The Botanical Description of Pergularia Daemia (Bala)
Understanding the botanical features of Pergularia daemia is essential to appreciate its unique characteristics and medicinal value. Here are nine key aspects of its botanical description:
1. Family: Pergularia daemia belongs to the Apocynaceae family, commonly known as the dogbane family.
2. Habit: It is a perennial herbaceous plant, meaning it lives for more than two years and lacks a woody stem.
3. Leaves: The leaves of Pergularia daemia are simple, opposite, and lanceolate, with a smooth texture and a dark green color.
4. Flowers: The plant produces small, attractive, star-shaped flowers that are typically pale purple or pink in color. These flowers have a pleasant fragrance.
5. Fruits: Bala bears slender, elongated fruits that contain numerous seeds. The fruits are dry and split open when ripe to disperse the seeds.
6. Roots: The roots of Pergularia daemia are fibrous and have a slightly bitter taste.
7. Height: It usually grows to a height of 30-60 cm (12-24 inches), making it a relatively small plant.
8. Habitat: Bala is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions, growing in sandy soils and wastelands.
9. Flowering Season: The plant typically flowers during the summer and autumn seasons, showcasing its vibrant blooms.
The Geographic Distribution of Pergularia Daemia
Understanding the geographic distribution of Pergularia daemia is crucial for conservation efforts and for those interested in its cultivation and utilization. This plant has a specific range that spans several regions. Here’s a list and explanation of its geographic distribution:
1. Native Range: Pergularia daemia is native to the Indian subcontinent, particularly India, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It thrives in various climatic conditions of this region.
2. Wider Distribution: Beyond its native range, Pergularia daemia can also be found in parts of Southeast Asia and East Africa, where it has naturalized.
3. Habitat: This plant typically grows in open, sunny areas, and is often found in wastelands, along roadsides, and in cultivated fields.
4. Altitude: Pergularia daemia is adapted to a wide range of altitudes, from sea level up to around 1,500 meters (4,921 feet) above sea level.
5. Climate Preferences: It prefers tropical and subtropical climates with warm temperatures and adequate rainfall.
6. Soil Requirements: This plant is adaptable to various soil types, including sandy, loamy, and clayey soils, as long as there is good drainage.
7. Invasive Potential: In some regions outside its native habitat, Pergularia daemia has become invasive, competing with native vegetation.
Understanding where Pergularia daemia naturally occurs and its adaptability to different environments is essential for its sustainable management and utilization.
The Chemical Composition of Pergularia Daemia
Pergularia daemia possesses a diverse chemical composition, which contributes to its medicinal properties. Here’s an explanation of the key components found in Pergularia daemia:
1. Alkaloids: Pergularia daemia contains alkaloids such as pergularinine, pergularidine, and pergularinine-N-oxide, which have various pharmacological effects.
2. Sterols: Sterols, including β-sitosterol and stigmasterol, are present in Pergularia daemia and have anti-inflammatory properties.
3. Flavonoids: Flavonoids, like quercetin and kaempferol, are known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
4. Tannins: Tannins contribute to the plant’s astringent properties and potential health benefits.
5. Glycosides: Certain glycosides are found in Pergularia daemia and may have therapeutic effects.
6. Resin: Resin content in the plant contributes to its traditional medicinal uses.
7. Phenolic Compounds: These compounds have antioxidant properties and are believed to play a role in the plant’s health benefits.
8. Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are essential for the plant’s growth and energy storage.
The Harvesting and Processing of Pergularia Daemia
Proper harvesting and processing of Pergularia daemia are essential to preserve its medicinal qualities and ensure its safety for consumption. Here, we’ll list and explain eight key steps in the harvesting and processing of Pergularia daemia:
1. Selection of Mature Plants: Harvesters should select mature Pergularia daemia plants with well-developed leaves and stems. Typically, harvesting is done when the plant is in its active growth phase.
2. Timing: Harvesting is often done during the flowering and fruiting seasons when the plant’s bioactive compounds are at their peak.
3. Manual Harvesting: Harvesters use traditional hand tools to carefully cut the plant at the stem, ensuring minimal damage.
4. Washing and Cleaning: After harvesting, the plant material is thoroughly washed and cleaned to remove dirt and contaminants.
5. Drying: The cleaned plant material is spread out in a well-ventilated area to dry naturally. Proper drying is essential to prevent mold and decay.
6. Storage: Once completely dry, the plant material is stored in a cool, dry place in airtight containers to maintain its quality.
7. Quality Control: Throughout the harvesting and processing stages, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the final product meets safety and efficacy standards.
8. Traditional Preparation: Depending on its intended use, Pergularia daemia can be further processed into various forms, such as powders, extracts, or teas, following traditional methods.
Read Also: The Health Benefits of Using Jeera Spice on your Cooking
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Pergularia Daemia (Bala)

Pergularia daemia, commonly known as Bala, is a medicinal plant celebrated for its various health benefits. Let’s explore 19 of these remarkable health benefits and their explanations:
1. Immune System Booster: Bala enhances the immune system, helping the body fight infections more effectively.
2. Respiratory Health: It aids in respiratory conditions like asthma and bronchitis by acting as a bronchodilator.
3. Anti-Inflammatory: Bala contains compounds that reduce inflammation and alleviate conditions like arthritis.
4. Pain Relief: It acts as a natural analgesic, relieving pain, including headaches and joint discomfort.
5. Digestive Aid: Bala supports digestion and alleviates issues like indigestion and bloating.
6. Diuretic Properties: It promotes toxin elimination by increasing urine production.
7. Cardiovascular Health: Bala helps regulate blood pressure and cholesterol levels, benefiting heart health.
8. Anti-diabetic Effects: Some studies suggest it may help manage blood sugar levels, particularly in diabetes.
9. Skin Health: Bala is used to treat skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis due to its anti-inflammatory and healing properties.
10. Wound Healing: It accelerates wound healing and soothes skin irritations when applied topically.
11. Anti-Anxiety: Bala has calming properties and can help reduce anxiety.
12. Antidepressant: It may alleviate symptoms of depression and improve mood.
13. Stress Reduction: Bala’s adaptogenic properties help the body cope with stress.
14. Anti-Aging: It contains antioxidants that combat free radicals and promote youthful skin.
15. Digestive Disorders: Bala eases symptoms of digestive disorders like gastritis and irritable bowel syndrome.
16. Anti-fungal: It has antifungal properties, making it useful for fungal infections.
17. Menstrual Relief: Bala may alleviate menstrual discomfort and regulate menstrual cycles.
18. Antispasmodic: It relaxes muscle spasms, providing relief from cramps.
19. Anti-cancer Properties: Some compounds in Bala have shown potential in cancer research.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Pergularia Daemia (Bala)
To harness the health benefits of Bala, various methods of usage are employed. Here are common methods and their explanations:
1. Herbal Teas: Preparing a tea from Bala leaves is a traditional and effective method for consumption.
2. Decoctions: Boiling Bala plant parts to make a concentrated liquid for oral consumption.
3. Tinctures: Liquid extracts made from Bala are used for precise dosing.
4. Capsules and Tablets: Bala is available in supplement form for easy daily intake.
5. Topical Creams: Creams containing Bala are applied to the skin for skin-related benefits.
6. Poultices: Mashed Bala plant material is applied directly to wounds or skin conditions.
7. Culinary Use: In some regions, Bala is incorporated into dishes for its potential health benefits.
8. Infused Oils: Bala-infused oils are used for massages and topical applications.
9. Inhalation: Inhaling the aroma of Bala essential oil can have respiratory benefits.
10. Gargles and Mouthwashes: Preparing gargles or mouthwashes with Bala for oral health.
11. Syrups: Bala syrup provides a sweet way to consume it, especially for children.
12. Smoking Mixtures: In some cultures, Bala is used in smoking mixtures for its calming effects.
The Side Effects Of Using Pergularia Daemia Medicinal Plant
While Bala offers numerous health benefits, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects. Here are some possible side effects and their explanations:
1. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to Bala, leading to allergic symptoms such as itching or hives.
2. Digestive Distress: In rare cases, Bala may cause digestive discomfort, including nausea or diarrhea.
3. Hormonal Effects: Due to its influence on hormones, Bala should be used cautiously by individuals with hormonal disorders.
4. Interaction with Medications: Bala may interact with certain medications, so consult a healthcare professional before use.
5. Skin Irritation: When used topically, it may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
6. Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid Bala due to limited safety data.
7. Liver Health: High doses may affect liver function, so monitor liver health when using Bala.
8. Overuse: Excessive use may lead to imbalances in the body’s systems, so follow recommended dosages.
Read Also: Growing Guide and Health Benefits of Slippery Elm Tree
The Scientific Research and Studies of Pergularia Daemia (Bala)
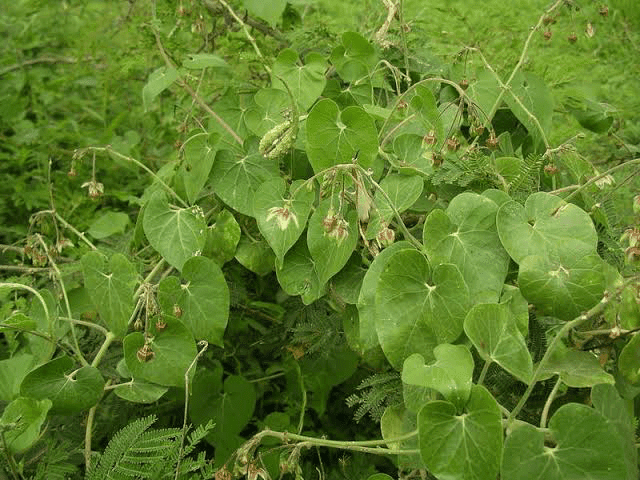
Pergularia daemia, commonly known as Bala, has been the subject of scientific research and studies to explore its medicinal properties and potential applications. Here are some key findings from scientific research:
1. Immunomodulatory Effects: Research has shown that Bala exhibits immunomodulatory properties, enhancing the body’s immune response.
2. Antioxidant Activity: Studies have confirmed its antioxidant properties, which help protect cells from oxidative damage.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Scientific investigations support Bala’s anti-inflammatory properties, making it relevant in the treatment of inflammatory conditions.
4. Antimicrobial Properties: Bala has demonstrated antimicrobial activity against various bacteria and fungi.
5. Respiratory Benefits: Research suggests that Bala’s bronchodilator effects can help individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma.
6. Pain Management: Studies indicate its potential as a natural analgesic, offering relief from pain and discomfort.
7. Cardiovascular Health: Some research suggests that Bala may have a positive impact on cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
8. Anti-diabetic Potential: Bala has shown promise in the management of diabetes by helping regulate blood sugar levels.
9. Wound Healing: Laboratory studies have shown that Bala can promote the healing of wounds and skin injuries.
10. Anti-Anxiety and Anti-Depressant Effects: Research hints at Bala’s potential to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
11. Anticancer Activity: Preliminary studies have explored Bala’s potential anticancer properties, although further research is needed.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Pergularia Daemia (Bala) Medicinal Plant
While Bala offers a range of health benefits, it’s essential to use it safely. Here are safety precautions and recommendations:
1. Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before using Bala for medicinal purposes, consult a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
2. Follow Dosage Instructions: Adhere to recommended dosages provided on product labels or by healthcare professionals.
3. Avoid During Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid Bala due to limited safety data.
4. Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Be vigilant for signs of allergic reactions, such as itching, hives, or difficulty breathing, and discontinue use if they occur.
5. Be Cautious with Hormonal Disorders: If you have hormonal disorders or imbalances, use Bala with caution, as it may affect hormone levels.
6. Monitor Liver Health: High doses of Bala may affect liver function, so keep an eye on liver health and consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms of liver problems.
7. Be Aware of Potential Interactions: Bala may interact with certain medications, so inform your healthcare provider of all medications and supplements you’re taking.
8. Use Moderation: Avoid excessive use of Bala to prevent imbalances in the body’s systems.
FAQs About Pergularia Daemia (Bala) Medicinal Plant
Here are 14 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Pergularia daemia to provide essential information to those interested in its use:
1. What is Pergularia Daemia? – Pergularia daemia, commonly known as Bala, is a medicinal plant used for its health benefits.
2. What are its common names? – Common names include Bala, Sutranabhi, and Utliganeri.
3. How is it traditionally used? – Bala is used in various forms, including teas, capsules, and tinctures.
4. What are its primary health benefits? – Benefits include immune support, respiratory health, and anti-inflammatory effects.
5. Are there any side effects? – Possible side effects include allergies, digestive discomfort, and hormonal effects.
6. Is it safe during pregnancy? – Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid it due to limited safety data.
7. Can it interact with medications? – Yes, it may interact with certain medications, so consult a healthcare provider.
8. How should it be stored? – Store it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
9. Is it safe for long-term use? – Long-term safety depends on individual factors, so consult a healthcare provider.
10. Can it be used topically? – Yes, it can be applied topically for skin-related benefits.
11. Does it have a scientific basis for its health claims? – Yes, scientific research supports many of its health benefits.
12. Where can I find Pergularia Daemia products? – They are available at herbal stores, online retailers, and through healthcare professionals.
13. Can Bala be used as a preventive measure? – Bala is often used as a preventive tonic to maintain overall health and immunity.
14. Are there any age restrictions for its use? – Bala can generally be used by adults and, in some cases, by children under medical supervision.
Read Also: 5 Barriers to Small Business Growth
