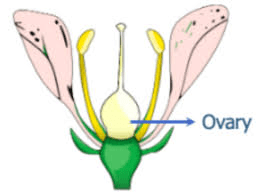
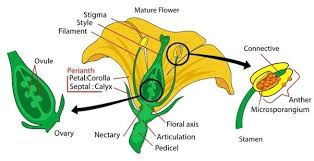
The mustard ovary is a crucial part of the mustard plant’s reproductive system, specifically within the flower’s pistil, which is the female reproductive organ. In mustard plants (genus Brassica), the ovary plays a pivotal role in the development of seeds, ensuring the continuation of the plant’s life cycle.
The ovary is located at the base of the pistil, just below the style and stigma. It is typically a swollen structure that contains the ovules, which are the potential seeds. In mustard flowers, the ovary is usually superior, meaning it is positioned above the point where the petals and sepals are attached. This positioning is typical for members of the Brassicaceae family.
The primary function of the ovary is to house and protect the ovules. Each ovary can contain multiple ovules, and the exact number can vary depending on the species and environmental conditions. During the process of pollination, pollen grains land on the stigma and germinate, growing a pollen tube down the style and into the ovary. The sperm cells travel through this tube to reach the ovules, where fertilization occurs. Once fertilized, the ovules develop into seeds.
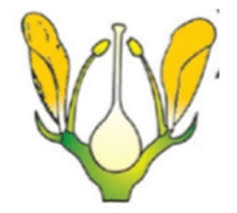
In mustard plants, the ovary transforms into a fruit known as a silique after fertilization. The silique is an elongated seed pod that contains the developing seeds. As the seeds mature, the silique grows and elongates, eventually drying out and splitting open to release the seeds. This process ensures that the seeds are dispersed into the environment, where they can germinate and grow into new plants.
The structure and development of the ovary are vital for the reproductive success of mustard plants. A healthy ovary is essential for producing viable seeds, which are necessary for the propagation of the species. Factors such as environmental conditions, nutrient availability, and genetic traits can all influence the development and functionality of the ovary.
In agricultural practices, understanding the ovary’s role and development can help improve crop yields and seed quality. For instance, breeding programs might focus on selecting plants with robust ovaries that produce a higher number of viable seeds. Additionally, managing environmental factors, such as soil quality and water availability, can enhance ovary development and seed production in mustard crops.
Research into the ovary’s function and development can also provide insights into broader plant reproductive biology. By studying how different plants regulate ovary development and seed production, scientists can better understand the mechanisms underlying plant reproduction and develop strategies to improve crop performance across various species.
In summary, the ovary in mustard plants is a key component of the pistil that houses the ovules and plays a crucial role in seed development. It transforms into a silique after fertilization, ensuring seed production and dispersal. Understanding the ovary’s structure and function is essential for optimizing agricultural practices and enhancing crop yields, making it a vital aspect of mustard plant biology.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Mustard Ovary
1. Seed Production: The mustard ovary develops into pods containing seeds, which are the primary economic product of mustard plants, used in culinary, medicinal, and industrial applications.
2. Agricultural Value: Mustard ovary contributes to the reproductive cycle of the plant, ensuring continuous production and supply of mustard seeds, which are crucial for agricultural sustainability.
3. Crop Breeding: Understanding the development of the mustard ovary is essential for crop breeding programs aimed at improving yield, disease resistance, and quality of mustard seeds.
4. Nutritional Value: The seeds developed from mustard ovaries are rich in essential nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and minerals, contributing to human and animal nutrition.
5. Culinary Use: Mustard seeds derived from ovaries are a staple in many cuisines, used in whole, powdered, or oil forms to add flavor and nutritional value to dishes.
6. Medicinal Use: Mustard seeds, produced from ovaries, are used in traditional medicine for their potential therapeutic properties, including anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
7. Oil Production: Mustard seeds are pressed to extract mustard oil, which is used for cooking, medicinal purposes, and as a biofuel.
8. Animal Feed: By-products from mustard seed processing, such as mustard seed cake, are used as nutritious animal feed.
9. Fertilizer: Mustard plant residues, including parts of the ovary, can be composted to produce organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility.
10. Natural Pesticide: Mustard plants, including their ovaries, are used in the production of natural pesticides that help manage agricultural pests.
11. Biofuel Research: Mustard seeds are explored as a potential source of biofuel, contributing to renewable energy solutions.
12. Food Preservation: Mustard seeds have preservative qualities due to their antimicrobial properties, making them useful in food preservation processes.
13. Skincare Products: Mustard seed oil, derived from seeds formed in the ovary, is used in skincare products for its moisturizing and anti-inflammatory benefits.
14. Industrial Uses: Mustard seeds are used in the production of lubricants, emulsifiers, and other industrial products.
15. Flavoring Agent: Mustard seeds are a key ingredient in condiments, sauces, and spice blends, enhancing the flavor of a wide variety of foods.
16. Economic Crop: Mustard cultivation, driven by seed production from ovaries, provides economic benefits to farmers and supports agricultural economies.
17. Research and Development: The mustard ovary is studied to improve understanding of plant reproduction and seed development, aiding in agricultural research.
18. Sustainable Agriculture: Utilizing the entire mustard plant, including the ovary, supports sustainable agricultural practices by maximizing resource use.
Read Also: Appraisal of Shifting and Continuous Cultivation
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Mustard Ovary
1. Mustard Seeds: Primary product used for culinary, medicinal, and industrial purposes.
2. Mustard Seed Oil: Extracted from seeds, used in cooking, medicine, and biofuel production.
3. Mustard Seed Cake: By-product of oil extraction, used as animal feed and fertilizer.
4. Mustard Powder: Ground seeds used in spice blends, condiments, and traditional medicine.
5. Mustard Sauce: Prepared mustard made from ground seeds and vinegar.
6. Mustard Seed Extract: Used in dietary supplements and medicinal products for potential health benefits.
7. Mustard Fertilizer: Organic fertilizer made from mustard plant residues, including ovaries.
8. Mustard Pesticide: Natural pesticide made from mustard plant parts, including ovaries.
9. Mustard Skincare Products: Creams, lotions, and soaps made with mustard seed oil and extracts.
10. Mustard Biofuel: Renewable energy source produced from mustard seeds.
11. Mustard Capsules: Dietary supplements containing mustard seed powder or extracts.
12. Mustard Dye: Natural dye made from mustard seeds and plant parts.
13. Mustard Infusion: Infused oils and liquids for culinary and medicinal uses.
14. Mustard Paste: Blended mustard seeds used in culinary applications.
15. Mustard Dressing: Salad dressings and marinades made with mustard as a key ingredient.
16. Mustard Flakes: Dehydrated mustard seed products used in specialty foods.
17. Mustard Flour: Ground seeds used as a gluten-free flour alternative in baking.
Read Also: Soil Temperature and Plant Growth
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Mustard Ovary
1. What is the mustard ovary? The mustard ovary is the part of the mustard flower that develops into pods containing seeds, which are the main economic product of mustard plants.
2. How does the mustard ovary contribute to seed production? The mustard ovary matures into seed pods that contain the mustard seeds, essential for reproduction and harvesting.
3. Can mustard seeds be used for cooking? Yes, mustard seeds are widely used in cooking for their flavor and nutritional benefits, available in whole, powdered, or oil forms.
4. Are mustard seeds beneficial for health? Mustard seeds are rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and minerals, and they may have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
5. How is mustard oil produced? Mustard oil is produced by pressing mustard seeds, which are developed from the ovary of the mustard flower.
6. What are the uses of mustard seed oil? Mustard seed oil is used for cooking, medicinal purposes, skincare products, and as a biofuel.
7. How is mustard used in traditional medicine? Mustard seeds and oil are used in traditional medicine for their potential therapeutic effects, including pain relief and antimicrobial action.
8. Can mustard residues be used as fertilizer? Yes, mustard plant residues, including parts of the ovary, can be composted to create organic fertilizer.
9. What is mustard seed cake? Mustard seed cake is a by-product of oil extraction, used as animal feed and organic fertilizer.
10. How does mustard contribute to sustainable agriculture? Utilizing the entire mustard plant, including the ovary, supports sustainable agricultural practices by maximizing resource use and reducing waste.
Read Also: Sa Recycling Process Complete Guide

