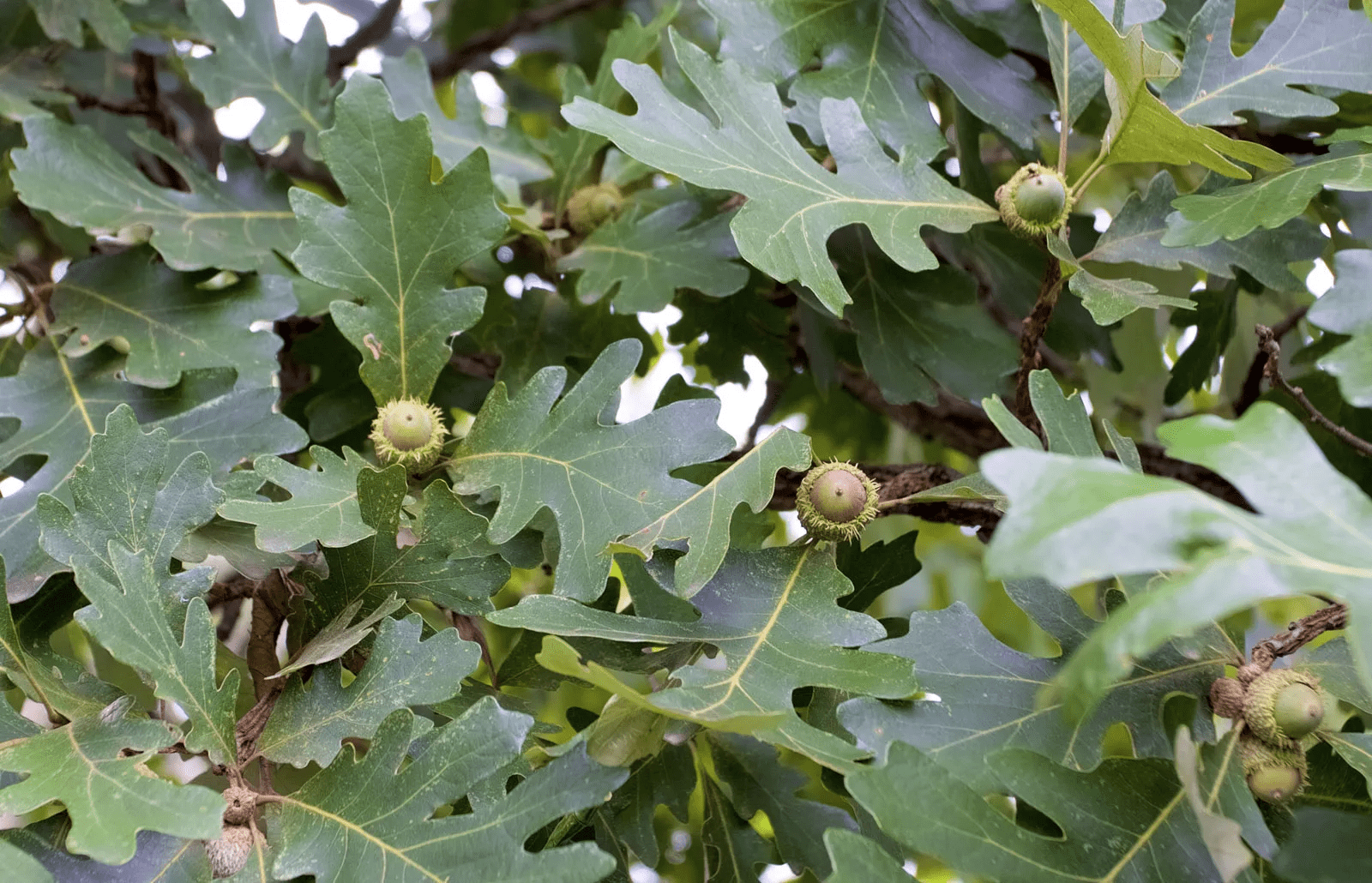
Quercus macrocarpa, commonly known as the Bur Oak, is a deciduous tree belonging to the family Fagaceae. This species is native to North America, with a range extending from the eastern United States to the central part of the continent, and northward into Canada. The Bur Oak is renowned for its large size, distinctive foliage, and acorns.
The Bur Oak is a robust tree, typically reaching heights of 70 to 100 feet (21 to 30 meters) and exhibiting a broad, spreading crown. The bark is deeply furrowed and develops a rugged, corky texture as the tree matures. The leaves of Quercus macrocarpa are alternately arranged, lobed, and can measure 6 to 12 inches (15 to 30 centimeters) in length. The lobes are often rounded, giving the leaves a distinctively coarse appearance. In the autumn, the foliage transforms into shades of yellow or brown, creating a visually striking display.
The Bur Oak is monoecious, meaning individual trees bear both male and female reproductive structures. The inconspicuous, greenish-yellow male flowers, known as catkins, appear in the spring before the emergence of leaves. Female flowers are borne in the leaf axils, developing into acorns that are large and distinctive, measuring about 1 to 2 inches (2.5 to 5 centimeters) in length. These acorns are encased in a scaly cupule, which can be quite fringed and covers approximately one-third to one-half of the acorn.
Quercus macrocarpa is adaptable to various soil types but is commonly found in well-drained upland sites. It is often observed in mixed deciduous forests, savannas, and along stream banks. The Bur Oak demonstrates a remarkable tolerance for drought conditions once established, making it a hardy species in diverse ecological settings. This tree is well-suited to climates with cold winters and warm summers.
The Bur Oak serves as a valuable habitat and food source for a variety of wildlife. Its acorns provide sustenance for numerous mammals, birds, and invertebrates. Additionally, the tree’s expansive canopy offers shade, contributing to the creation of a diverse and stable ecosystem.
Quercus macrocarpa holds cultural significance in Native American traditions, and historically, its wood has been utilized for various purposes, including construction and fuel. Due to its stately appearance and adaptability, the Bur Oak is commonly planted in urban and suburban landscapes as an ornamental shade tree
The Botanical Description of Quercus Macrocarpa
1. Family and Genus: Quercus Macrocarpa, commonly known as the bur oak, belongs to the Fagaceae family and the Quercus genus. This genus is known for its diverse species of oaks, and the bur oak is one of its notable members.
2. Size and Growth Habit: The bur oak is a large deciduous tree that can reach impressive heights of up to 100 feet (30 meters). It typically has a broad, rounded crown, with branches extending widely. Its growth habit is described as robust and stately.
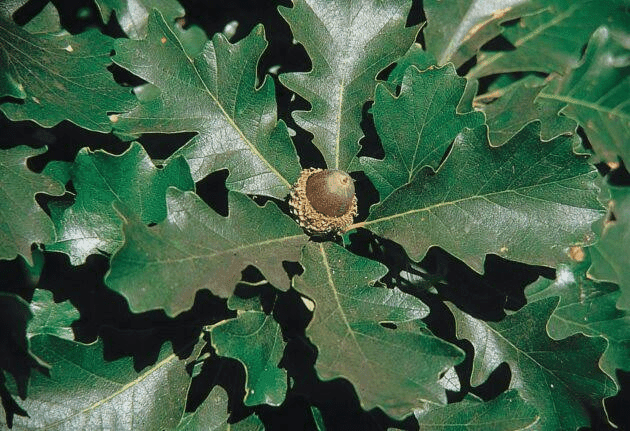
3. Leaves: The leaves of Quercus Macrocarpa are distinct and play a significant role in its identification. They are typically 6 to 12 inches long, with a unique shape characterized by deeply lobed margins. The lobes are rounded and give the leaves a distinct appearance. The upper surface of the leaves is dark green, while the underside is paler and may have fine hairs.
4. Bark: The bark of the bur oak is deeply furrowed and rough, often with ridges that create a distinctive pattern. The color of the bark varies from grayish-brown to dark brown, adding to its visual appeal.
5. Acorns: One of the remarkable features of Quercus Macrocarpa is its acorns. These are among the largest of all oak species, typically 1 to 1.5 inches long. They are covered by a fringed cap, known as a bur, which gives the tree its common name. These acorns are an essential food source for wildlife.
6. Flowers and Fruits: The bur oak produces inconspicuous flowers in the spring. The female flowers develop into the iconic acorns that are instrumental in the tree’s reproduction.
7. Habitat and Range: Quercus Macrocarpa is native to North America and is found in a wide range of habitats. It thrives in diverse conditions, including upland forests, bottomland forests, savannas, and even urban areas. Its adaptability makes it a significant tree species.
8. Lifespan: Bur oaks have a long lifespan and can live for several centuries. Some old bur oaks are known to be over 400 years old, showcasing their resilience and endurance.
9. Fall Foliage: In the fall, the leaves of Quercus Macrocarpa turn various shades of yellow, adding a burst of color to the landscape. This makes it a popular ornamental tree for landscaping and urban beautification.
10. Wildlife Habitat: The bur oak is an ecologically valuable tree, providing food and shelter to a variety of wildlife. Its acorns are a vital food source for deer, squirrels, and many species of birds. Additionally, the tree’s dense branches and foliage offer nesting sites for birds.
11. Growth Rate: The growth rate of Quercus Macrocarpa is relatively slow, especially in its early years. However, as the tree matures, it becomes a majestic and imposing presence in the landscape.
The botanical description of Quercus Macrocarpa, or the bur oak, provides valuable insights into the distinctive characteristics that make this tree a significant and cherished species. Its large acorns, distinctive leaves, and long lifespan contribute to its ecological importance and its popularity in landscaping and urban settings.
The Geographic Distribution of Quercus Macrocarpa
1. Native Range: Quercus Macrocarpa, commonly known as the bur oak, is native to North America. Its natural range spans a vast portion of the continent, covering much of the central and eastern United States and extending into parts of Canada. This tree is well adapted to the diverse climates and ecosystems found within its native range.
2. Habitat Diversity: One of the notable features of the bur oak’s geographic distribution is its ability to thrive in a wide range of habitats. It can be found in upland forests, bottomland forests, savannas, and even urban areas. This adaptability contributes to its widespread distribution.
3. North American Range: In North America, Quercus Macrocarpa is distributed from the northeastern United States, including states like New York, down to the southern United States, reaching Texas and Oklahoma. It extends westward to the Dakotas and Nebraska and northward into parts of Canada, including Manitoba and Ontario.
4. Eastern United States: In the eastern United States, the bur oak’s range includes states like Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, and Kentucky. It is a common tree species in these regions, contributing to local ecosystems.
5. Western United States: Moving westward, the bur oak’s distribution extends into states like Kansas, Nebraska, and South Dakota. It is particularly prevalent in the Great Plains region.
6. Canadian Presence: Quercus Macrocarpa’s distribution reaches into Canada, where it can be found in the southern parts of Manitoba and Ontario. Its presence in these Canadian provinces highlights its adaptability to northern climates.
7. Urban Landscapes: Beyond its natural habitat, the bur oak is often planted in urban areas as an ornamental tree. This intentional introduction expands its presence and contributes to its cultural significance.
8. Wildlife Corridors: The bur oak’s acorns serve as a vital food source for wildlife, including deer, squirrels, and various bird species. Its presence in forests and along wildlife corridors is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems.
9. Environmental Adaptability: Quercus Macrocarpa’s ability to tolerate different soil types and environmental conditions makes it a resilient species. It can thrive in dry, sandy soils as well as in more moist, loamy soils, further extending its geographic reach.
10. Conservation Efforts: Given its ecological importance and widespread distribution, conservation efforts are often focused on preserving the health of bur oak populations and their habitats.
The Chemical Composition of Quercus Macrocarpa
1. Tannins: Quercus Macrocarpa is known for its high tannin content. Tannins are natural compounds found in various parts of the tree, including the bark and leaves. These tannins have astringent properties and can be used in traditional medicine and in tanning processes.
2. Quercetin: Quercetin is a flavonoid found in the leaves and acorns of Quercus Macrocarpa. This compound has antioxidant properties and is being studied for its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory effects.
3. Gallic Acid: Gallic acid is another phenolic compound present in the bur oak. It has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and is being researched for its potential in various health applications.
4. Ellagic Acid: Ellagic acid is found in the acorns of Quercus Macrocarpa. It is an antioxidant and is of interest in the study of potential health benefits, particularly its role in protecting cells from oxidative damage.
5. Nutrients in Acorns: The acorns of the bur oak are a source of essential nutrients for wildlife. They provide carbohydrates, fats, and proteins for animals that rely on them as a primary food source.
6. Wood Composition: Quercus Macrocarpa wood is valued for its strength and durability. It has a dense grain and is used in various applications, including for furniture and flooring.
7. Phytochemical Diversity: The chemical composition of the bur oak showcases its rich phytochemical diversity. These compounds contribute to its ecological interactions, potential medicinal uses, and commercial value.
8. Potential Medicinal Applications: Some of the compounds found in Quercus Macrocarpa, such as quercetin and gallic acid, are being studied for their potential in traditional and modern medicine. Research is ongoing to understand their health benefits.
The geographic distribution and chemical composition of Quercus Macrocarpa, or the bur oak, provides valuable insights into the ecological significance and potential uses of this tree species. Its adaptability across a broad range of habitats and the presence of bioactive compounds make it a valuable resource in both natural ecosystems and human applications.
Read Also: 23 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Melilotus officinalis (Yellow Sweet Clover)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Quercus Macrocarpa (Bur Oak)

1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Quercus Macrocarpa has been traditionally used for its anti-inflammatory properties. Extracts from various parts of the tree have been employed in herbal remedies to alleviate inflammation and related conditions.
2. Antioxidant Effects: Compounds like quercetin and gallic acid found in Quercus Macrocarpa have antioxidant properties. These antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, potentially reducing oxidative stress.
3. Traditional Healing: Indigenous cultures have utilized the bark and leaves of the bur oak in traditional healing practices. These uses range from treating skin conditions to addressing gastrointestinal discomfort.
4. Potential for Wound Healing: The astringent properties of tannins present in the bur oak have led to their use in wound care. Tannin-rich extracts have been applied topically to promote wound healing and reduce bleeding.
5. Oral Health Benefits: The bark and leaves of Quercus Macrocarpa have been used in natural oral hygiene products due to their astringent properties. They can help tighten gum tissues and reduce the risk of gum diseases.
6. Support for Gastrointestinal Health: Traditional medicine has employed bur oak remedies to address digestive issues. The astringency of tannins is believed to help alleviate diarrhea and soothe upset stomachs.
7. Potential in Herbal Teas: Preparations of Quercus Macrocarpa, such as herbal teas made from its leaves or bark, are consumed for their potential health benefits. These teas may be used to manage various health concerns.
8. Exploration in Modern Medicine: While traditional uses are well-documented, modern scientific research is exploring the potential of Quercus Macrocarpa in modern medicine, particularly in the management of inflammatory conditions.
9. Preservation of Traditional Knowledge: Understanding and documenting the traditional medicinal uses of Quercus Macrocarpa is essential for preserving cultural heritage and indigenous knowledge.
10. Ecosystem Health: The presence of Quercus Macrocarpa in natural ecosystems contributes to overall ecosystem health by providing food and shelter for wildlife.
11. Contribution to Herbal Remedies: Quercus Macrocarpa and its traditional uses contribute to the diversity of herbal remedies available for various health concerns.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Quercus Macrocarpa (Bur Oak)
1. Herbal Tea: One of the common methods of using Quercus Macrocarpa for its health benefits is by preparing herbal tea. This can be done by steeping the leaves or bark in hot water. The tea is then consumed to potentially benefit from its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
2. Topical Applications: For wound healing and oral health, tinctures and ointments made from the bark or leaves of the bur oak can be applied topically. These products are used to address specific skin conditions, promote wound healing, and support oral hygiene.
3. Traditional Remedies: Indigenous cultures have specific methods of preparation and usage for Quercus Macrocarpa. These methods are passed down through generations and vary based on the specific health concern.
4. Tannin-Rich Preparations: Tannins extracted from Quercus Macrocarpa are used in various forms, including mouthwashes and astringent solutions for skin care.
5. Herbal Supplements: Bur oak extracts and supplements are available in various forms, including capsules and tinctures. These products are used for their potential health benefits and are often taken orally.
6. Responsible Harvesting: Those who use Quercus Macrocarpa for medicinal purposes may engage in responsible harvesting practices, ensuring that the tree is not harmed in the process.
7. Oral Rinses: Oral rinses made from bur oak preparations are used for their astringent effects on gum tissues and potential oral health benefits.
8. Commercial Products: Some commercial products incorporate Quercus Macrocarpa extracts or compounds into their formulations for various health and wellness purposes.
The Side Effects Of Using Quercus Macrocarpa Medicinal Plant
1. Skin Sensitivity: In some individuals, topical applications of Quercus Macrocarpa may lead to skin sensitivity or allergic reactions. It is advisable to perform a patch test before applying products containing bur oak extracts to a larger area of skin.
2. Gastrointestinal Discomfort: The traditional use of Quercus Macrocarpa to address digestive issues is based on its astringency. However, in some cases, excessive consumption may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including constipation.
3. Potential Allergies: Individuals with known allergies to oak trees or related species should exercise caution when using products derived from Quercus Macrocarpa.
4. Drug Interactions: There is limited information on potential drug interactions, so it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using bur oak products if you are taking medications.
5. Pregnancy and Nursing: Pregnant and nursing individuals should use bur oak products with caution, as their safety in these situations is not well-documented.
6. Individual Variability: Responses to Quercus Macrocarpa can vary among individuals. Some may experience side effects, while others may not. It is essential to be aware of your body’s response when using such products.
7. Sustainable Harvesting: Responsible harvesting practices should be followed to ensure the continued health of bur oak populations and their ecosystems.
8. Respect for Traditional Knowledge: When using Quercus Macrocarpa for its health benefits, it is important to respect the traditional knowledge and practices associated with the plant, particularly when it comes from indigenous traditions.
The potential health benefits, methods of usage, and potential side effects of Quercus Macrocarpa (Bur Oak) is essential for making informed decisions about its use. While this tree offers a range of traditional and potential health advantages, it should be used with care and attention to individual circumstances.
Read Also: 26 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Cayaponia tayuya (Tayuya)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Quercus Macrocarpa (Bur Oak)

1. Antioxidant Properties: Scientific research has delved into the antioxidant potential of Quercus Macrocarpa. Studies have explored the presence of compounds like quercetin and gallic acid and their role in reducing oxidative stress in the body.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Investigations into the anti-inflammatory properties of Quercus Macrocarpa have been conducted. These studies aim to understand how extracts from various parts of the tree may help mitigate inflammation, potentially offering new avenues for managing inflammatory conditions.
3. Wound Healing: Research has examined the wound-healing properties of bur oak preparations. This includes both traditional applications and modern scientific investigations into the astringent qualities of tannins found in the tree.
4. Oral Health Benefits: Scientific studies have explored the use of Quercus Macrocarpa in oral health. This research seeks to understand the impact of the tree’s astringency on gum health and its potential in preventing gum diseases.
5. Potential for Gastrointestinal Health: Studies have investigated the traditional use of Quercus Macrocarpa to address gastrointestinal discomfort. These investigations aim to determine the effectiveness of bur oak remedies in managing digestive issues.
6. Phytochemical Analysis: Scientists have conducted phytochemical analyses of Quercus Macrocarpa to identify and quantify the compounds present in different parts of the tree. This research sheds light on the chemical composition of the bur oak.
7. Modern Medicinal Applications: Ongoing studies explore the potential of incorporating Quercus Macrocarpa into modern medicinal practices, particularly in the context of managing chronic health conditions.
8. Conservation and Ethnobotany: Research extends to the conservation of Quercus Macrocarpa populations and the documentation of traditional knowledge related to the tree’s uses. Ethnobotanical studies contribute to the preservation of cultural heritage.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Quercus Macrocarpa (Bur Oak) Medicinal Plant
1. Patch Testing: Before applying products containing Quercus Macrocarpa extracts to a larger area of skin, it is advisable to perform a patch test to check for skin sensitivity or allergic reactions.
2. Controlled Usage: Products derived from the bur oak should be used in controlled amounts to prevent potential gastrointestinal discomfort or adverse effects.
3. Allergies: Individuals with known allergies to oak trees or related species should exercise caution when using products derived from Quercus Macrocarpa.
4. Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: If you are taking medications or are pregnant or nursing, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before using bur oak products to ensure safety and avoid potential interactions.
5. Individual Variation: Recognize that individuals may respond differently to Quercus Macrocarpa. Pay attention to your body’s response and discontinue use if adverse effects occur.
6. Sustainable Harvesting: Responsible harvesting practices should be followed to ensure the continued health of bur oak populations and their ecosystems.
7. Respect for Traditional Knowledge: When using Quercus Macrocarpa for its health benefits, it is important to respect the traditional knowledge and practices associated with the plant, particularly when it comes from indigenous traditions.
FAQs About Quercus Macrocarpa (Bur Oak) Medicinal Plant
Q1: Can I use bur oak remedies to address skin conditions?
A1: Bur oak preparations have been traditionally used for certain skin conditions. However, it is essential to be cautious and perform a patch test to check for skin sensitivity or allergies before broader application.
Q2: Are there any potential interactions with medications when using bur oak products?
A2: Limited information is available on potential drug interactions. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional if you are taking medications to ensure safety.
Q3: Is Quercus Macrocarpa safe for pregnant or nursing individuals?
A3: Safety in pregnancy and nursing is not well-documented. It is recommended to exercise caution and consult with a healthcare professional before using bur oak products.
Q4: How can I contribute to the conservation of Quercus Macrocarpa?
A4: You can contribute to the conservation of bur oak by supporting responsible harvesting practices and respecting the traditional knowledge associated with the tree.
Q5: What is the potential for Quercus Macrocarpa in modern medicine?
A5: Ongoing research explores the potential of incorporating Quercus Macrocarpa into modern medicinal practices, particularly in managing chronic health conditions. However, more research is needed to establish its efficacy.
Q6: Can I use bur oak products to address digestive issues?
A6: Traditional uses of Quercus Macrocarpa suggest potential benefits for digestive issues. However, controlled usage is recommended to prevent gastrointestinal discomfort.
These frequently asked questions provide valuable information on the safe usage, potential interactions, and conservation efforts related to Quercus Macrocarpa (Bur Oak) and its medicinal applications. It is important to exercise caution, respect traditional knowledge, and stay informed when using this tree for its health benefits.