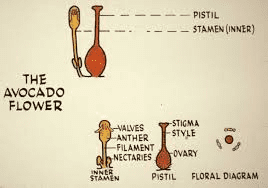
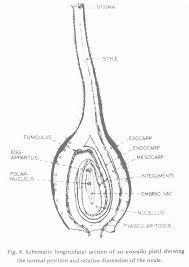
female reproductive organ of the avocado flower. Comprising the stigma, style, and ovary, the pistil plays a crucial role in the pollination and fertilization process, ultimately leading to fruit formation.
Economically, the avocado pistil is of great importance as it is essential for avocado tree reproduction, which is the foundation of the avocado industry.
The stigma of the pistil receives pollen during pollination, typically facilitated by bees or other pollinators.
The pollen travels down the style to reach the ovary, where fertilization occurs. This process initiates fruit development, leading to the production of avocados, which are highly valued in the global market for their nutritional content and culinary versatility.
Moreover, beyond its role in fruit production, the avocado pistil contributes to various applications and by-products. Avocado flowers, including the pistil, contain bioactive compounds that have potential medicinal and nutritional benefits.
Extracts from avocado pistils are being explored for their antioxidant properties and potential use in pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Avocado Pistil
1. Fruit Production: The avocado pistil is crucial for fruit production in avocado trees. It receives pollen from the stamens, facilitating fertilization of the ovules within the ovary, which ultimately results in the development of avocado fruit.
2. Commercial Avocado Industry: The successful pollination facilitated by the avocado pistil is essential for the commercial avocado industry. Avocado fruit is a valuable commodity globally, and its production contributes significantly to agricultural economies.
3. Export Trade: Avocado fruit, made possible by the pollination process involving the pistil, is traded internationally, generating revenue for producing countries through exports. Avocado exports are an important source of income for countries such as Mexico, Chile, and Peru.
4. Culinary Use: Avocado fruit produced from successful pollination by the pistil is widely consumed in various culinary dishes, such as salads, sandwiches, and dips like guacamole. Avocado has become a staple ingredient in many cuisines worldwide.
5. Food Processing: Avocado fruit is processed into various food products, including avocado oil, purees, sauces, and spreads. These processed products have diverse culinary applications and contribute to the food processing industry’s economic output.
6. Horticultural Industry: Avocado trees, cultivated for their fruit-bearing capabilities, are integral to the horticultural industry. Nurseries propagate avocado trees for commercial orchards and home gardeners, contributing to the ornamental and landscape sectors.
7. Job Creation: The avocado industry, supported by the pollination process involving the avocado pistil, creates employment opportunities in farming, harvesting, packing, transportation, and marketing sectors, both locally and internationally.
8. Agricultural Innovation: Research and development in avocado cultivation, including advancements in pollination techniques and breeding programs involving the pistil, drive agricultural innovation and improve crop productivity and quality.
9. Environmental Stewardship: Sustainable avocado production practices, which prioritize pollinator habitat conservation and biodiversity preservation, promote environmental stewardship and contribute to ecosystem health and resilience.
10. Rural Development: Avocado cultivation, sustained by successful pollination facilitated by the pistil, supports rural development initiatives by providing livelihood opportunities, infrastructure development, and community empowerment.
11. Crop Diversity: Avocado trees, cultivated for their fruit production, contribute to crop diversity and agricultural resilience by diversifying farming systems and providing alternative income sources for farmers.
12. Value-added Products: Avocado-derived products such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and nutraceuticals capitalize on the nutritional and medicinal properties of avocado fruit, enhancing value-added product markets and economic diversification.
13. Research Funding: Avocado research, including studies on pollination biology and pistil function, receives funding from government agencies, academic institutions, and private industry stakeholders, driving scientific advancements and innovation.
14. Tourism: Avocado orchards in bloom, showcasing the pollination process involving the pistil, attract tourists and visitors, contributing to agritourism ventures and local economies in avocado-growing regions.
15. Sustainable Development Goals: The avocado industry, supported by pistil-mediated pollination, aligns with sustainable development goals related to food security, poverty alleviation, gender equality, and environmental sustainability.
16. Global Supply Chains: Avocado fruit, produced through pollination involving the pistil, is integrated into global supply chains, facilitating trade and commerce between producing and consuming regions across continents.
17. Climate Resilience: Avocado cultivation systems, sustained by effective pollination mechanisms involving the pistil, demonstrate resilience to climate variability and contribute to climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts.
Read Also: How to Control Feeding Struggle among Fishes in the same Pond
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Avocado Pistil
1. Avocado Seed Oil: Avocado pits, which develop from fertilized ovules within the pistil’s ovary, can be processed to extract avocado seed oil, valued for its culinary, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical applications.
2. Avocado Seed Flour: Avocado pits can be ground into a fine powder to produce avocado seed flour, a nutritious ingredient used in baking, cooking, and food manufacturing.
3. Avocado Seed Extracts: Extracts obtained from avocado pits contain bioactive compounds with potential health benefits, leading to the development of nutraceutical supplements and functional food products.
4. Avocado Seed Husk Mulch: The husk surrounding avocado pits can be shredded and used as mulch in agriculture and gardening to improve soil moisture retention, suppress weed growth, and enhance soil fertility.
5. Avocado Seed-based Biomaterials: Avocado seed-derived materials, such as bioplastics and biocomposites, are explored for their potential as sustainable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based plastics and synthetic materials.
6. Avocado Seed-based Animal Feed: Avocado seed meal, obtained from processing avocado pits, can be incorporated into animal feed formulations to provide supplemental nutrients for livestock and poultry.
7. Avocado Seed-based Dyes: Compounds extracted from avocado pits are used as natural dyes in textile and cosmetic industries, offering eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic dyes.
8. Avocado Seed-based Bioenergy: Avocado seed biomass can be utilized in bioenergy production processes such as anaerobic digestion or pyrolysis, generating renewable energy sources while reducing organic waste.
9. Avocado Seed-based Nutraceuticals: Avocado seed extracts are studied for their potential as nutraceutical supplements, providing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other health-promoting properties.
10. Avocado Seed-based Soil Amendments: Avocado seed compost or vermicompost can be used as organic soil amendments to enhance soil fertility, structure, and microbial activity in agricultural and horticultural applications.
Read Also: Sudangrass (Sorghum × drummondii) Complete Guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Avocado Pistil
1. How does the avocado pistil contribute to fruit production?
The avocado pistil receives pollen from the stamens and facilitates fertilization of the ovules within the ovary, leading to the development of avocado fruit.
2. Can avocado pistils self-pollinate?
While avocado flowers have mechanisms for both self-pollination and cross-pollination, successful fruit set often requires cross-pollination facilitated by pollinators.
3. What factors affect avocado pistil pollination?
Factors such as weather conditions, availability of pollinators, genetic compatibility between avocado varieties, and orchard management practices can influence pistil pollination and fruit set.
4. How long does it take for avocado fruit to develop after pistil pollination?
After successful pistil pollination, avocado fruit typically takes several months to develop and mature, with the exact timing varying depending on environmental factors and avocado variety.
5. Can avocado pistils produce fruit without pollination?
Avocado pistils require pollination to produce fruit, as the fertilization process initiated by pollen transfer is necessary for ovule development and fruit formation.
6. Are avocado pistils edible?
No, avocado pistils are not typically consumed as they are part of the reproductive structure of the avocado flower and are not considered edible.
7. Do avocado pistils have a fragrance?
Avocado pistils do not produce a noticeable fragrance, as their primary function is reproductive rather than attracting pollinators through scent.
8. How can growers optimize pistil pollination in avocado orchards?
Growers can optimize pistil pollination by maintaining healthy bee populations, planting compatible avocado varieties, providing suitable nesting habitat for pollinators, and implementing orchard management practices that promote pollinator activity.
9. What role do pollinators play in avocado pistil pollination?
Pollinators such as bees play a crucial role in avocado pistil pollination by transferring pollen between flowers, facilitating fertilization and fruit set in avocado trees.
10. Can avocado pistils be genetically modified?
While avocado pistils are not typically subject to genetic modification, research on avocado genetics and breeding may explore genetic traits related to pistil function and reproductive biology for crop improvement purposes.
Read Also: The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Potential of Garbage Wastes
