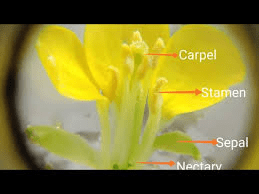
Mustard stamen, the male reproductive part of the mustard plant, plays a crucial role in the plant’s reproduction. Comprising the anther and filament, the stamen is integral to the process of pollen production and dispersal. In mustard plants (genus Brassica), the stamen structure is consistent with that of many angiosperms, facilitating effective pollination and ensuring genetic diversity.
The stamen’s filament is a slender stalk that supports the anther, positioning it optimally for pollen transfer. The filament’s length and strength are crucial, as they must ensure the anther is accessible to pollinators or wind currents. In mustard plants, the filaments are typically of moderate length, which suits their natural pollinators, such as bees and other insects. The anther, located at the tip of the filament, is the pollen-producing organ. It consists of four microsporangia, which are pollen sacs where meiosis occurs, leading to the formation of pollen grains.
Pollen grains are the carriers of the male gametes and are crucial for the fertilization process. In mustard plants, the pollen grains are relatively small and lightweight, which aids in their dispersal by wind or insects. Each pollen grain contains two cells: a generative cell, which will divide to form two sperm cells, and a tube cell, which will develop into a pollen tube upon reaching a compatible pistil.
The anther of the mustard stamen undergoes a maturation process where it dehisces, or splits open, to release the pollen grains. This process is timed to coincide with the flower’s receptive phase, maximizing the chances of successful pollination. The release of pollen can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, ensuring that the pollen is dispersed under optimal conditions.
Mustard plants often exhibit a form of pollination known as self-incompatibility, which prevents self-fertilization and promotes cross-pollination. This mechanism enhances genetic diversity within the species, making the population more resilient to diseases and environmental changes. The stamen’s structure and function are integral to this process, as they ensure the pollen is effectively transferred to the stigma of another flower.
The mustard stamen’s role extends beyond just pollen production and release. It also plays a part in attracting pollinators through its position and sometimes its coloration. While the primary visual attractant in mustard flowers is the petals, the stamens’ positioning ensures that visiting insects come into contact with the anthers and collect pollen. As they move from flower to flower, these insects inadvertently transfer pollen to the stigmas, facilitating cross-pollination.
In addition to its reproductive functions, the stamen can also contribute to the structural integrity of the flower. The filaments help support the flower’s overall structure, ensuring that the reproductive organs are properly positioned. This structural role is especially important in windy conditions, where the stability of the flower can impact its ability to successfully reproduce.
The mustard stamen is a complex and vital component of the plant’s reproductive system. Its design and function are perfectly adapted to ensure the successful production and transfer of pollen, promoting genetic diversity and the continued survival of the species.
From the filament’s support to the anther’s pollen production and release, each part of the stamen works in harmony to achieve the ultimate goal of fertilization. This intricate system highlights the remarkable adaptations plants have evolved to thrive in their environments and maintain their populations through effective reproductive strategies.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Mustard Stamen

1. Pollination: The mustard stamen produces pollen necessary for the fertilization of the ovary, leading to seed development. This process is essential for mustard crop production.
2. Crop Breeding: Understanding the function of the mustard stamen helps in crop breeding programs aimed at improving yield, disease resistance, and the quality of mustard plants.
3. Genetic Diversity: The stamen’s role in pollination contributes to genetic diversity through cross-pollination, enhancing the adaptability and resilience of mustard crops.
4. Agricultural Research: Studying the stamen aids in agricultural research focused on improving reproductive efficiency and overall crop performance.
5. Sustainable Agriculture: Effective pollination through the stamen supports sustainable farming practices by ensuring high seed yield and quality.
6. Education: The mustard stamen is a key subject in botanical education, helping students and researchers understand plant reproductive systems.
7. Economic Stability: Successful pollination facilitated by the stamen contributes to the economic stability of farmers who rely on mustard crops for income.
8. Food Security: The stamen’s role in seed production is crucial for food security, ensuring a steady supply of mustard seeds for culinary and industrial use.
9. Pollination Efficiency: Research on the stamen helps develop better practices for enhancing pollinator efficiency, which is crucial for mustard crop yields.
10. Genetic Studies: The stamen is studied in genetics to understand the inheritance of traits, aiding in the development of improved mustard varieties.
11. Pharmaceutical Research: Compounds found in the stamen and other reproductive parts of the mustard plant are studied for potential pharmaceutical applications.
12. Bioengineering: Insights into the stamen’s function can lead to bioengineering advancements, such as developing mustard plants with enhanced traits.
13. Climate Adaptation: Research on the stamen’s role in reproduction can help develop mustard varieties that are more resilient to climate change.
14. Crop Rotation: Mustard plants, including their reproductive parts, are used in crop rotation to improve soil health and manage pests, contributing to sustainable farming.
15. Food Industry: Mustard seeds produced via the stamen are used in various food products, including condiments, spices, and oils.
16. Natural Pesticides: The study of mustard reproductive biology can lead to the development of natural pesticides derived from mustard plants.
17. Cultural Significance: Mustard plants, including their reproductive parts, hold cultural significance in various cuisines and traditional practices around the world.
18. Environmental Impact: Sustainable production of mustard seeds through efficient stamen function helps reduce the environmental impact of agriculture.
Read Also: Anemone Flowers – All you need to know
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Mustard Stamen
1. Mustard Seeds: Primary product resulting from successful fertilization, used in culinary, medicinal, and industrial applications.
2. Mustard Oil: Extracted from mustard seeds, used for cooking, medicinal purposes, and as a biofuel.
3. Mustard Seed Cake: By-product of oil extraction, used as animal feed and fertilizer.
4. Mustard Powder: Ground seeds used in spice blends, condiments, and traditional medicine.
5. Mustard Sauce: Prepared mustard made from ground seeds and vinegar.
6. Mustard Seed Extract: Used in dietary supplements and medicinal products for potential health benefits.
7. Mustard Fertilizer: Organic fertilizer made from mustard plant residues, including stamens and other parts.
8. Mustard Pesticide: Natural pesticide made from mustard plant parts, including stamens.
9. Mustard Skincare Products: Creams, lotions, and soaps made with mustard seed oil and extracts.
10. Mustard Biofuel: Renewable energy source produced from mustard seeds.
11. Mustard Capsules: Dietary supplements containing mustard seed powder or extracts.
12. Mustard Dye: Natural dye made from mustard seeds and plant parts.
13. Mustard Infusion: Infused oils and liquids for culinary and medicinal uses.
14. Mustard Paste: Blended mustard seeds used in culinary applications.
15. Mustard Dressing: Salad dressings and marinades made with mustard as a key ingredient.
16. Mustard Flakes: Dehydrated mustard seed products used in specialty foods.
17. Mustard Flour: Ground seeds used as a gluten-free flour alternative in baking.
Read Also: 22 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Dysphania graveolens (Epazote)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Mustard Stamen

1. What is the mustard stamen? The mustard stamen is the male reproductive part of the mustard flower, responsible for producing pollen necessary for fertilization.
2. How does the mustard stamen contribute to seed production? The stamen produces pollen that fertilizes the ovary, leading to the development of mustard seeds.
3. Can the stamen be used directly in any products? The stamen itself is not directly used in products, but its role in pollen production is crucial for generating mustard seeds, oil, and other products.
4. How does the stamen affect crop yield? A healthy stamen ensures successful pollination and seed development, directly impacting the yield and quality of mustard crops.
5. What research is done on the mustard stamen? Research on the mustard stamen focuses on improving reproductive efficiency, understanding genetic traits, and enhancing crop yields.
6. How does the stamen support sustainable agriculture? Efficient pollination through the stamen ensures high seed yield and quality, supporting sustainable farming practices.
7. Can studying the stamen lead to better mustard varieties? Yes, studying the stamen helps in developing improved mustard varieties with better yield, disease resistance, and quality.
8. What role does the stamen play in pollination? The stamen produces pollen that is transferred to the pistil, facilitating fertilization and seed development in mustard plants.
9. How does the stamen impact genetic diversity? The stamen contributes to genetic diversity through cross-pollination, which is essential for the adaptability and resilience of mustard crops.
10. Why is the stamen important for food security? The stamen’s role in pollen production ensures a steady supply of mustard seeds, which are important for culinary and industrial uses, thus supporting food security.
Read Also: Computer Recycling Complete Beginners Guide






