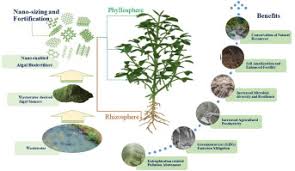
Biofertilizer is a natural organic fertilizer that provides essential nutrients to plants and enhances soil quality through the activity of beneficial microorganisms. These microorganisms create a natural environment that supports plant growth and soil health.
Application and Benefits of Biofertilizers in Farming Practices
The fertilizers are composed entirely of natural organic materials sourced from the nutrient-rich lands of Costa Rica. They can be easily applied with water at any stage of plant growth or used as a base to create potent, concentrated natural organic liquid fertilizers.
These fertilizers are suitable for various growing mediums and have shown excellent production results in organic farming, industrial agriculture, and home gardening.
Read Also: Popular Breeds of Ruminant Animals
Advancements in Biofertilizer Technology for Sustainable Agriculture

Biofertilizers represent advanced biotechnology essential for supporting the development of organic, sustainable, green, and non-polluting agriculture.
These bio-organic fertilizers can increase crop yields, improve quality, and contribute positively to the agricultural environment. They are now widely used across various plant types and countries, delivering excellent results.
Addressing the Impact of Chemical Fertilizers on Soil Health
Continuous use and overuse of petrochemical-based fertilizers and toxic pesticides have adversely affected soils, water supplies, food quality, animals, and human health. A more sustainable approach involves utilizing both scientific and natural resources to achieve better production results.
For centuries, peat moss has been recognized for its ability to enrich soil with beneficial bacteria, fungi, earthworms, and other bio-organisms, leading to safe, nutritious, and abundant crops.
All-natural organic fertilizers made from pure peat moss have been developed to harness these benefits.
Composition and Functionality of Biofertilizers in Crop Production
Biofertilizers contain a wide range of naturally chelated plant nutrients and trace elements, carbohydrates, amino acids, and other growth-promoting substances. Kelp, a component of these fertilizers, acts as a soil conditioner by stimulating microbial activity.
This leads to improved air-water relationships in the soil, enhanced fertility, and reduced susceptibility to compaction and erosion.
Organic growers incorporating kelp into their fertility programs report increased yields, improved quality, extended shelf-life, and greater resistance to environmental stresses such as drought, extreme heat, early frost, pests, and diseases.
Foliar Application of Biofertilizers: Enhancing Nutrient Absorption
This blend serves as an excellent foliar fertilizer. Being nutritionally complete, including calcium, its nutrients are readily absorbed by plant leaves. The nitrogen present in fish is in the form of amino acids, which plants can directly utilize, unlike inorganic fertilizers that require conversion into usable forms.
Additionally, the micronutrients in fish and kelp are naturally chelated, allowing for quick and efficient absorption through leaf surfaces. Regular foliar applications can enhance plant health, vigor, and yield due to this easily absorbed nutrition.
Read Also: The Ratio of a Male to Female Ruminants
Comparing Organic and Chemical Fertilizers in Agricultural Practices
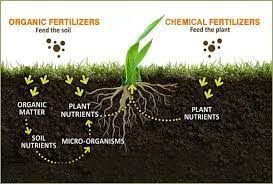
Organic fertilizers differ from chemical fertilizers by feeding plants while simultaneously adding organic material to the soil. Soils rich in organic matter remain loose and airy, retain more moisture and nutrients, support soil organism growth, and promote healthier plant root development.
In contrast, exclusive use of chemical fertilizers leads to the gradual depletion of organic matter and microbiotic activity, resulting in compacted, lifeless soil with diminished capacity to hold water and nutrients.
This necessitates increased chemical fertilizer usage to sustain plant growth. Organic fertilizers, derived from renewable resources, offer a sustainable alternative.
Utilizing Biofertilizers for Nutrient-Poor Soils
The biofertilizer is a premium natural fertilizer composed solely of certified organic ingredients, specifically designed for nutrient-poor Western soils. This organic fertilizer excels in nourishing beneficial soil microorganisms, significantly increasing humus content and enhancing the soil’s capacity to support healthy, vibrant plants.
It can be applied by the handful when planting individual plants, broadcast and mixed deeply into the soil for flower beds, or spread around established plants and incorporated into the soil. It is also highly effective in vegetable gardens, container plantings, and as a compost-pile activator.
The Role of Peat Moss in Water and Nutrient Retention
Peat moss thrives in low-oxygen environments, and its decomposition process can take thousands of years. This characteristic imparts unique properties to its cells, making them larger and capable of retaining water and nutrients for later plant use.
Economic Advantages of Biofertilizers in Agriculture
Biofertilizer offers the best economic value as a proven, top-quality product. Consistent use of biofertilizer ensures immediate top-quality results and long-term profitability.
Research trials conducted by an independent research center in a professional greenhouse compared various soils amended with peat, coir, compost, and blends. The conclusion:
“Sphagnum peat can be considered the best overall performer as a soil amendment and substrate: it is homogeneous, easy to handle, and has shown the best growth results; all of this at a highly competitive price.”
Defining Biofertilizers in Agricultural Context
The term “biofertilizer” refers to fertilizers that enhance land fertility using biological wastes, hence the name. These biological wastes are free from harmful chemicals, making them beneficial for enriching the soil with microorganisms that produce organic nutrients and combat diseases.
Consequently, farm produce grown with biofertilizers is free from hazardous and poisonous materials, making them globally accepted as organic products. Therefore, the use of biofertilizers is essential in organic farming.
Types of Biofertilizers and Their Agricultural Significance
1. Phospho: Releases insoluble phosphorus in the soil and fixes it in clay minerals, significantly benefiting agriculture.
2. Rhizo: Rhizobacterial plays a crucial role in agriculture by inducing nitrogen-fixing nodules on the roots of legumes such as peas, beans, clover, and alfalfa.
3. Azotobacter: Atmospheric nitrogen, constituting 78% of the atmosphere, is vital for plant growth. Azotobacter fixes atmospheric nitrogen in the soil, making it available to plants and protecting roots from soil pathogens.
4. Trichoderma: A non-pathogenic and eco-friendly product that acts as an antagonistic hyperparasite against various field pathogens, serving as an economically viable biocontrol agent.
5. Composter (Decomposing Culture): Breaks down organic matter such as dead plants, farmyard waste, and cattle waste, thereby increasing soil productivity.
6. Tricho-Card: Trichogramma effectively destroys the eggs of many leaf and flower eaters, stems, fruit, and shoot borers. It is applicable to various crops and ornamental plants, including sugarcane, cotton, brinjal, tomato, corn, jowar, vegetables, citrus, paddy, and apple.
7. Vermi Compost: A 100% pure, eco-friendly organic fertilizer containing nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, organic carbon, sulfur, hormones, vitamins, enzymes, and antibiotics, which improve the quality and quantity of yield.
Continuous misuse of chemical fertilizers leads to soil fertility loss and salinity. Natural farming, with vermicompost as a key component, offers a solution to these problems.
8. Biocompost: An eco-friendly organic fertilizer prepared from sugar industry waste, decomposed and enriched with various plant- and human-friendly bacteria and fungi. Biocompost contains nitrogen, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, and useful fungi like decomposing fungi and Trichoderma viride, which protect plants from soil-borne diseases and enhance soil fertility, resulting in high-quality produce for farmers.
Innovative Techniques in Biofertilizer Application
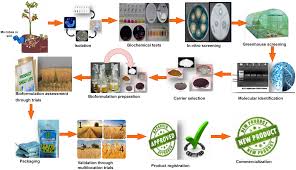
Traditionally, biofertilizers are carrier-based and available in powder form, with lignite being the most common carrier due to its high organic matter content and water-holding capacity, enhancing microorganism growth. Before use, a slurry is made and applied to seeds a universal method unless seed application poses difficulties.
Recently, the University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore, developed a method involving dry complex fertilizer for direct soil application. This method uses granules (1-2 mm) made from tank bed clay (TBC), baked at 200°C in a muffle furnace to sterilize the material and create porosity.
The baked granules are soaked overnight in a suspension of nitrogen-fixing bacteria grown in a suitable medium and then air-dried at room temperature under aseptic conditions.
These granules contain over a billion bacteria per gram and are suitable for field application alongside seeds and fertilizers in furrows. However, the quantity of biofertilizer applied will be slightly higher than that used in seed applications.
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or contributions? If so, please feel free to use the comment box below to share your thoughts. We also encourage you to kindly share this information with others who might benefit from it. Since we can’t reach everyone at once, we truly appreciate your help in spreading the word. Thank you so much for your support and for sharing!