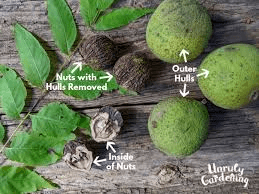
The walnut husk, also known as the hull, is the outermost layer of the walnut fruit that encases the hard shell and the edible kernel. The husk plays a crucial role in protecting the developing nut from physical damage, pests, and environmental factors. As the walnut matures, the husk changes in texture and color, eventually splitting open to release the nut inside. Walnut husks have various applications, both practical and medicinal, owing to their rich composition of bioactive compounds.
Walnut husks are typically green and fleshy when the fruit is young. As the walnut ripens, the husk transitions to a darker color, often turning brown or black. This change indicates that the walnut is mature and ready for harvest. The husk is composed of several layers, with the outer layer being thick and tough, providing a sturdy barrier against external threats.
One of the most significant uses of walnut husks is in traditional medicine. They contain a variety of bioactive compounds, including juglone, tannins, flavonoids, and essential fatty acids. Juglone, in particular, has potent antibacterial and antifungal properties, making walnut husks useful for treating infections and skin conditions. Tannins, known for their astringent properties, help reduce inflammation and promote healing of wounds and sores.
In traditional remedies, walnut husks have been used to treat a range of ailments. For instance, husk extracts are often employed to address digestive issues, such as intestinal parasites. The antimicrobial properties of the husk help cleanse the digestive tract and expel harmful organisms. Additionally, walnut husks have been used to create herbal teas and tinctures believed to boost overall health and immunity.
The cosmetic industry also benefits from the properties of walnut husks. Ground walnut husks are used as natural exfoliants in skincare products. The abrasive texture helps remove dead skin cells, leaving the skin smooth and rejuvenated. The astringent and antimicrobial properties of the husks further enhance skin health by reducing acne and other skin blemishes.
In agriculture, walnut husks are often left in orchards to decompose naturally, enriching the soil with organic matter. This practice improves soil structure, enhances microbial activity, and contributes to the overall health of the orchard ecosystem. The decomposed husks release nutrients that benefit the growth of subsequent crops, making them an essential component of sustainable agricultural practices.
The dyeing industry utilizes walnut husks for their natural pigments. The husks produce a rich, dark brown dye that can be used to color fabrics, yarns, and even hair. This natural dye is valued for its earthy tones and is often preferred over synthetic dyes for eco-friendly and organic products. The dyeing process typically involves boiling the husks to extract the pigments, which are then used to color various materials.
Despite their many uses, handling walnut husks requires care. Fresh green husks contain juglone, a compound that can be toxic to certain plants through a phenomenon known as allelopathy. Juglone inhibits the growth of sensitive plants, which means care must be taken when using fresh walnut husks in gardens or compost. Proper composting can reduce the juglone content, making the resulting compost safe for a wider range of plants.
The environmental impact of walnut husk disposal is another consideration. While they can be beneficial when used correctly, improper disposal can lead to environmental issues. Sustainable practices, such as composting and repurposing husks for various applications, help mitigate these impacts and promote a more eco-friendly approach to walnut cultivation and processing.
Walnut husks are a valuable byproduct of the walnut industry with diverse applications. Their rich composition of bioactive compounds makes them useful in traditional medicine, cosmetics, agriculture, and dyeing. By utilizing walnut husks in various ways, industries can reduce waste and maximize the benefits of this natural resource, contributing to more sustainable and efficient practices.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Walnut Husk

1. Natural Dye: Walnut husks are used to produce natural dyes for textiles and hair, providing a rich brown color.
2. Composting: Walnut husks are composted to enrich soil with organic matter, improving soil health and fertility.
3. Livestock Bedding: Dried walnut husks are used as bedding material for livestock, providing a soft and absorbent surface.
4. Animal Feed: Ground walnut husks are sometimes added to animal feed as a source of fiber and nutrients.
5. Soil Amendment: Walnut husks are used as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and water retention.
6. Mulch: Walnut husks are used as mulch in gardens to suppress weeds and retain soil moisture.
7. Traditional Medicine: Walnut husks are used in traditional remedies for their purported health benefits, such as treating skin conditions and parasites.
8. Biochar Production: Walnut husks can be converted into biochar, a form of charcoal used to improve soil health and sequester carbon.
9. Craft and Decoration: Walnut husks are used in crafts and decorations, adding a natural aesthetic to various items.
10. Insect Repellent: Walnut husks are used as a natural insect repellent, particularly against moths and other pests.
11. Cleaning and Polishing: Ground walnut husks are used as a mild abrasive in cleaning and polishing products.
12. Fuel Source: Walnut husks can be burned as a biomass fuel, providing a renewable energy source.
13. Eco-friendly Packaging: Walnut husks are used to create biodegradable packaging materials.
14. Dye Fixative: Walnut husks are used as a fixative in natural dyeing processes to help set the dye in fabrics.
15. Livestock Health: Walnut husks are used in some animal health products for their purported antiparasitic properties.
16. Research and Development: Walnut husks are studied for their potential uses in various industries, including agriculture, energy, and materials science.
17. Erosion Control: Walnut husks are used in erosion control products to stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
18. Bio-based Materials: Walnut husks are used in the production of bio-based materials, such as composites and resins.
Read Also: Bacterial Leaf Spot: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Walnut Husk
1. Natural Dyes: Walnut husks processed to create natural brown dyes for textiles and hair.
2. Compost: Walnut husks composted to produce nutrient-rich organic matter for soil enrichment.
3. Livestock Bedding: Dried walnut husks used as absorbent bedding material for animals.
4. Animal Feed Additive: Ground walnut husks added to animal feed for fiber and nutrients.
5. Soil Amendments: Walnut husks used to improve soil structure and water retention.
6. Mulch: Walnut husks applied as mulch to gardens for weed suppression and moisture retention.
7. Traditional Remedies: Products based on traditional uses of walnut husks for health benefits.
8. Biochar: Walnut husks converted into biochar for soil improvement and carbon sequestration.
9. Craft Materials: Walnut husks used in craft projects and decorative items.
10. Insect Repellents: Products made from walnut husks to repel insects and pests.
11. Cleaning Products: Ground walnut husks used in cleaning and polishing products.
12. Biomass Fuel: Walnut husks used as a renewable fuel source.
13. Biodegradable Packaging: Walnut husks processed into eco-friendly packaging materials.
14. Dye Fixatives: Walnut husks used to set natural dyes in fabrics.
15. Animal Health Products: Walnut husks included in products for livestock health.
16. Research Applications: Walnut husks studied for new industrial applications.
17. Erosion Control Products: Walnut husks used in products to stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
18. Bio-based Materials: Walnut husks used in the production of bio-based composites and resins.
Read Also: Health Benefits and Side Effects of Opium Poppy (Papaver Somniferum)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Walnut Husk

1. What is a walnut husk? A walnut husk is the outer green covering of the walnut fruit that surrounds the shell.
2. How are walnut husks used in natural dyeing? Walnut husks are processed to produce a natural brown dye for textiles and hair.
3. Can walnut husks be composted? Yes, walnut husks can be composted to produce nutrient-rich organic matter for soil enrichment.
4. Are walnut husks used in animal feed? Ground walnut husks are sometimes added to animal feed as a source of fiber and nutrients.
5. How do walnut husks benefit soil health? Walnut husks are used as soil amendments to improve soil structure and water retention.
6. What are the traditional medicinal uses of walnut husks? Walnut husks are used in traditional remedies for treating skin conditions and parasites.
7. Can walnut husks be used as mulch? Yes, walnut husks are used as mulch in gardens to suppress weeds and retain soil moisture.
8. How are walnut husks used in biochar production? Walnut husks are converted into biochar, which is used to improve soil health and sequester carbon.
9. What is the role of walnut husks in erosion control? Walnut husks are used in products designed to stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
10. Are walnut husks used in eco-friendly packaging? Yes, walnut husks are processed to create biodegradable packaging materials.
Read Also: The Different Types of Manure and How they Work

