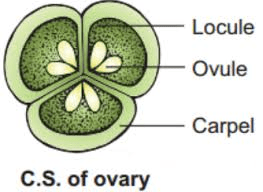
The Onion ovary is a critical part of the onion flower’s pistil and plays an essential role in the plant’s reproductive process. Located at the base of the pistil, the ovary houses the ovules, which are the structures that will develop into seeds once fertilized. The structure and function of the ovary are fundamental to the successful reproduction of the onion plant.
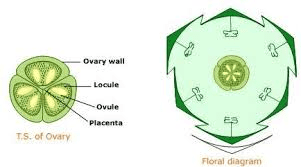
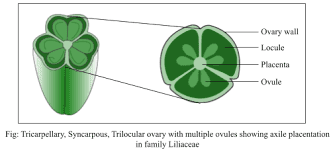
Structurally, the ovary is a rounded or bulbous chamber that contains one or more ovules. In onions, the ovary is typically a single-chambered structure, but it can house multiple ovules. Each ovule contains an egg cell and is surrounded by protective layers. The ovary is connected to the style, a slender stalk that channels the pollen tube from the stigma (the pollen-receptive part of the pistil) to the ovules.
The primary function of the ovary is to protect and nurture the developing ovules. Once pollen reaches the ovary via the pollen tube, it enters the ovule and releases sperm cells. One of these sperm cells fertilizes the egg cell, resulting in the formation of a zygote. This zygote will develop into an embryo, and the ovule will become a seed. The other sperm cell usually fuses with other cells in the ovule to form the endosperm, which provides essential nutrients to the developing embryo.
The ovary also undergoes significant transformation after fertilization. The fertilized ovules develop into seeds, and the ovary itself begins to mature into a fruit, often referred to as a seed pod or capsule in onions. This fruit encases the seeds and provides protection as they mature. The ovary’s walls thicken and develop a protective outer layer that helps safeguard the seeds from environmental stresses and potential predators.
In addition to its protective role, the ovary contributes to the dispersal of seeds. As the fruit matures, it eventually releases the seeds, allowing them to be dispersed by various means such as wind, water, or animals. This dispersal is crucial for the propagation of the onion plant, enabling seeds to germinate and grow into new plants.
From an anatomical perspective, the ovary is composed of several layers of tissues. The outermost layer, the ovary wall, provides structural support and protection. Inside, the ovule chambers are lined with nutritive tissues that support the development of the ovules. The overall structure of the ovary is adapted to optimize the chances of successful fertilization and seed development.
The ovary’s role in reproduction extends beyond mere seed production. It also plays a part in the genetic diversity of the plant. By facilitating fertilization and seed development, the ovary ensures the mixing of genetic material from different plants. This genetic diversity enhances the adaptability and resilience of onion populations, making them better equipped to survive and thrive in various environments.
The ovary of the onion flower is a crucial component of the pistil, responsible for housing and nurturing the ovules. Its primary functions include protecting the ovules, facilitating fertilization, and eventually developing into a fruit that encases the seeds. The ovary’s role in seed production and dispersal is essential for the propagation and survival of the onion plant, contributing to its ecological success and agricultural significance.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Onion Ovary
1. Nutritional Supplements: Onion ovaries contain beneficial nutrients that can be extracted and used in dietary supplements.
2. Natural Dyes: They can be utilized to create natural dyes for textiles, providing an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic dyes.
3. Antimicrobial Agents: Onion ovaries have antimicrobial properties, making them useful in creating natural preservatives for food products.
4. Animal Feed: They can be processed into feed for livestock, providing a nutritious supplement to animal diets.
5. Fertilizers: Onion ovaries can be composted to create organic fertilizers, enriching soil health for agriculture.
6. Biofuels: Research is exploring the potential of onion ovaries in the production of biofuels, contributing to renewable energy sources.
7. Medicinal Uses: Onion ovaries are studied for their potential in herbal medicine, offering remedies for various ailments.
8. Cosmetic Products: Extracts from onion ovaries can be used in cosmetics for their skin-soothing properties.
9. Food Flavoring: They can be dried and ground into a powder to add flavor to various culinary dishes.
10. Pest Repellent: The strong odor of onion ovaries can be used to create natural pest repellents for gardens and crops.
11. Biodegradable Packaging: They can be processed into biodegradable packaging materials, reducing plastic waste.
12. Paper Production: Onion ovaries can be utilized in making eco-friendly paper products.
13. Wastewater Treatment: They have properties that can aid in the filtration and treatment of wastewater.
14. Antioxidant Sources: Onion ovaries are rich in antioxidants, which can be extracted for health supplements.
15. Plant Growth Regulators: They can be processed to create natural growth regulators for agricultural use.
16. Dietary Fiber: Onion ovaries are a good source of dietary fiber, which can be added to various food products.
17. Enzyme Production: They can be used in the production of certain enzymes for industrial applications.
18. Traditional Remedies: In some cultures, onion ovaries are used in traditional remedies and healing practices.
Read Also: 25 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Astragalus amphioxys (Crescent milkvetch)
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Onion Ovary
1. Nutritional Supplements: Extracting vitamins and minerals from onion ovaries for health supplements.
2. Natural Dye: Using onion ovaries to produce a natural dye for fabrics and textiles through boiling and soaking processes.
3. Antimicrobial Agents: Creating natural preservatives for food by extracting antimicrobial compounds.
4. Animal Feed: Drying and grinding onion ovaries to add to livestock feed.
5. Organic Fertilizer: Composting onion ovaries to produce nutrient-rich organic fertilizer.
6. Biofuel: Processing onion ovaries through fermentation to produce bioethanol.
7. Herbal Medicine: Extracting active compounds for use in natural remedies and treatments.
8. Skincare Products: Formulating creams and lotions with onion ovary extracts for skin benefits.
9. Culinary Powder: Drying and grinding ovaries into a fine powder for use as a spice.
10. Pest Repellent: Creating a spray by infusing onion ovaries in water to repel insects.
11. Biodegradable Plastics: Developing packaging materials from onion ovary fibers.
12. Eco-friendly Paper: Processing onion ovaries into pulp for paper production.
13. Water Filter: Using onion ovaries in the creation of natural filtration systems for water treatment.
14. Antioxidant Extracts: Extracting antioxidants for use in health supplements.
15. Plant Growth Stimulants: Creating natural growth enhancers for plants from onion ovaries.
16. Fiber Supplements: Adding processed onion ovaries to dietary fiber products.
17. Enzyme Production: Cultivating enzymes from onion ovaries for industrial use.
Read Also: Growing Guide and Health Benefits of Chaste Tree
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Onion Ovary
1. What are onion ovaries?
Onion ovaries are the part of the onion flower that contains the ovules, often discarded but rich in beneficial compounds.
2. How can onion ovaries be used in cooking?
They can be dried and ground into a powder to add flavor to soups, stews, and other dishes.
3. Are onion ovaries safe for consumption?
Yes, they are safe and can be used in various culinary and medicinal applications.
4. Can onion ovaries be used in skincare?
Yes, extracts from onion ovaries can be used in skincare products for their soothing properties.
5. How do onion ovaries contribute to sustainability?
They can be used to create biodegradable products, reducing environmental waste.
6. What nutritional benefits do onion ovaries offer?
Onion ovaries are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, making them a nutritious addition to diets.
7. Can onion ovaries be used as animal feed?
Yes, they can be dried and added to livestock feed as a nutritious supplement.
8. How are onion ovaries used in traditional medicine?
In some cultures, they are used in remedies to treat various health issues due to their medicinal properties.
9. What industrial applications do onion ovaries have?
They can be used in biofuel production, wastewater treatment, and enzyme production.
10. Are there any environmental benefits to using onion ovaries?
Yes, using onion ovaries in various applications reduces waste and promotes eco-friendly practices.
Read Also: Business Planning Process and Importance of Business Plan