Medicinal plants have played a vital role in human health and well-being for centuries. These plants possess natural compounds that can be used to treat various ailments, promote healing, and enhance overall health. With the growing interest in natural remedies and holistic approaches to health, the use of medicinal plants is experiencing a resurgence.
Many cultures worldwide have a rich history of utilizing local flora for medicinal purposes, passed down through generations as traditional knowledge. From ancient civilizations to modern practices, the exploration and application of medicinal plants have laid the foundation for many contemporary medicines.
The significance of medicinal plants extends beyond mere historical interest. Today, scientists and researchers are increasingly recognizing the potential of these plants in developing new pharmaceuticals.
The discovery of active compounds in plants has led to the formulation of essential drugs used in treating a wide range of health issues, from pain relief to cancer treatment. Many modern drugs are derived from plant sources, highlighting the importance of continued research in this field.
Understanding the processing of medicinal plants is crucial to harnessing their therapeutic properties effectively. Proper processing techniques can maximize the benefits of these plants, ensuring that their medicinal qualities are preserved and enhanced.
Methods such as drying, extraction, and formulation play a significant role in transforming raw plant materials into usable medicines. Each step in the processing journey is critical, from selecting the right species to ensuring that the active ingredients remain intact during preparation.
The therapeutic applications of medicinal plants are vast. They can be used in various forms, including teas, tinctures, capsules, and topical ointments. Commonly known medicinal plants such as ginger, turmeric, and aloe vera have gained popularity for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and healing properties.
Traditional medicine systems, such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine, emphasize the use of these plants for preventative care and treatment of diseases.
Moreover, the increasing awareness of the side effects and limitations of synthetic drugs has prompted a shift toward natural alternatives. Patients are now more inclined to explore herbal remedies as part of their health regimen.
This trend has led to the integration of medicinal plants into mainstream healthcare practices. Hospitals and wellness centers are beginning to incorporate herbal medicine into their treatment protocols, often in conjunction with conventional medicine.
However, despite the growing interest in medicinal plants, it is essential to approach their use with caution. Not all plants are safe for consumption, and proper identification is critical to avoid harmful effects.
Additionally, the potency and effectiveness of medicinal plants can vary based on factors such as growing conditions, harvesting methods, and processing techniques. Therefore, individuals interested in using medicinal plants should consult with qualified healthcare practitioners to ensure safe and effective use.
Medicinal plants are an invaluable resource in promoting health and wellness. Their rich history, coupled with modern research and applications, underscores their significance in healthcare.
As we continue to explore the potential of these natural remedies, understanding the processing of medicinal plants becomes increasingly vital to harnessing their full therapeutic potential. With careful consideration and respect for traditional knowledge, medicinal plants can continue to play a crucial role in the future of medicine.
Historical Use of Medicinal Plant

Medicinal plants have been used for thousands of years across various cultures worldwide, forming the backbone of traditional healing practices and medical systems.
Their historical use highlights humanity’s deep connection to nature and the innate desire to harness the therapeutic properties of plants for health and well-being.
The earliest recorded use of medicinal plants can be traced back to ancient civilizations. In Egypt, medical practices involved the extensive use of plants, as documented in texts such as the Ebers Papyrus, dating back to around 1550 BCE.
This ancient manuscript contains over 700 medicinal recipes, many of which utilize common plants like garlic, myrrh, and juniper for their healing properties. The Egyptians not only used these plants for their medicinal qualities but also combined them with spiritual beliefs, illustrating an understanding of the mind-body connection.
In China, traditional healing practices also relied heavily on herbal medicine. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), which has roots over 2,500 years old, emphasizes the use of herbs to restore balance and harmony in the body. The “Shennong Bencao Jing,” a foundational text of TCM, details numerous medicinal plants and their applications. Herbs like ginseng, ginger, and licorice have been used for centuries to treat various ailments, showcasing the ancient Chinese commitment to understanding the healing potential of plants.
The Indian subcontinent boasts its own rich tradition of herbal medicine through Ayurveda, which has been practiced for over 3,000 years. Ayurvedic texts, such as the “Charaka Samhita,” describe the therapeutic properties of a wide range of plants. Turmeric, ashwagandha, and holy basil (tulsi) are among the prominent herbs used in Ayurvedic practice, emphasizing holistic health and the prevention of disease through natural means.
The Greeks and Romans also made significant contributions to the historical use of medicinal plants. The Greek physician Hippocrates, often referred to as the “Father of Medicine,” advocated for the use of herbal remedies and emphasized observation in medical practice around 400 BCE.
His writings laid the groundwork for understanding plant-based treatments. The Roman scholar Dioscorides authored “De Materia Medica,” a five-volume encyclopedia that documented over 600 plants and their medicinal uses. This work remained influential for centuries, guiding herbalists and physicians in Europe and beyond.
During the Middle Ages, the use of medicinal plants continued, particularly in monastic communities where monks preserved and expanded upon ancient knowledge. They cultivated herb gardens and compiled herbal texts that detailed the preparation and application of various plants. Hildegard von Bingen, a notable figure in this era, wrote extensively on the medicinal properties of plants, combining spirituality and healing practices.
The Renaissance sparked renewed interest in herbal medicine, leading to significant advancements in the study of botany and pharmacology. Herbalists began to document plants systematically, creating herbals illustrated books that detailed plant characteristics and their medicinal uses. This period marked the transition of herbal medicine into a more scientific approach, paving the way for modern pharmacology.
Despite the rise of synthetic drugs in the 19th and 20th centuries, the historical use of medicinal plants remains relevant today. There is a growing interest in natural remedies, with many people seeking alternatives to conventional medicine.
Scientific research continues to validate many traditional claims about the efficacy of medicinal plants, leading to the development of new treatments and a greater appreciation for herbal medicine.
The historical use of medicinal plants is a testament to humanity’s enduring relationship with nature. From ancient Egyptian texts to modern scientific studies, the knowledge and practices surrounding medicinal plants have evolved but remain rooted in cultural traditions.
This rich legacy not only informs contemporary health practices but also emphasizes the importance of preserving and respecting traditional knowledge as we continue to explore the therapeutic potential of plants in the modern world.
Key Components of Medicinal Plants
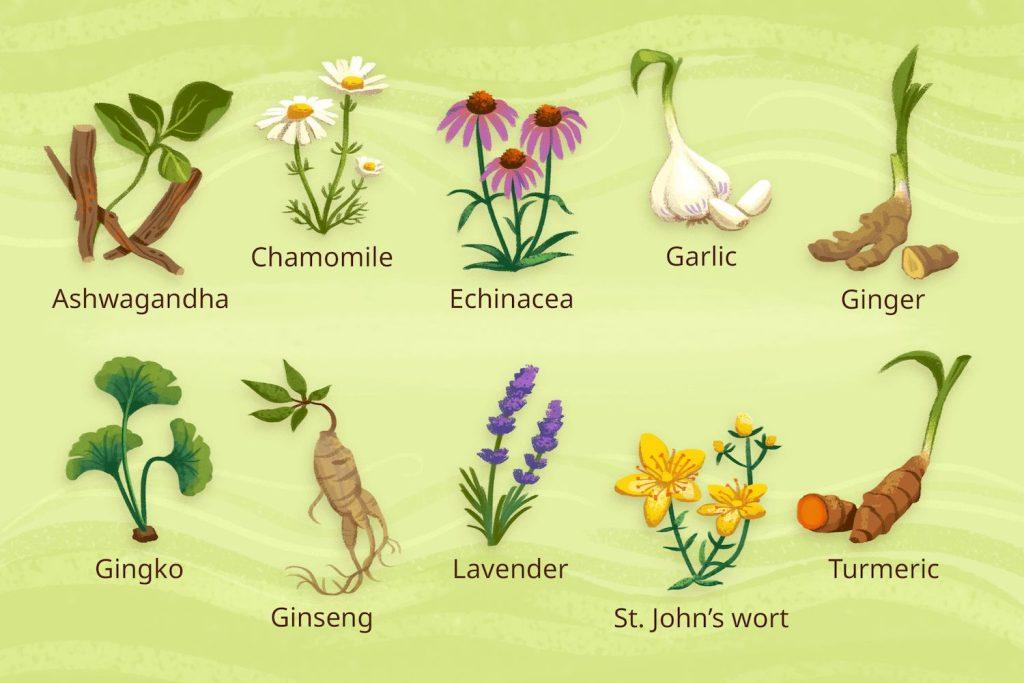
Medicinal plants contain various bioactive compounds that contribute to their therapeutic effects.
1. Active Compounds: Medicinal plants contain various bioactive compounds, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, and phenolics, which contribute to their therapeutic effects. These compounds interact with the body’s biological systems to promote health and alleviate symptoms.
2. Essential Oils: Many medicinal plants produce essential oils, which are concentrated extracts that carry the plant’s fragrance and therapeutic properties. For example, tea tree oil is known for its antiseptic properties, while lavender oil is often used for its calming effects.
3. Nutrients: Medicinal plants are often rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are essential for maintaining overall health. For instance, garlic contains allicin, a compound with various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
4. Tannins: Tannins are polyphenolic compounds found in many medicinal plants that have astringent properties. They can help reduce inflammation and combat infections. For example, witch hazel is used for its astringent properties in treating skin irritations.
5. Saponins: These compounds have immune-boosting properties and may also help lower cholesterol levels. Saponins are found in plants like ginseng and soybeans, which are used in traditional medicine for their health benefits.
6. Glycosides: Glycosides are compounds that can be converted into active forms in the body, contributing to various therapeutic effects. An example is foxglove, which contains digoxin, used in modern medicine to treat heart conditions.
Read Also: How to Increase Egg Production in Commercial Layers
Common Medicinal Plants and Their Uses

1. Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing properties, aloe vera is commonly used to treat burns, cuts, and skin irritations. Its gel is often applied topically for its anti-inflammatory and hydrating effects.
2. Ginger: A popular herbal remedy, ginger is used to alleviate nausea, improve digestion, and reduce inflammation. It can be consumed as tea, in food, or as a supplement.
3. Echinacea: Often used to boost the immune system, echinacea is believed to help prevent and treat colds and respiratory infections. It can be taken as a tea, tincture, or capsule.
4. Peppermint: This herb is known for its digestive benefits, helping to relieve bloating, gas, and indigestion. Peppermint tea or oil is commonly used for these purposes.
5. Turmeric: With its active compound curcumin, turmeric is celebrated for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It is used to support joint health and may help reduce chronic inflammation.
6. Chamomile: This gentle herb is often used for its calming effects and is commonly consumed as tea to promote sleep and relieve anxiety.
Traditional vs. Modern Medicine: A Comparison
1. Approach to Healing: Traditional medicine often takes a holistic approach, focusing on the whole person and addressing the root causes of illness. In contrast, modern medicine typically emphasizes treating specific symptoms or diseases, often using pharmaceuticals.
2. Evidence and Research: Modern medicine is heavily based on scientific research and clinical trials, providing evidence for the efficacy and safety of treatments. Traditional medicine relies on historical use and anecdotal evidence, though some traditional practices have gained scientific support.
3. Treatment Methods: Traditional medicine utilizes herbal remedies, acupuncture, and other natural therapies, while modern medicine often employs advanced technologies, pharmaceuticals, and surgical interventions to treat health issues.
4. Accessibility: Traditional medicine can be more accessible and culturally relevant for many people, particularly in rural areas where conventional healthcare may be limited. Modern medicine is often available through established healthcare systems but may be less accessible in certain regions.
5. Integration: In recent years, there has been a growing interest in integrating traditional and modern medicine, leading to complementary approaches that utilize the strengths of both systems for comprehensive patient care.
Cultivating Medicinal Plants at Home
1. Choosing the Right Plants: Start by selecting medicinal plants that are suitable for your climate and space. Common choices include basil, mint, rosemary, and thyme, which are relatively easy to grow and have various uses.
2. Site Selection: Choose a sunny location for your medicinal garden, as most herbs thrive in full sunlight. Ensure the area has good drainage and access to water for regular irrigation.
3. Soil Preparation: Prepare the soil by removing weeds and rocks, then enrich it with organic matter such as compost. Aim for a well-draining soil mix to prevent waterlogging, which can harm plant roots.
4. Planting Techniques: Depending on the herb, you can either sow seeds directly into the ground or transplant seedlings. Follow the specific planting depth and spacing recommendations for each plant to promote healthy growth.
5. Care and Maintenance: Water your plants regularly, keeping the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Fertilize with organic fertilizers to provide essential nutrients. Regular pruning will encourage bushier growth and prevent overcrowding.
6. Pest Management: Monitor your plants for pests and diseases, using organic methods for control. Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs or use natural repellents to protect your herbs without harmful chemicals.
7. Harvesting and Storage: Harvest your herbs when they are at their peak potency, usually before flowering. Dry them by hanging in a cool, dark place or using a dehydrator. Store dried herbs in airtight containers away from light to preserve their properties.
Harvesting and Preparing Medicinal Plants
1. Timing of Harvest: The timing of harvesting medicinal plants is crucial for maximizing their potency. Generally, the best time to harvest is when the plants are at their peak growth, usually just before or during the flowering stage. This is when the concentration of active compounds is highest.
2. Tools for Harvesting: Use sharp, clean tools such as pruning shears or scissors to minimize damage to the plants. Always sterilize your tools before use to prevent the spread of diseases. Harvesting should be done gently to avoid bruising the plant material.
3. Parts of the Plant: Different parts of the plant may be harvested for different medicinal properties. For example, leaves, flowers, stems, roots, and bark may all be used, depending on the specific plant and its intended use. Always refer to reliable sources to determine which parts are beneficial.
4. Preparation Methods:
i. Drying: After harvesting, medicinal plants can be dried to preserve their properties. This can be done by hanging them in a well-ventilated, dark area. Alternatively, a food dehydrator can be used for faster results. Proper drying is essential to prevent mold and retain the plant’s medicinal properties.
ii. Infusions and Decoctions: Many medicinal plants can be prepared as teas. Infusions are made by steeping leaves or flowers in hot water, while decoctions involve boiling harder parts like roots or bark to extract their beneficial compounds.
iii. Tinctures: Tinctures are concentrated herbal extracts made by soaking plant material in alcohol or vinegar. This method extracts both water-soluble and alcohol-soluble compounds, creating a potent remedy.
iv. Oils and Salves: Medicinal plants can also be infused into carrier oils (like olive or coconut oil) to create herbal oils, which can be used for topical applications. When mixed with beeswax, these oils can form salves for skin conditions.
Safety and Precautions in Using Medicinal Plants
1. Proper Identification: One of the most critical safety precautions is accurately identifying medicinal plants. Misidentification can lead to adverse effects or toxicity. Always consult reliable sources or experienced herbalists before using any plant.
2. Dosage Guidelines: Understanding the correct dosage is vital. While some plants are safe in small amounts, larger doses can be harmful. Start with small quantities and gradually increase if needed, while monitoring your body’s response.
3. Allergies and Interactions: Be aware of potential allergies or sensitivities to certain plants. Additionally, medicinal plants can interact with prescription medications, potentially altering their effectiveness. Always consult with a healthcare professional before combining herbal remedies with medications.
4. Pregnancy and Nursing Considerations: Many medicinal plants are not safe for pregnant or nursing women. It’s essential to research and consult a healthcare provider to avoid potential risks.
5. Side Effects: Just like conventional medications, medicinal plants can have side effects. These can range from mild digestive issues to severe allergic reactions. Pay attention to how your body responds and discontinue use if adverse effects occur.
6. Quality Control: Ensure that the plants you use are sourced from reputable suppliers or grown in safe, chemical-free environments. Contaminants such as pesticides, heavy metals, or other harmful substances can compromise safety.
Scientific Research on Medicinal Plants
1. Evidence-Based Studies: Scientific research on medicinal plants has grown significantly, with studies investigating their efficacy and safety. Many plants previously used in traditional medicine have gained recognition for their therapeutic properties, backed by clinical trials and laboratory studies.
2. Phytochemistry Research: The field of phytochemistry focuses on the chemical compounds found in plants. Research in this area has identified various bioactive compounds responsible for the therapeutic effects of medicinal plants. For example, studies on curcumin from turmeric have revealed its potential in reducing inflammation and fighting cancer.
3. Clinical Trials: Many medicinal plants are now undergoing clinical trials to evaluate their effectiveness for specific health conditions. For instance, ginseng has been studied for its effects on energy levels and cognitive function, while echinacea is researched for its immune-boosting properties.
4. Challenges in Research: Despite the growing body of evidence, challenges remain in standardizing plant materials and dosages for research. The variability of active compounds due to factors like growing conditions, harvest time, and processing methods can complicate studies.
5. Integrative Approaches: An increasing number of healthcare professionals recognize the value of integrating medicinal plants into conventional medical practices. This integrative approach can enhance patient care and broaden treatment options.
The Role of Medicinal Plants in Global Health

1. Traditional Medicine Practices: Medicinal plants are central to traditional medicine systems worldwide, such as Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine, and Indigenous healing practices. These systems emphasize the importance of natural remedies and holistic approaches to health.
2. Accessibility and Affordability: Medicinal plants often serve as accessible and affordable healthcare options, particularly in low-resource settings where conventional medicines may be scarce or costly. This makes them invaluable in addressing public health issues.
3. Health Education and Empowerment: Utilizing medicinal plants fosters health education and community empowerment. Teaching individuals about the benefits and proper use of medicinal plants can enhance their capacity to manage health conditions naturally.
4. Biodiversity Conservation: The cultivation and use of medicinal plants promote biodiversity conservation and sustainable agricultural practices. Protecting these plants is crucial for maintaining the ecosystem and preserving traditional knowledge.
5. Global Health Initiatives: Organizations and initiatives are increasingly recognizing the potential of medicinal plants in addressing global health challenges, such as combating infectious diseases, managing chronic illnesses, and promoting mental health.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!
Read Also: CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS OF EGG GLUT IN EGG PRODUCTION
Summary of Things You Should Know About Medicinal Plants

| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Medicinal plants have been used for centuries to treat ailments, promote healing, and enhance health; modern resurgence due to interest in natural remedies. |
| Historical Use | Traced to ancient Egypt (Ebers Papyrus), China (TCM, Shennong Bencao Jing), India (Ayurveda), Greece/Rome (Hippocrates, Dioscorides), Middle Ages, and Renaissance. |
| Key Components | Active compounds (alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, phenolics), essential oils, nutrients, tannins, saponins, glycosides. |
| Common Medicinal Plants | Aloe Vera (skin healing), Ginger (digestion, nausea), Echinacea (immune boost), Peppermint (digestion), Turmeric (anti-inflammatory), Chamomile (calming). |
| Traditional vs Modern Medicine | Traditional: holistic, natural therapies; Modern: symptom-focused, evidence-based; growing integration. |
| Home Cultivation | Choose suitable plants (basil, mint, etc.), sunny site, good soil, proper planting, care, pest control, and harvesting. |
| Harvesting & Preparation | Harvest at peak potency, use clean tools; methods include drying, infusions, tinctures, oils/salves. |
| Safety & Precautions | Proper identification, correct dosage, awareness of allergies/interactions, caution in pregnancy, quality control. |
| Scientific Research | Evidence-based studies, phytochemistry, clinical trials; challenges in standardization; integrative approaches. |
| Global Health Role | Central to traditional systems, affordable access, health education, biodiversity conservation, global initiatives. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are medicinal plants?
Medicinal plants are natural plants containing bioactive compounds used for treating, preventing, or managing various health conditions in traditional and modern medicine.
2. Why are medicinal plants becoming more popular today?
They are gaining popularity due to concerns about side effects of synthetic drugs, interest in holistic and natural health approaches, and scientific validation of traditional uses.
3. What are some common medicinal plants and their benefits?
Common examples include Aloe Vera for skin healing, Ginger for digestion and nausea relief, Turmeric for anti-inflammatory effects, Echinacea for immune support, Peppermint for digestive issues, and Chamomile for relaxation and sleep.
4. How do I safely use medicinal plants at home?
Start with proper identification, use recommended dosages, consult a healthcare professional (especially if on medications or pregnant), and source from reputable suppliers to avoid contaminants.
5. Can medicinal plants replace conventional medicine?
No, they should not fully replace conventional medicine; many are best used complementarily, and serious conditions require professional medical treatment.
6. What is the importance of proper harvesting and processing?
Proper timing, tools, and methods (like drying or making tinctures) preserve the maximum potency of active compounds and prevent degradation or contamination.
7. Are there any risks or side effects when using medicinal plants?
Yes, risks include allergies, drug interactions, toxicity from misidentification or overdose, and side effects like digestive upset; always use with caution and professional guidance.
8. How can I grow medicinal plants at home?
Select easy-to-grow herbs like mint, basil, or rosemary, choose a sunny spot with good drainage, prepare rich soil, water regularly, and harvest at peak potency for best results.
9. What role do medicinal plants play in global health?
They provide accessible, affordable healthcare in many regions, support traditional systems, promote biodiversity, and contribute to research for new treatments and integrative medicine.
10. Is there scientific evidence supporting the use of medicinal plants?
Yes, extensive research, including phytochemistry and clinical trials, has validated many traditional uses (e.g., curcumin in turmeric for inflammation) while ongoing studies address standardization and efficacy.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you very much for your support and for sharing!
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. The health benefits described are based on scientific research and traditional knowledge. They ayre not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before using any herb or natural remedy for medical purposes.
Read Also: Homeowners Insurance Complete Guide

