Farm bookkeeping systems play a crucial role in managing the financial records of a farm. They help farmers organize and track their financial activities such as income, expenses, purchases, and sales.
Farmers can maintain clear and accurate records that contribute to informed decision-making and better financial management by using a structured bookkeeping system.
Proper bookkeeping is essential for ensuring the long-term success and sustainability of the farm. There are different types of farm bookkeeping systems, each catering to different farm sizes and needs.
Some systems are simple and easy to manage, while others provide more detailed financial insights. Farmers must choose a system that best suits the complexity and scale of their operations. The main goal of any bookkeeping system is to keep financial records organized and up-to-date.
Accurate bookkeeping is essential for tracking profits, managing expenses, and preparing for tax obligations. It helps farmers monitor the financial performance of their business over time and make necessary adjustments to optimize productivity and profitability.
Without an organized bookkeeping system, it would be difficult for farmers to evaluate the financial health of their farm.
A good farm bookkeeping system supports better financial planning, helping farmers prepare for future investments, equipment purchases, or expansion plans. Farmers can make projections and allocate resources more efficiently by reviewing historical records.
Bookkeeping also aids in securing loans or financial support, as lenders typically require detailed financial information.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of farm bookkeeping systems, so farmers can choose the most suitable one for their operations and better manage their farm’s finances effectively.
Read Also: How to Market your Matured Fishes for Profit
Types of Farm Bookkeeping Systems

Farm bookkeeping systems are essential for managing the financial operations of a farm, ensuring that all income, expenses, and investments are accurately tracked.
There are various types of bookkeeping systems available, each suited for different sizes and complexities of farm operations.
Understanding these systems helps farmers make better financial decisions, plan for growth, and maintain the financial health of their farm. Below is the list of types of farm bookkeeping systems;
1. Single-Entry Bookkeeping
Single-entry bookkeeping is the simplest and most basic form of bookkeeping. It involves recording each financial transaction only once, either as income or expense.
This system is often used by small-scale or family farms where the operations are simple and straightforward. For example, a farmer may record the sale of produce or livestock as income and the purchase of feed or equipment as an expense.
The major advantage of single-entry bookkeeping is its simplicity and ease of use, which makes it accessible for farmers with minimal accounting knowledge.
However, it has limitations in providing a complete financial picture since it lacks the ability to track assets, liabilities, or equity.
For small farms where detailed financial reports are not necessary, single-entry bookkeeping can suffice. However, as the farm grows and the financial transactions become more complex, a more detailed system may be required.
2. Double-Entry Bookkeeping
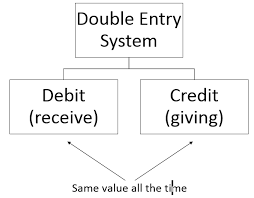
Double-entry bookkeeping is a more sophisticated system that records each transaction twice once as a debit and once as a credit.
This system helps maintain balance in the books, with every transaction affecting two accounts. For example, if a farmer buys new equipment for the farm, the purchase is recorded as an asset (debit) and as a decrease in cash (credit).
This method is widely used in larger farming operations because it provides a more comprehensive view of the farm’s financial situation.
Double-entry bookkeeping helps track all aspects of the farm’s finances, such as income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity.
It also reduces the chances of errors, as the books must always balance. For farmers who need detailed financial reports, such as balance sheets and profit and loss statements, double-entry bookkeeping is essential for accurate financial analysis.
Read Also: Introduction and Feasibility Study on Fish Farming
3. Manual Bookkeeping
Manual bookkeeping refers to the traditional method of recording financial transactions by hand in physical books or ledgers.
While this method is becoming less common, some small-scale or traditional farmers still rely on it, especially when they have limited access to technology or prefer a hands-on approach.
Manual bookkeeping involves keeping detailed logs of income, expenses, and other financial data in various books, such as a cash book, sales book, and expense book.
Although manual bookkeeping allows farmers to have direct control over their records, it can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
It also lacks the ability to generate detailed reports quickly. Manual systems are best for small farms with fewer transactions.
As the farm expands or becomes more complex, transitioning to a computerized system may become necessary for greater efficiency and accuracy.
4. Computerized Bookkeeping
Computerized bookkeeping systems use software to automate the process of recording and managing farm financial transactions.
These systems are widely used in modern farming operations because they simplify bookkeeping tasks and provide real-time data analysis.
Farmers can input income, expenses, and other transactions into the software, which will automatically categorize and organize them.
Computerized systems, such as QuickBooks, FarmLogs, and AgLeader, can generate detailed reports, track inventory, and even provide financial forecasting.
These tools are particularly useful for large-scale farms with complex operations, as they offer increased accuracy, speed, and the ability to handle large amounts of data.
With computerized bookkeeping, farmers can easily analyze their financial performance, prepare for tax filing, and make better-informed business decisions.
5. Cash-Based Bookkeeping
Cash-based bookkeeping records transactions when cash is actually received or paid out. For example, income is recorded when the payment is received from a customer, and expenses are recorded when the payment is made for goods or services.
This system is typically used by smaller farms that do not engage in credit transactions or where cash flow is straightforward.
The main advantage of cash-based bookkeeping is its simplicity, as it only tracks actual cash flow. It is easy to maintain and works well for farmers who deal primarily with cash transactions.
For more complex farming operations, this system may not provide enough detail for making long-term financial decisions.
6. Accrual-Based Bookkeeping
Accrual-based bookkeeping records transactions when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash changes hands.
For example, income is recorded when the sale is made, even if the payment will be received at a later date. Similarly, expenses are recorded when they are incurred, even if the payment is made later.
Accrual-based bookkeeping provides a more accurate picture of a farm’s financial position, especially for those with credit transactions or where income and expenses are not immediately settled in cash.
This method is particularly beneficial for larger farms that sell on credit or have complex financial dealings.
It allows for a clearer understanding of profitability over time, as it includes all earned revenue and incurred expenses, even if they have not yet been paid. This system requires more detailed record-keeping and can be more complex to manage.
In conclusion each type of farm bookkeeping system offers different benefits depending on the size, complexity, and needs of the farm.
Smaller farms may find single-entry or cash-based systems sufficient for managing their finances, while larger, more complex farms may need double-entry or accrual-based systems to provide a comprehensive view of their financial situation.
Manual and computerized bookkeeping systems also cater to different levels of technological preference and complexity, with computerized systems offering greater efficiency and accuracy.
Choosing the right bookkeeping system is crucial for farmers to maintain accurate records, make informed financial decisions, and secure the long-term growth and sustainability of their farm.
A well-structured record-keeping system not only ensures day-to-day operations run smoothly but also lays the foundation for future success. As farming evolves and challenges arise, a reliable system empowers farmers to adapt, plan strategically, and keep their businesses thriving for generations to come.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!
Read Also: Household Hazardous Waste (HHW)

