls are used in educational settings to teach plant biology. Example: Classroom resources featuring mustard hypocotyl samples.
17. Pest Management Products: Hypocotyls are used in natural pest management solutions. Example: Organic pest control products incorporating mustard hypocotyls.
Read Also: Anemone Flowers – All you need to know
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Mustard Hypocotyl
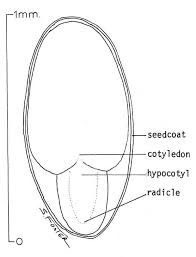
1. What is a mustard hypocotyl?
The mustard hypocotyl is the part of the seedling that lies between the seed leaves (cotyledons) and the root.
2. How does the mustard hypocotyl contribute to plant growth?
The hypocotyl helps the seedling emerge from the soil and supports the initial growth of the plant.
3. Can mustard hypocotyls be used in composting?
Yes, mustard hypocotyls can be composted to create nutrient-rich compost for soil improvement.
4. Are mustard hypocotyls used in animal feed?
Yes, mustard hypocotyls are used in animal feed due to their nutritional value.
5. How do mustard hypocotyls aid in soil stabilization?
The hypocotyl helps anchor the mustard plant, stabilizing the soil and preventing erosion.
6. What are the medicinal uses of mustard hypocotyls?
Mustard hypocotyls have applications in traditional medicine for their potential therapeutic properties.
7. Can mustard hypocotyls be used in bioremediation?
Yes, mustard hypocotyls are used in bioremediation to help remove contaminants from the soil.
8. How are mustard hypocotyls used in sustainable agriculture?
Mustard hypocotyls support sustainable agriculture by improving soil health and reducing the need for chemical inputs.
9. Can mustard hypocotyls be used as green manure?
Yes, mustard hypocotyls can be incorporated into the soil as green manure to enhance soil fertility.
10. How are mustard hypocotyls used in research?
Mustard hypocotyls are used in botanical research to study plant development and growth patterns.
Read Also: What Are The Different Types Of Agricultural Careers