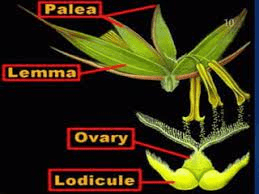
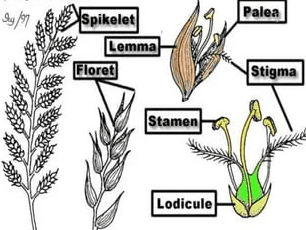
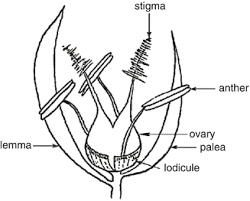
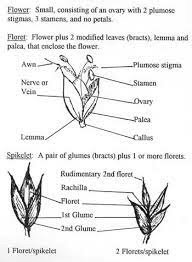
Sorghum Palea, also known as the palea of Sorghum, is a crucial yet often overlooked component in the anatomy of sorghum grains, a staple cereal crop widely cultivated around the world. Sorghum is a genus of grasses that includes several species important for food, fodder, and biofuel production. The palea is one of the two bracts or protective layers surrounding the seed, the other being the lemma. Together, these structures help safeguard the seed and contribute to its development.
The palea is a thin, membranous structure located on the outer part of the sorghum seed. Its primary role is to protect the developing seed and to aid in its eventual dispersal. The palea, along with the lemma, forms a protective casing around the seed, helping to shield it from environmental factors like moisture and pests. This protection is vital for maintaining seed viability and ensuring successful germination and growth.
Structurally, the palea is characterized by its delicate, transparent, or semi-transparent nature. It is often thinner and less robust compared to the lemma. Its translucency allows for a clear view of the seed within, while still providing a degree of physical protection. The palea is composed of layers of cells that can vary in thickness depending on the sorghum variety and growing conditions. In many cases, the palea is covered with tiny, fine hairs or trichomes that may serve additional protective functions, such as deterring herbivores or reducing water loss.
The palea plays a crucial role during the maturation of the sorghum grain. As the grain develops, the palea helps to regulate the internal environment of the seed, ensuring that it remains conducive to proper seed development. This includes maintaining appropriate moisture levels and protecting the seed from excessive temperature fluctuations. The palea also aids in the dispersal of the seed once it has matured. When the seed is released from the plant, the palea can help facilitate its movement by aiding in its detachment from the parent plant.
In terms of agricultural practices, the palea’s structure and function are significant for breeding programs aimed at improving sorghum varieties. Researchers may study the palea to understand how it influences seed protection, germination rates, and overall seed health. Modifications to the palea’s structure through selective breeding or genetic engineering could potentially lead to improved sorghum varieties with better resistance to environmental stresses or pests.
Moreover, the palea is also of interest in the context of sorghum processing and utilization. In some cases, the palea and lemma may be removed during milling to produce a more refined product. However, this process needs to be carefully managed to avoid compromising the nutritional value of the grain. The palea, though often discarded in processing, contains valuable nutrients and fibers that can be utilized in various ways, such as animal feed or as a component in compost.
Sorghum Palea is a small but significant part of the sorghum grain’s anatomy. Its protective role, along with its contribution to seed dispersal and its potential uses in agricultural and industrial applications, underscores its importance in both the natural and cultivated environments. Understanding the function and characteristics of the palea can lead to better sorghum cultivation practices and innovations in grain processing.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Sorghum Palea
1. Grain Protection: The palea is one of the outer structures that protect sorghum grains from environmental damage and pests.
2. Animal Feed: The fibrous material from the palea can be used as high-fiber feed for livestock.
3. Biofuel Production: The palea’s biomass can be processed into bioethanol or biogas, contributing to renewable energy sources.
4. Soil Improvement: Decomposed palea adds organic matter to the soil, enhancing its fertility and structure.
5. Erosion Control: Plant residues from the palea contribute to soil stabilization and help prevent erosion.
6. Organic Mulch: The palea can be used as mulch to retain soil moisture and suppress weed growth.
7. Composting: The palea is excellent for composting, contributing to the creation of nutrient-rich compost.
8. Crafting Materials: Dried palea can be utilized in crafting and traditional art, such as making decorative items.
9. Animal Bedding: The palea can be used as bedding material for livestock, providing comfort and hygiene.
10. Biodegradable Products: Processed palea can be used to create biodegradable packaging materials.
11. Green Manure: Residues from the palea can be used as green manure to enhance soil fertility.
12. Carbon Sequestration: Sorghum cultivation, including the palea, helps capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, contributing to climate change mitigation.
13. Natural Pest Repellents: Extracts from the palea can be used to create natural pest repellents.
14. Nutrient Cycling: The palea plays a role in nutrient cycling, making essential minerals available to plants.
15. Agroforestry Systems: The palea can be integrated into agroforestry systems to support sustainable land management and improve biodiversity.
16. Natural Adhesives: Extracts from the palea can be processed into natural adhesives.
17. Green Building Materials: Processed palea can be used to produce eco-friendly construction materials.
18. Water Filtration: The palea can be used in natural water filtration systems to remove impurities.
Read Also: Goat Milk Production Complete Guide
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Sorghum Palea
1. Animal Feed: The fibrous material from the palea can be used as high-fiber feed for livestock.
2. Bioethanol: The palea can be processed into bioethanol through fermentation.
3. Compost: Decomposed palea contributes to nutrient-rich compost for gardening and farming.
4. Mulch: The palea can be used as mulch to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds.
5. Craft Materials: Dried palea is used to make crafts, such as decorative items and traditional art.
6. Biodegradable Packaging: Processed palea can be used to create biodegradable packaging materials.
7. Natural Pest Repellents: Extracts from the palea are used to create natural pest repellents.
8. Renewable Energy: The palea can be used to produce heat energy through direct combustion.
9. Green Manure: The palea can be plowed back into the soil to improve fertility as green manure.
10. Natural Adhesives: Extracts from the palea can be processed into natural adhesives.
11. Water Filtration Systems: The palea can be used in natural water filtration systems.
12. Green Building Materials: Processed palea can be used to create eco-friendly construction materials.
13. Textile Fibers: Fibers from the palea can be used in textile manufacturing.
14. Nutrient Additives: Processed palea can be added to animal feed as a source of additional nutrients.
15. Bioremediation Agents: The palea can be used in bioremediation products to clean contaminated soils.
16. Soil Conditioner: Decomposed palea improves soil health and structure.
17. Natural Dyes: Extracts from the palea can be used to produce natural dyes for textiles.
18. Organic Fertilizers: The palea can be used in the production of organic fertilizers.
Read Also: Worm Infestation on Ruminant Animals: Symptoms and Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Sorghum Palea
1. What is the primary function of the sorghum palea?
The sorghum palea primarily protects the grain from environmental damage and pests.
2. Can sorghum palea be used as animal feed?
Yes, the fibrous material from the palea can be used as high-fiber feed for livestock.
3. How does sorghum palea contribute to soil health?
When decomposed, the palea adds organic matter to the soil, improving its fertility and structure.
4. Can sorghum palea be used in biofuel production?
Yes, the fibrous material from the palea can be processed into biomass for bioethanol or biogas.
5. Are there any crafting uses for sorghum palea?
Yes, dried palea can be used to make decorative items and traditional crafts.u
6. How does sorghum palea help with erosion control?
The plant residues from the palea help stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
7. Can sorghum palea be used for composting?
Yes, the palea is excellent for composting, contributing to the production of nutrient-rich compost.
8. Are sorghum palea residues beneficial for traditional medicine?
While not commonly used in traditional medicine, extracts from palea might be explored for potential benefits.
9. How does sorghum palea contribute to carbon sequestration?
Sorghum cultivation, including the palea, helps capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, aiding in climate change mitigation.
10. Can sorghum palea residues be used in natural pest control?
Yes, extracts from sorghum palea can be used to create natural pest repellents.