Soybean axillary buds are small, dormant structures located in the leaf axils along the stem of the soybean plant. These buds are found at the junction where the leaf meets the stem and are capable of developing into new branches, leaves, or flowers under certain conditions.
Axillary buds serve as a reserve of meristematic cells, which are undifferentiated plant cells capable of rapid division and growth. They remain inactive or dormant until triggered by environmental cues or hormonal signals to initiate growth and development.
Under favorable conditions, such as adequate sunlight, nutrients, and hormonal balance, axillary buds may be activated to produce new growth. This can result in the formation of lateral branches, which contribute to the overall branching architecture of the soybean plant.
In addition to branching, axillary buds can also give rise to new leaves or flowers, depending on the plant’s growth stage and environmental factors. This ability to produce new growth from axillary buds contributes to the soybean plant’s ability to adapt and respond to changing environmental conditions.
Farmers and researchers often manipulate axillary bud growth through pruning or hormonal treatments to optimize soybean plant architecture and maximize yield potential. Understanding the factors that regulate axillary bud development is essential for crop management strategies aimed at enhancing soybean productivity.
In summary, soybean axillary buds are dormant structures with the potential to develop into new branches, leaves, or flowers under appropriate conditions. Their role in branching architecture and adaptation to environmental changes makes them an important aspect of soybean plant growth and development.
Economic Importance and Uses of Soybean Axillary Buds
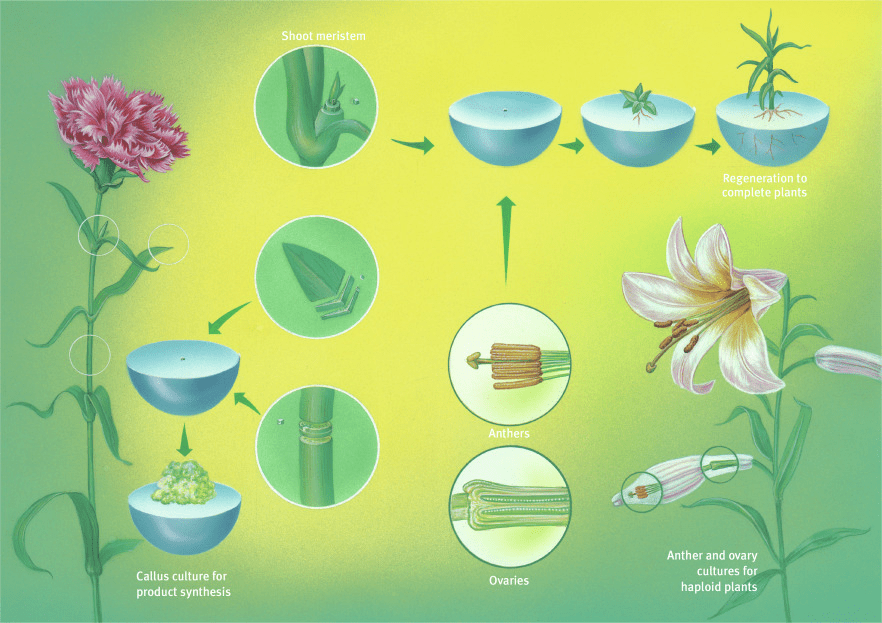
1. Crop Propagation: Soybean axillary buds play a crucial role in the propagation of soybean crops. These buds serve as the primary sites for the formation of new shoots, allowing the plant to branch out and increase its vegetative growth.
2. Yield Enhancement: Axillary buds contribute to increasing the overall yield of soybean plants by promoting branching and the development of additional reproductive structures such as flowers and pods. This leads to higher crop productivity and enhanced profitability for farmers.
3. Genetic Diversity: The genetic diversity of soybean varieties can be enriched through the selection and propagation of plants with desirable traits exhibited in their axillary buds. This genetic variability is essential for breeding programs aimed at developing improved cultivars with enhanced agronomic traits.
4. Forage Production: Soybean axillary buds can be harvested and utilized as forage for livestock feed, providing a nutritious source of protein and energy for ruminant animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats.
5. Green Manure: In sustainable agricultural practices, soybean axillary buds are incorporated into the soil as green manure, enriching soil fertility, improving structure, and enhancing microbial activity. This organic matter contributes to long-term soil health and productivity.
6. Crop Rotation: Soybean axillary buds play a role in crop rotation systems, where soybeans are alternated with other crops to break pest and disease cycles, improve soil structure, and optimize nutrient cycling, leading to more resilient and sustainable farming systems.
7. Phytoremediation: Soybean plants, including their axillary buds, are utilized in phytoremediation projects to mitigate soil and water pollution by absorbing and metabolizing contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and organic pollutants.
8. Medicinal Uses: Extracts derived from soybean axillary buds contain bioactive compounds with potential medicinal properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects, contributing to the development of pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products.
9. Soil Erosion Control: The extensive root system developed from soybean axillary buds helps to stabilize soil, reduce erosion, and prevent nutrient runoff, especially in sloping or vulnerable landscapes prone to soil degradation.
10. Biomass Production: Soybean axillary buds contribute to biomass production, where the entire plant, including stems, leaves, and pods, can be harvested and utilized for bioenergy production, such as biogas, biofuels, and biochar.
11. Silage Production: Soybean axillary buds, along with other plant parts, can be ensiled and preserved as silage for livestock feed, providing a valuable source of nutrition during periods of feed scarcity or low forage availability.
12. Industrial Applications: Compounds derived from soybean axillary buds are utilized in various industrial applications, including the production of bio-based materials, bioplastics, adhesives, and lubricants, contributing to the bioeconomy and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Read Also: 10 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Convolvulus prostratus (Bindweed)
Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Soybean Axillary Buds
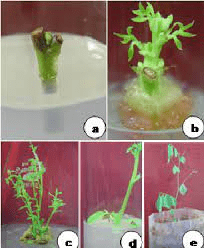
1. Soybean Oil: Extracted from soybean axillary buds, soybean oil is a versatile and widely used vegetable oil in cooking, frying, salad dressings, and food processing industries.
2. Soy Protein Isolate: Through a process of extraction and purification, soy protein isolate is obtained from soybean axillary buds and utilized as a protein-rich ingredient in food products, beverages, and supplements.
3. Soy Lecithin: Soybean axillary buds contain lecithin, a natural emulsifier extracted and utilized in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic applications for its stabilizing and smoothing properties.
4. Soybean Meal: After oil extraction, the remaining soybean meal from axillary buds is used as a high-protein feed ingredient for livestock, poultry, and aquaculture industries.
5. Soy Flour: Ground soybean axillary buds produce soy flour, which is incorporated into bakery products, meat analogs, and gluten-free formulations for its nutritional value and functional properties.
6. Soy Wax: Soybean axillary buds yield soy wax, a renewable and biodegradable alternative to paraffin wax, used in candle making, cosmetics, and surfboard waxes.
7. Soybean Hulls: The outer hulls of soybeans are separated during processing and utilized as dietary fiber supplements, livestock feed, or biomass for energy production.
8. Soybean Grits: Coarsely ground soybean axillary buds produce soybean grits, used in food products such as breakfast cereals, snacks, and meat extenders.
9. Soy-based Ink: Soybean oil derivatives are used in the production of environmentally friendly printing inks, reducing volatile organic compound emissions and promoting sustainability in printing industries.
10. Soy Biodiesel: Soybean oil extracted from axillary buds is converted into biodiesel, a renewable fuel source with lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional diesel.
11. Soybean Extracts: Various bioactive compounds extracted from soybean axillary buds are used in the formulation of dietary supplements, herbal remedies, and functional foods for health and wellness purposes.
12. Soy-based Adhesives: Soybean proteins and derivatives are utilized in the manufacturing of adhesives and coatings for wood products, paperboard, and construction materials.
13. Soy Ink Removers: Environmentally friendly ink removers are produced from soybean oil derivatives, offering safer alternatives for cleaning printing equipment and surfaces.
14. Soy Noodles: Soybean flour is processed into noodles, a staple food in Asian cuisines, offering a nutritious and versatile option for culinary applications.
15. Soy-based Paints: Soybean oil derivatives are used as binders in the production of eco-friendly paints, providing durable coatings with low toxicity and volatile organic compound emissions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Soybean Axillary Buds
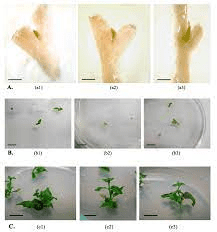
1. What are soybean axillary buds?
Soybean axillary buds are small, dormant buds found in the leaf axils of soybean plants, capable of developing into new shoots, branches, or flowers under suitable growing conditions.
2. How do soybean axillary buds contribute to crop growth?
Soybean axillary buds play a crucial role in branching, vegetative growth, and reproductive development, ultimately influencing crop yield and productivity.
3. Are soybean axillary buds harvested for commercial purposes?
Yes, soybean axillary buds can be harvested and utilized for various commercial applications, including food production, animal feed, industrial processing, and pharmaceuticals.
4. What are the nutritional benefits of soybean axillary buds?
Soybean axillary buds contain essential nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients, contributing to their value as a nutritious food and feed source.
5. How are soybean axillary buds processed into value-added products?
Soybean axillary buds undergo processing methods such as extraction, purification, grinding, and refining to obtain valuable products and by-products used in various industries.
6. Are there any environmental benefits associated with soybean axillary buds?
Yes, soybean axillary buds contribute to soil health, erosion control, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration, supporting sustainable agriculture practices and environmental conservation efforts.
7. Can soybean axillary buds be used in alternative energy production?
Yes, soybean axillary buds can be utilized for bioenergy production through processes such as biomass combustion, biogas digestion, and biofuel extraction, contributing to renewable energy sources.
8. Are there any challenges in the cultivation of soybean axillary buds?
Challenges in soybean cultivation include pest and disease management, environmental stressors, market fluctuations, and agronomic practices to optimize yield, quality, and sustainability.
9. What research and innovations are underway in soybean axillary bud utilization?
Ongoing research focuses on enhancing soybean genetics, agronomy, processing technologies, and value-added product development to meet evolving market demands and sustainability goals.
10. How do soybean axillary buds contribute to food security and economic development?
Soybean axillary buds support food security by providing nutritious food and feed ingredients, income opportunities for farmers, and sustainable livelihoods along the agricultural value chain.
Read Also: Practical Steps to Convert Wood Wastes into Particleboard





