The inflorescence of pineapple (Ananas comosus) is a remarkable botanical structure that plays a crucial role in the development of the pineapple fruit. The pineapple plant, a member of the Bromeliaceae family, produces a distinctive flowering spike that ultimately gives rise to the fruit we recognize and enjoy.
The pineapple plant is a perennial herbaceous plant that thrives in tropical and subtropical regions. It has a rosette of long, stiff, and spiny leaves, which can grow up to 1.5 meters in length. From the center of this rosette, the inflorescence, or flower head, emerges on a sturdy stalk known as the peduncle. The peduncle can reach a length of 15 to 20 centimeters and supports the dense cluster of flowers that make up the inflorescence.
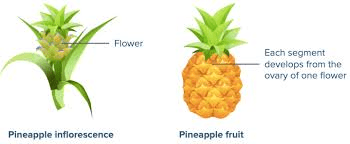
The pineapple inflorescence is a compact, cylindrical structure composed of numerous small, individual flowers. These flowers are arranged in a spiral pattern around the central axis of the inflorescence, creating a visually striking and efficient arrangement. The number of flowers in a pineapple inflorescence can vary, but it typically ranges from 100 to 200.
Each flower within the inflorescence is small, tubular, and usually exhibits a color spectrum from pale lavender to deep purple. The flowers are structurally complete, containing sepals, petals, stamens, and a pistil. The sepals, which form the outermost part of the flower, are green and leaf-like, protecting the flower bud before it opens. The petals, often fused into a tubular shape, are the colorful part of the flower, designed to attract pollinators.
However, in commercial pineapple cultivation, natural pollination is usually discouraged. This is because pollination can lead to seed formation within the fruit, which is undesirable for commercial purposes. Instead, pineapples are propagated vegetatively, using suckers or slips that grow from the base of the plant.
The reproductive organs of each pineapple flower include the stamens (male) and the pistil (female). The stamens consist of a filament and an anther, which produces pollen. The pistil is composed of an ovary, style, and stigma. The ovary contains ovules, which can develop into seeds if fertilized. However, as mentioned earlier, seed formation is typically avoided in commercial cultivation.
As the flowers of the pineapple inflorescence develop and mature, they undergo a process called coalescence. This involves the individual flowers fusing together to form the multiple fruit structure characteristic of pineapples. Each hexagonal segment, or “eye,” on the surface of a pineapple represents a single flower from the inflorescence.
The transformation from flowers to a mature pineapple fruit takes several months. Initially, the developing fruit is green and firm, but as it ripens, it turns golden-yellow and becomes juicier and sweeter. Pineapples are harvested when fully ripe, as they do not ripen significantly after being picked.
The pineapple inflorescence is a vital and intricate structure that leads to the formation of the pineapple fruit. The spiral arrangement of numerous small flowers, the avoidance of natural pollination in commercial cultivation, and the process of coalescence all contribute to the unique development of this beloved tropical fruit. Understanding the pineapple inflorescence provides insight into the complex and fascinating world of plant reproduction and fruit formation.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Pineapple Inflorescence

1. Fruit Production: The primary use of pineapple inflorescence is fruit production. Pineapples are economically significant fruits used worldwide in fresh and processed forms.
2. Ornamental Plants: Pineapple plants, including their inflorescence, are used as ornamental plants in gardens and landscapes for their unique and exotic appearance.
3. Food Industry: Pineapple inflorescence is processed into various food products such as canned pineapple, pineapple juice, jams, and preserves.
4. Culinary Uses: Fresh pineapple inflorescence is used in culinary dishes, including salads, desserts, and beverages.
5. Export Goods: Pineapples are a major export commodity for many tropical countries, contributing significantly to their economies.
6. Beverages: Pineapple inflorescence is used to make alcoholic beverages such as pineapple wine and piña colada.
7. Natural Sweetener: Pineapple extracts from the inflorescence are used as natural sweeteners in food and beverages.
8. Nutritional Supplements: Extracts from pineapple inflorescence are used in dietary supplements for their vitamins and minerals.
9. Flavoring Agents: Pineapple inflorescence is used to produce natural flavoring agents for various food and beverage products.
10. Confectionery: Pineapple inflorescence is used in the confectionery industry to make candies, jellies, and other sweet treats.
11. Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, pineapple inflorescence is used in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory and digestive properties.
12. Cosmetics: Extracts from pineapple inflorescence are used in cosmetics and skincare products for their hydrating and anti-aging properties.
13. Animal Feed: The by-products of pineapple inflorescence can be used as feed for livestock.
14. Textile Industry: Fibers from pineapple leaves, including those associated with the inflorescence, are used to make fabrics and textiles.
15. Biofuel: Organic matter from pineapple inflorescence can be processed into biofuel.
16. Vinegar Production: Pineapple inflorescence is used to produce vinegar through fermentation.
17. Enzyme Production: The inflorescence contains bromelain, an enzyme used in meat tenderizers and various industrial applications.
18. Eco-Friendly Packaging: The fibrous material from the inflorescence can be used to create biodegradable packaging materials.
Read Also: Best Number of Ruminant Animals per Housing Unit for Fattening
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Pineapple Inflorescence

1. Pineapple Fruit: The primary product derived from the inflorescence, used fresh, canned, or processed into juice.
2. Pineapple Juice: Extracted from the fruit and used as a beverage or in food products.
3. Pineapple Jam and Preserves: Made from the fruit and used as spreads and in baking.
4. Dried Pineapple: The fruit is dried and used as a snack or in culinary dishes.
5. Pineapple Vinegar: Produced through the fermentation of pineapple inflorescence.
6. Pineapple Wine: An alcoholic beverage made from fermented pineapple juice.
7. Pineapple Fibers: Extracted from the leaves and used in textiles and eco-friendly packaging.
8. Pineapple Extract: Used as a natural flavoring agent and in nutritional supplements.
9. Bromelain Enzyme: Extracted from the inflorescence and used in meat tenderizers and pharmaceuticals.
10. Pineapple Essential Oil: Extracted from the inflorescence and used in aromatherapy and cosmetics.
11. Animal Feed: By-products of the inflorescence used as livestock feed.
12. Pineapple Candy: Made from the fruit and used in confectionery.
13. Pineapple Tea: Made from dried pineapple inflorescence and enjoyed as a herbal tea.
14. Pineapple Skincare Products: Extracts used in cosmetics for their hydrating properties.
15. Pineapple Natural Dye: Extracted from the inflorescence for use in textiles.
16. Biodegradable Packaging: Made from the fibrous material of the inflorescence.
17. Pineapple Beverages: Non-alcoholic beverages such as smoothies and flavored water.
Read Also: Common Rabbit Diseases and How to Cure them
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Pineapple Inflorescence
1. What is pineapple inflorescence? Pineapple inflorescence is the flowering part of the pineapple plant from which the fruit develops.
2. How is pineapple inflorescence used in the food industry? It is used to produce fresh fruit, juices, jams, and various processed food products.
3. Can pineapple inflorescence be used in traditional medicine? Yes, it is used for its anti-inflammatory and digestive properties in some traditional medicine practices.
4. What is bromelain, and how is it derived from pineapple inflorescence? Bromelain is an enzyme extracted from the inflorescence and used in meat tenderizers and medical applications.
5. Are there non-food uses for pineapple inflorescence? Yes, it is used in cosmetics, textiles, animal feed, and as a natural dye.
6. How does pineapple inflorescence contribute to the economy? It supports the food industry, export markets, and various by-product industries, contributing significantly to economies.
7. What are the environmental benefits of using pineapple inflorescence? The fibrous material can be used to make biodegradable packaging, reducing plastic waste.
8. Can pineapple inflorescence be used in beverages? Yes, it is used to make pineapple wine, vinegar, and flavored beverages.
9. What are the cosmetic uses of pineapple inflorescence? Extracts are used in skincare products for their hydrating and anti-aging properties.
10. How is pineapple inflorescence processed for animal feed? The by-products are processed into nutritious feed for livestock.

