Rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum) is a perennial plant celebrated for its vibrant red stalks and distinctively tart taste. Known for its culinary versatility, rhubarb has a rich history of use in both sweet and savory dishes.
Rhubarb is native to Asia, specifically the region around the Volga River in Russia, where it has been cultivated for over 2,000 years. It made its way to Europe in the late 18th century and quickly became a sought-after ingredient.
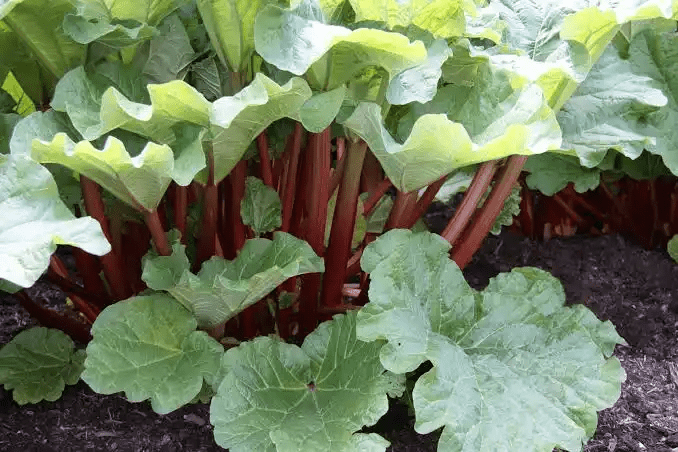
One of the most striking features of rhubarb is its robust growth, with large, triangular, and somewhat heart-shaped leaves that can span up to two feet in width.
The stalks, which are the edible part of the plant, are known for their intense crimson hue, although some varieties produce green or pink stalks. Rhubarb’s appearance is reminiscent of celery, yet its flavor is unmistakably unique.
The taste of rhubarb is characterized by its sharp, tangy, and slightly astringent profile. This distinct flavor is a result of the oxalic acid present in the plant.
When cooked and sweetened, rhubarb transforms into a delightful balance of sweet and sour, making it a beloved component of various culinary creations.
Rhubarb is typically harvested in the spring and early summer, with the stalks being the primary focus. The leaves are not edible due to their high oxalic acid content, which can be toxic if consumed in large quantities.
To prepare rhubarb, one must remove the leaves and any tough, fibrous parts from the stalks. The remaining stalks can then be sliced into pieces for use in a wide range of dishes.
Rhubarb’s acidity makes it an excellent complement to rich meats, such as pork and duck. It can be used in savory sauces, where its tartness cuts through the richness of the meat, creating a harmonious flavor balance.
Chefs have also experimented with rhubarb in salads, where its crisp texture and bright taste add a refreshing elem
Rhubarb has been used for its medicinal properties throughout history. Traditional Chinese medicine and herbal remedies have incorporate rhubarb’s potential for its supposed digestive and laxative benefits.
However, it’s important to note that consuming large quantities of rhubarb can have adverse effects on health due to its oxalic acid content.
The Botanical Description of Rhubarb
1. Rhubarb Plant Structure: Rhubarb, scientifically known as Rheum rhabarbarum, is a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the Polygonaceae family.
It is characterized by large, heart-shaped leaves with long, thick petioles. The plant’s robust structure allows it to withstand various weather conditions, making it a popular choice among gardeners.
2. Leaves and Stems: The leaves of the rhubarb plant are typically dark green and can grow up to 1-2 feet in diameter. They have prominent veins and a slightly rough texture.
The stems, which are the edible part of the plant, vary in color from shades of green to vibrant red. Rhubarb stems are crisp and succulent, making them ideal for culinary use.
3. Flowers and Reproduction: Rhubarb plants produce small, greenish-yellow flowers that are arranged in dense clusters on tall, erect stems.
The plant is dioecious, meaning it has separate male and female flowers on different plants. Rhubarb primarily reproduces via division of established crowns or by planting its seeds, although the latter method is less common.
The Geographic Distribution of Rhubarb
1. Native Habitat: Rhubarb is native to several regions in Asia, including Siberia and Western China. It thrives in areas with cool climates and well-drained soil.
The plant has adapted to grow in mountainous regions, riverbanks, and other damp locations, where it benefits from adequate sunlight and moderate rainfall.
2. Cultivation Worldwide: Over the centuries, rhubarb has been introduced and cultivated in various parts of the world. It is now grown in Europe, North America, and other temperate regions.
Different varieties of rhubarb have been developed to suit specific climates, leading to the widespread availability of this versatile plant.
3. Ideal Growing Conditions: Rhubarb plants require a cold period, known as winter chill, to break dormancy and stimulate growth. They prefer soil that is rich in organic matter and well-draining.
While they can tolerate partial shade, rhubarb plants thrive in full sunlight. Regions with distinct seasons, such as spring and summer, are conducive to the successful cultivation of rhubarb.
The Chemical Composition of Rhubarb
1. Nutritional Components: Rhubarb is not only known for its unique taste but also for its rich nutritional content. It is a good source of dietary fiber, vitamin K, vitamin C, calcium, and potassium.
The high fiber content in rhubarb contributes to digestive health, while vitamin K plays a crucial role in blood clotting and bone health.
2. Active Compounds: Rhubarb contains several active compounds, including anthraquinones, stilbenes, and flavonoids. Anthraquinones, such as emodin and chrysophanol, are responsible for the plant’s laxative properties.
These compounds have been studied for their potential medicinal applications, including in traditional herbal remedies.
3. Culinary and Medicinal Uses: Rhubarb is widely used in culinary preparations, especially in desserts and jams. Its tart flavor adds a unique taste to various recipes.
Rhubarb has been utilized in traditional medicine for its potential health benefits. Some cultures use rhubarb as a natural remedy for digestive issues, while others explore its antioxidant properties.
Read Also: How To Prevent Rats From Invading Your Poultry House
The Medicinal Health Benefits of Rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum)
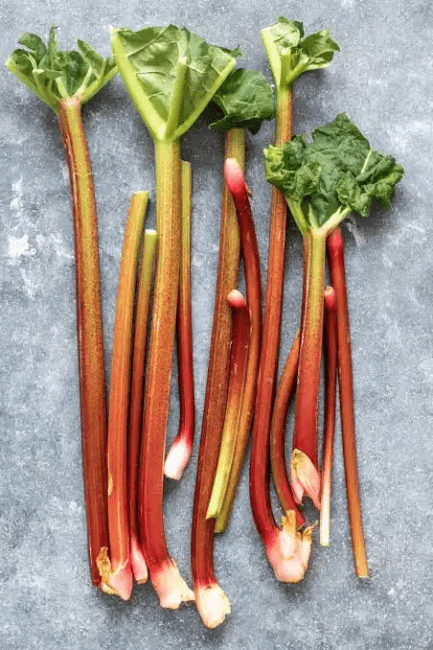
1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Rhubarb exhibits anti-inflammatory effects due to its compounds, making it valuable for conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases. It helps reduce inflammation and alleviate related discomfort.
2. Digestive Health: Rhubarb promotes digestive health by regulating bowel movements. Its high fiber content acts as a natural laxative, aiding in relieving constipation and maintaining regularity in the digestive system.
3. Antioxidant Effects: Rich in antioxidants like quercetin and anthocyanins, rhubarb helps combat oxidative stress in the body. These antioxidants protect cells from damage, contributing to overall health and well-being.
4. Cardiovascular Support: Studies suggest that rhubarb may contribute to cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure. It contains compounds that help relax blood vessels, potentially reducing hypertension and promoting a healthy heart.
5. Weight Management: Rhubarb is low in calories and high in fiber, making it beneficial for weight management. Its fiber content enhances satiety, helping control appetite and support weight loss efforts.
6. Liver Detoxification: Rhubarb has detoxifying properties that support liver function. It aids in flushing out toxins from the liver, promoting a healthy and properly functioning organ.
7. Blood Sugar Regulation: Rhubarb may help regulate blood sugar levels due to its fiber content and active compounds. It can be beneficial for individuals managing diabetes or insulin resistance.
8. Bone Health: Rhubarb contains essential minerals like calcium and vitamin K, which are vital for bone health. Regular consumption can contribute to maintaining strong and healthy bones.
9. Immune System Boost: The antioxidants in rhubarb strengthen the immune system, providing better resistance against infections and diseases. A robust immune system is essential for overall health.
10. Skin Health: Rhubarb’s antioxidants contribute to skin health by preventing oxidative damage. It helps maintain youthful skin, reducing the signs of aging and promoting a clear complexion.
11. Respiratory Health: Rhubarb has been used traditionally to alleviate respiratory issues. It may help in reducing symptoms of respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis.
12. Cognitive Function: Certain compounds in rhubarb have neuroprotective effects, potentially enhancing cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
13. Anti-Cancer Properties: Some studies suggest that rhubarb contains compounds with anti-cancer properties. While research is ongoing, these properties show promise in cancer prevention and treatment.
14. Pain Relief: Rhubarb’s anti-inflammatory properties make it useful for pain relief. It can help alleviate pain associated with arthritis, muscle soreness, and other inflammatory conditions.
15. Stress Reduction: Rhubarb’s nutritional components, particularly vitamin C, contribute to stress reduction. A balanced intake supports the body’s ability to manage stress and boosts overall mental well-being.
16. Digestive Disorders: Rhubarb is used to alleviate various digestive disorders, including indigestion, bloating, and gastritis. It can soothe the digestive tract and promote a healthier gastrointestinal system.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits of Rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum)
1. Culinary Uses: Rhubarb can be used in a variety of culinary creations, such as pies, sauces, and desserts. Cooking rhubarb retains its health benefits while making it delicious and easy to incorporate into meals.
2. Herbal Teas: Dried rhubarb can be used to make herbal teas. Steeping rhubarb in hot water creates a flavorful and health-enhancing beverage that can be consumed daily.
3. Tinctures and Extracts: Rhubarb tinctures and extracts are available and provide a concentrated form of its medicinal properties. These can be added to drinks or taken directly in small quantities as a supplement.
4. Capsules and Supplements: Rhubarb supplements, available in capsule form, offer a convenient way to incorporate its benefits into your daily routine. Always follow recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider before use.
5. Fresh Juices: Fresh rhubarb juice is a nutritious option. Blending rhubarb with other fruits and vegetables creates a refreshing and health-boosting beverage.
The Side Effects of Using Rhubarb Medicinal Plant
1. Digestive Discomfort: Excessive consumption of rhubarb can cause digestive issues, including stomach cramps, diarrhea, and nausea. It is important to consume rhubarb in moderation to avoid these discomforts.
2. Kidney Stones: Rhubarb contains oxalates, which can contribute to kidney stone formation, especially in individuals prone to such conditions. People with kidney stone history should limit their rhubarb intake.
3. Interactions with Medications: Rhubarb may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and heart medications. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider if you are on medication and considering rhubarb supplementation.
4. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to rhubarb, leading to skin rashes, itching, or swelling. If allergic symptoms occur, discontinue use and seek medical advice.
5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should exercise caution when using rhubarb medicinally. Its safety during these periods is not well-documented, and professional medical advice is advisable before use.
Read Also: 20 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Bambusa vulgaris (Bamboo)
The Scientific Research and Studies of Rhubarb (Rheum rhabarbarum)

1. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Scientific research has extensively explored the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of rhubarb. Studies have shown that compounds in rhubarb, such as quercetin and anthocyanins, possess significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which can be beneficial for various health conditions.
2. Gastrointestinal Benefits: Numerous studies have investigated the gastrointestinal benefits of rhubarb. Its high fiber content and laxative properties have been scientifically proven to promote digestive health, including the alleviation of constipation and the maintenance of regular bowel movements.
3. Cardiovascular Health: Research suggests that rhubarb may have a positive impact on cardiovascular health. Some studies indicate that compounds in rhubarb can help relax blood vessels, potentially lowering blood pressure and supporting a healthy heart.
4. Weight Management: Scientific investigations have demonstrated that rhubarb, with its low-calorie and high-fiber nature, can contribute to weight management. Its fiber content enhances satiety, helping control appetite and support weight loss efforts.
5. Liver Detoxification: Research has explored rhubarb’s role in liver detoxification. Studies indicate that it may aid in flushing out toxins from the liver, promoting its healthy functioning.
6. Blood Sugar Regulation: Studies have shown that rhubarb may help regulate blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for individuals managing diabetes or insulin resistance.
7. Bone Health: Scientific research supports the role of rhubarb in maintaining bone health. Its content of essential minerals like calcium and vitamin K is crucial for strong and healthy bones.
8. Immune System Boost: Scientific studies have demonstrated that the antioxidants in rhubarb strengthen the immune system, enhancing resistance against infections and diseases.
9. Skin Health: Research has indicated that rhubarb’s antioxidants play a role in preserving skin health by preventing oxidative damage and promoting a youthful complexion.
10. Respiratory Health: Some scientific investigations suggest that rhubarb may help alleviate respiratory issues, such as symptoms associated with asthma and bronchitis.
11. Cognitive Function: Research on specific compounds in rhubarb has shown neuroprotective effects, potentially improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
12. Anti-Cancer Properties: Ongoing studies indicate that rhubarb contains compounds with potential anti-cancer properties, showing promise in cancer prevention and treatment.
13. Pain Relief: Scientific research has supported rhubarb’s anti-inflammatory properties as beneficial for pain relief, particularly for conditions like arthritis and muscle soreness.
14. Stress Reduction: Scientifically, rhubarb’s nutritional components, particularly vitamin C, contribute to stress reduction, promoting overall mental well-being.
15. Digestive Disorders: Research indicates that rhubarb is used effectively to alleviate various digestive disorders, including indigestion, bloating, and gastritis, by soothing the digestive tract.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations in Using Rhubarb Medicinal Plant
1. Moderation is Key: One of the essential safety precautions when using rhubarb is to consume it in moderation. Excessive consumption can lead to digestive discomfort, including stomach cramps and diarrhea.
2. Oxalate Awareness: Rhubarb contains oxalates, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones, especially in individuals prone to such conditions. People with a history of kidney stones should limit their rhubarb intake.
3. Medication Interactions: It’s important to be aware of potential interactions between rhubarb and certain medications, especially blood thinners and heart medications. Always inform your healthcare provider if you are on medication and considering rhubarb supplementation.
4. Allergy Consideration: Some people may be allergic to rhubarb, leading to skin rashes, itching, or swelling. If allergic symptoms occur, discontinue use and seek medical advice.
5. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should exercise caution when using rhubarb as a medicinal plant. Its safety during these periods is not well-documented, and professional medical advice is advisable before use.
FAQs About Rhubarb Medicinal Plant
1. Is rhubarb safe for everyone to consume? Rhubarb is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderate amounts. However, individuals with a history of kidney stones, certain medical conditions, or those taking specific medications should consult a healthcare provider before using rhubarb.
2. How can I include rhubarb in my diet for its health benefits? You can include rhubarb in your diet by using it in various culinary creations, such as pies, sauces, and desserts. Cooking rhubarb retains its health benefits while making it delicious and easy to incorporate into meals.
3. Can rhubarb help with weight loss? Rhubarb’s high fiber content can promote a feeling of fullness, which may help with weight management. It can be a valuable addition to a balanced diet focused on weight loss or maintenance.
4. Are there any potential side effects of rhubarb consumption? While rhubarb is generally safe, excessive consumption can lead to digestive discomfort, and its oxalate content may contribute to kidney stone formation in some individuals. Always use rhubarb in moderation.
5. Is rhubarb safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women? Pregnant and breastfeeding women should be cautious when using rhubarb as a medicinal plant, as its safety during these periods is not well-documented. Consult with a healthcare provider before use.
Read Also: Banana Tree Care: What You Need to Know
