Potato eyes are small buds found on the surface of potato tubers, and they play a critical role in the reproduction and growth of potato plants. These eyes are not just surface features; they are the points from which new shoots emerge, allowing the potato plant to propagate vegetatively. Each eye is a dormant bud that contains the potential to sprout and develop into a new plant under the right conditions.
Potato eyes are arranged in a spiral pattern around the tuber, and their number and arrangement can vary depending on the potato variety. When conditions are favorable, such as appropriate temperature and moisture levels, these eyes will begin to sprout. The sprouts emerge as small, green shoots, which will eventually grow into stems and leaves above the ground. This process is vital for the vegetative propagation of potatoes, as it allows farmers and gardeners to grow new plants from sections of existing tubers, rather than relying on seeds.
Each potato eye contains meristematic tissue, which is a type of tissue composed of undifferentiated cells capable of rapid cell division and growth. This tissue is similar to the growth points found in other parts of plants, such as the tips of roots and shoots. The meristematic cells in the eyes give rise to new stems, leaves, and roots, enabling the potato plant to establish itself and produce new tubers.
The development of potato eyes and their ability to sprout is influenced by several factors. Temperature is one of the most important factors; potatoes typically sprout best at temperatures between 50°F and 70°F (10°C and 21°C). Moisture levels also play a crucial role, as adequate moisture is necessary for the sprouts to grow. Additionally, exposure to light can stimulate sprouting, which is why potatoes stored in dark, cool conditions tend to have fewer sprouts.
While sprouting is essential for potato propagation, it can be undesirable for storage. Sprouted potatoes can become shriveled and lose quality, and the sprouts themselves can develop higher levels of glycoalkaloids, such as solanine, which are toxic in large quantities. To prevent sprouting during storage, potatoes should be kept in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated environment. Commercially, sprout inhibitors are sometimes used to extend the shelf life of stored potatoes.
In addition to their role in propagation, potato eyes are also of interest in various scientific and agricultural research areas. Understanding the mechanisms that control dormancy and sprouting in potato eyes can help improve storage practices, reduce post-harvest losses, and enhance crop yields. Research in this area also has implications for breeding new potato varieties with desirable traits, such as improved resistance to pests and diseases or enhanced nutritional content.
Potato eyes also have cultural and culinary significance. In some cuisines, potatoes with visible eyes are used for specific dishes, as the sprouts can add a unique texture and flavor. However, it is generally recommended to remove the eyes and sprouts before cooking, as they can have a bitter taste and contain higher levels of glycoalkaloids.
In summary, potato eyes are crucial for the vegetative propagation of potato plants, serving as the starting points for new shoots and stems. These small buds contain meristematic tissue capable of rapid growth, allowing potatoes to reproduce efficiently. The development and sprouting of potato eyes are influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and light. While sprouting is necessary for propagation, it can be undesirable for storage, requiring proper storage conditions to minimize sprout growth. Understanding the biology of potato eyes is important for agricultural practices and research, contributing to improved potato cultivation and storage methods.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Potato Eyes

1. Seed Production: Potato eyes, or sprouts, are essential for growing new potato plants. They are used by farmers to propagate potato crops, ensuring a continuous supply of potatoes.
2. Agricultural Sustainability: Using potato eyes for planting promotes sustainability by allowing farmers to regenerate their crops without needing to purchase new seeds every season.
3. Genetic Diversity: Potato eyes can be used to cultivate different potato varieties, maintaining and enhancing genetic diversity within potato crops, which is vital for disease resistance and adaptability.
4. Home Gardening: Potato eyes are commonly used by home gardeners to grow their own potatoes, promoting self-sufficiency and local food production.
5. Research and Development: Potato eyes are used in scientific research to study plant growth, disease resistance, and genetic modifications, contributing to agricultural advancements.
6. Educational Purposes: Potato eyes are often used in educational settings to teach students about plant biology, growth cycles, and sustainable farming practices.
7. Small-Scale Farming: Potato eyes are essential for small-scale farmers who rely on their crops for food and income, providing a cost-effective way to maintain their potato fields.
8. Food Security: By enabling the propagation of potato crops, potato eyes contribute to food security, especially in regions where potatoes are a staple food.
9. Organic Farming: Potato eyes are used in organic farming practices to grow potatoes without synthetic inputs, promoting environmentally friendly agriculture.
10. Rural Development: The cultivation of potatoes using eyes supports rural economies by providing jobs and income for farming communities.
11. Biodiversity Conservation: Potato eyes can be used to grow heirloom and rare potato varieties, helping to preserve agricultural biodiversity.
12. Local Markets: Farmers use potato eyes to grow crops for local markets, ensuring a steady supply of fresh potatoes and supporting local economies.
13. Crop Rotation: Potato eyes are used in crop rotation systems to improve soil health and reduce pest and disease buildup, promoting sustainable farming practices.
14. Low Input Agriculture: Growing potatoes from eyes requires minimal inputs compared to other crops, making it an economical choice for resource-poor farmers.
15. Climate Resilience: Potato eyes can be planted in various climates, helping farmers adapt to changing environmental conditions and maintain crop production.
16. Community Gardening: Potato eyes are used in community gardens to grow potatoes, fostering community engagement and providing fresh produce to local residents.
17. Renewable Resource: Potato eyes represent a renewable resource for potato cultivation, reducing dependency on commercial seed suppliers and promoting agricultural independence.
18. Economic Viability: By using potato eyes, farmers can maintain economically viable operations with lower production costs, ensuring the sustainability of their farming enterprises.
Read Also: Prevention and Methods of Controlling Coccidiosis Among Chickens
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Potato Eyes
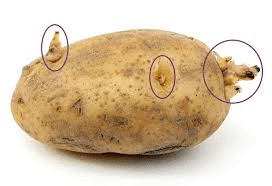
1. Seed Potatoes: Potato eyes are used to produce seed potatoes, which are then planted to grow new potato crops.
2. Potato Plants: The primary product from potato eyes is the potato plant itself, which produces edible tubers.
3. Potato Vine: The vines grown from potato eyes can be used as animal feed or composted to enrich soil.
4. Sprouted Potatoes: Potatoes with eyes can be sold as sprouted potatoes for home gardeners and small-scale farmers.
5. Plant Extracts: Extracts from potato plants grown from eyes can be used in various industrial and research applications.
6. Potato Flowers: Flowers from potato plants can be used in breeding programs to develop new potato varieties.
7. Potato Leaves: Leaves from potato plants can be composted or used in organic mulching systems.
8. Potato Stem: Stems from potato plants can be used in composting or as a green manure crop to improve soil health.
9. Mini Tubers: Small tubers produced from potato eyes can be used in seed production or as gourmet potatoes in niche markets.
10. Micropropagation: Potato eyes can be used in tissue culture and micropropagation techniques to produce disease-free plantlets.
11. Potato-Based Biofertilizers: Residues from potato plants grown from eyes can be processed into biofertilizers.
12. Disease-Resistant Varieties: Potato eyes are used in breeding programs to develop disease-resistant potato varieties.
13. Genetic Research: Potato eyes are used in genetic research to study plant development and disease resistance.
14. Bioengineering: Potato eyes can be used in bioengineering to develop potatoes with enhanced nutritional profiles or other beneficial traits.
15. Crop Improvement: Potato eyes are used in crop improvement programs to enhance yield, quality, and stress tolerance.
16. Agro-ecological Studies: Potato eyes are used in agro-ecological studies to understand interactions between potato plants and their environment.
17. Potato Biomass: Biomass from potato plants grown from eyes can be used in bioenergy production.
Read Also: Time and Methods of Fertilizer Application on Crops
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Potato Eyes

1. What are potato eyes?
Potato eyes are small buds or sprouts found on the surface of potato tubers that can grow into new potato plants.
2. How do you plant potato eyes?
Potato eyes are planted in well-drained soil, usually cut from a larger potato, with each piece containing at least one eye.
3. Can you eat potatoes with eyes?
Yes, you can eat potatoes with eyes, but it is recommended to remove the eyes before cooking as they can contain small amounts of toxins.
4. How long does it take for potato eyes to sprout?
Potato eyes typically sprout within one to two weeks under favorable conditions, such as warmth and moisture.
5. Are potato eyes safe for planting?
Yes, potato eyes are safe and commonly used for planting new potato crops.
6. Can potato eyes be used for all potato varieties?
Yes, potato eyes can be used to propagate all varieties of potatoes, including heirloom and commercial types.
7. How do you store potatoes with eyes for planting?
Store potatoes with eyes in a cool, dark, and dry place until you are ready to plant them.
8. What conditions are best for planting potato eyes?
Potato eyes should be planted in well-drained soil with adequate sunlight and regular watering.
9. Do potato eyes affect the quality of the potato crop?
Using healthy potato eyes ensures good crop quality, while diseased or damaged eyes can affect plant health and yield.
10. Can you grow potatoes indoors from potato eyes?
Yes, you can grow potatoes indoors in containers using potato eyes, provided they receive enough light and proper care.
Read Also: Measurement and Definition of the term water yield

