The tomato pericarp, or outer layer of the tomato fruit, plays a crucial role both economically and in culinary applications. This tissue, composed mainly of parenchyma cells, surrounds the seeds and pulp, providing protection and contributing to the fruit’s structural integrity. Its economic importance stems from its widespread cultivation and versatile uses across various industries.
Tomatoes are one of the most cultivated and consumed fruits globally. Beyond their culinary appeal, tomatoes are economically significant due to their high demand in fresh and processed forms. The pericarp’s role in this lies in its ability to protect the fruit during growth and transportation, ensuring the tomato reaches consumers in optimal condition. This protective function reduces spoilage and extends shelf life, crucial for the economic viability of tomato production and distribution.
In terms of uses, the pericarp serves as a key ingredient in numerous culinary dishes worldwide. Its vibrant color, firm texture, and juicy nature make it ideal for fresh consumption in salads, sandwiches, and salsas. Additionally, tomatoes are extensively processed into various products such as sauces, pastes, and juices, where the pericarp’s flavor and thickening properties are highly valued.
These processed forms not only cater to culinary preferences but also enhance convenience and storage capabilities, contributing further to the economic value of tomatoes.
Beyond direct consumption, the pericarp and its by-products find applications in diverse industries. Tomato seeds and skins, extracted during processing, are utilized in the production of oils, extracts, and dietary supplements due to their rich nutrient content, including antioxidants like lycopene. These products are marketed for their health benefits, ranging from cardiovascular support to antioxidant protection.
Moreover, tomato waste products, including peels and pulps, are increasingly utilized in biotechnological applications. These by-products can be processed into biofuels or used as feedstock in biorefineries, contributing to sustainable practices within the agricultural sector. Such innovations not only reduce waste but also create additional economic opportunities by tapping into alternative energy sources and reducing environmental impact.
The tomato pericarp represents more than just a protective layer around the fruit. Its economic importance is underscored by its role in ensuring the viability of tomato production and its versatile applications across various industries.
From culinary delights to nutritional supplements and biotechnological innovations, the pericarp and its by-products continue to play a significant role in global agriculture and commerce. As consumer preferences evolve and technologies advance, the economic significance of the tomato pericarp is likely to expand, driving further innovation and sustainability in its utilization.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Tomato Pericarp
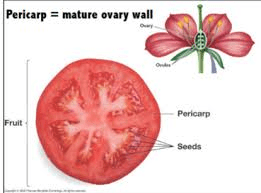
1. Fresh Consumption: The pericarp is the main edible part of the tomato, consumed fresh in salads, sandwiches, and as a snack.
2. Food Processing: Tomato pericarp is processed into products like tomato sauce, paste, and ketchup.
3. Canning Industry: The pericarp is used in the production of canned tomatoes, including diced, whole, and crushed varieties.
4. Culinary Ingredient: It is a staple ingredient in various cuisines, enhancing the flavor and texture of dishes.
5. Nutritional Value: Rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as antioxidants, the pericarp contributes to a healthy diet.
6. Export Revenue: The sale of fresh and processed tomatoes generates significant export revenue for many countries.
7. Employment: Tomato cultivation and processing provide jobs for millions of people worldwide.
8. Culinary Education: Tomatoes are fundamental in culinary training, teaching chefs about flavor profiles and cooking techniques.
9. Agricultural Research: The pericarp is studied to improve tomato varieties for better yield and disease resistance.
10. Organic Farming: Tomatoes are a key crop in organic farming systems, promoting sustainable agriculture.
11. Biodegradable Packaging: Tomato pericarp waste can be used to create biodegradable packaging materials.
12. Food Festivals: Tomato festivals, such as Spain’s La Tomatina, boost local economies and tourism.
13. Nutraceuticals: Extracts from the pericarp are used in supplements for their health benefits.
14. Cosmetic Industry: Tomato pericarp extracts are used in skincare products for their antioxidant properties.
15. Animal Feed: Leftover pericarp material is sometimes used as animal feed.
16. Soil Fertilization: Composting tomato pericarp waste enriches soil health and fertility.
17. Seed Production: The pericarp protects the seeds, which are harvested and sold for planting.
18. Food Science Research: The pericarp is studied for its textural and nutritional properties in food science.
Read Also: Honey Production Guide: The Basics to Get Started
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Tomato Pericarp
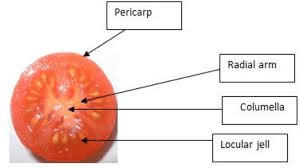
1. Tomato Sauce: The pericarp is cooked and pureed into a sauce used in countless recipes.
2. Tomato Paste: Concentrated tomato pericarp used as a base in many dishes.
3. Ketchup: A condiment made from processed tomato pericarp, vinegar, sugar, and spices.
4. Canned Tomatoes: Pericarp used in producing canned whole, diced, and crushed tomatoes.
5. Tomato Juice: Extracted from the pericarp for a refreshing beverage.
6. Tomato Powder: Dehydrated and ground pericarp used as a seasoning or food ingredient.
7. Sun-dried Tomatoes: Pericarp dried in the sun or dehydrators, used in various culinary applications.
8. Salsa: A condiment made from chopped tomato pericarp, onions, peppers, and spices.
9. Tomato Soup: A popular soup made from pureed tomato pericarp.
10. Tomato Jam: A sweet and savory spread made by cooking the pericarp with sugar and spices.
11. Marinara Sauce: A simple sauce made from the pericarp, garlic, onions, and herbs.
12. Pizza Sauce: Tomato pericarp pureed and seasoned for use on pizzas.
13. Gazpacho: A cold soup made from pureed tomato pericarp and other vegetables.
14. Bloody Mary Mix: A spiced tomato beverage mixer made from the pericarp.
15. Food Coloring: Natural red pigment extracted from the pericarp used as a food colorant.
16. Fermented Products: Tomato pericarp used in the production of fermented foods and beverages.
17. Bioactive Compounds: Extracts from the pericarp used in supplements and pharmaceuticals for their health benefits.
Read Also: Facts About Honey Bees
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Tomato Pericarp
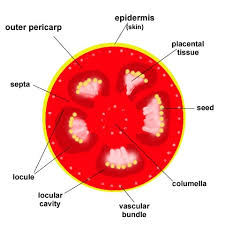
1. What is the tomato pericarp?
The tomato pericarp is the fleshy, edible part of the tomato fruit that surrounds the seeds.
2. What nutrients are found in tomato pericarp?
Tomato pericarp is rich in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as antioxidants like lycopene.
3. How is tomato pericarp used in cooking?
The pericarp is used fresh in salads, cooked in sauces, soups, and many other dishes.
4. Can tomato pericarp be eaten raw?
Yes, the pericarp is commonly eaten raw in salads and sandwiches.
5. What are the health benefits of tomato pericarp?
It provides essential vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber, contributing to overall health.
6. How is tomato pericarp processed into tomato paste?
The pericarp is cooked down and concentrated into a thick paste used in cooking.
7. What products are made from tomato pericarp?
Products include tomato sauce, paste, ketchup, canned tomatoes, and more.
8. Can tomato pericarp be used in cosmetics?
Yes, extracts from the pericarp are used in skincare products for their antioxidant properties.
9. How is sun-dried tomato pericarp made?
The pericarp is sliced and dried in the sun or dehydrators until all moisture is removed.
10. Is tomato pericarp used in animal feed?
Yes, leftover pericarp material can be used as a component of animal feed.
Read Also: Financial Projections for Waste Management Business

