European Eggplant botanically known as Solanum melongena is a hardly species that can be grown all year round in tropical areas. It needs good irrigation management and rigorous control of nitrogen fertilization (to make fruit setting easier) during the hot and rainy season. Hybrid eggplant can be pruned to keep two or three main stems.
Eggplant is a member of the Solanaceae, or nightshade family, which includes tomatoes, peppers and potatoes, eggplant is thought to be a native of India where it grows wild as a perennial. Many of us are familiar with the most common eggplant variety, Solanum melongena, but there are a plethora of eggplant types available.
A variety of eggplant that is particularly prized in some regions, including the United States, is one with a large, cylindrical or egg-shaped fruit, with smooth, dark purple, glossy skin.
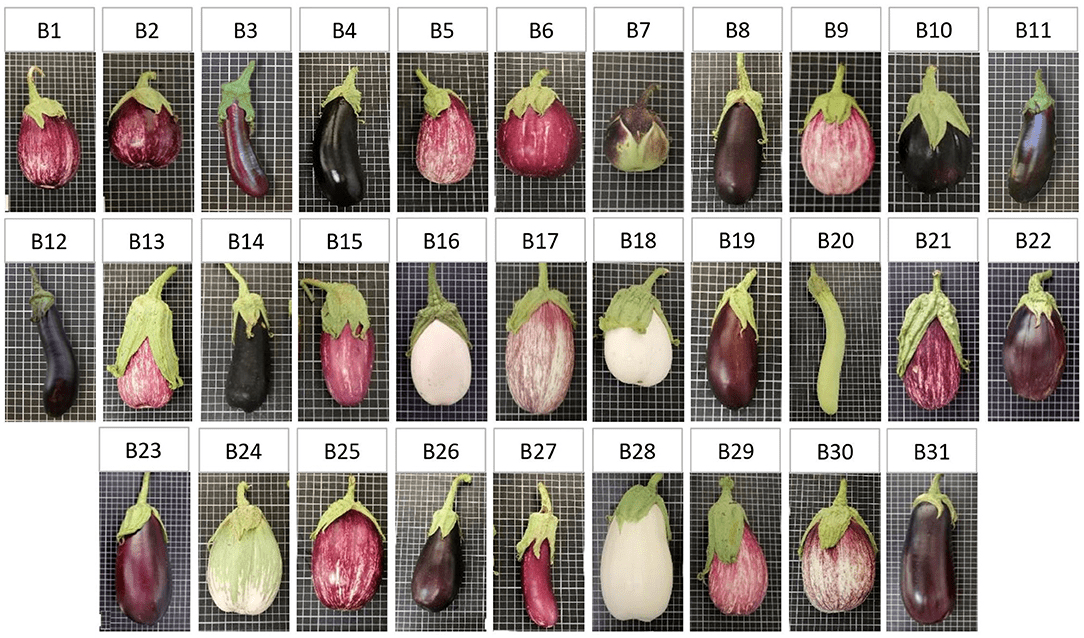
However, human creativity has resulted in a wide variety of cultivars, varying in tastes, shapes, sizes, and colors. Depending on the cultivar, the fruit can vary from small to large and pendulous, from oblong to round, and might be such colors as green, white, or yellow, among others, or even striated shades and color gradients.
Before we proceed to the different varieties of European Eggplant we have, I want to briefly explain some diseases abbreviations/common names along with their Pathogen or causal agent as follows:
| Abbreviation / Common name | Pathogen or Causal Agent |
| Anthracnose | Colletotrichum lagenanum |
| Bacterial Wilt | Ralstonia solanacearum |
| CMV | Cucumber Mosaic Virus |
| TMV | Tobacco Mosaic Virus |
Now let us proceed to discuss some of the varieties of European Eggplant:
F1 KALENDA (INRA):
This is one of the best varieties of European eggplant for the tropical and subtropical areas. It is the solution to eggplant grower’s problem with regards to the disease known as “Bacterial Wilt (Ralstonia) due to its resistance to Bacterial Wilt.
This hybrid eggplant can be grown during hot and humid season and it produces excellent result for the farmer. It also has a very attractive color as its glossy purplish black fruits correspond to the export market quality. Meanwhile F1 Kalenda (INRA) farmers should also know that during the rainy season nitrogen fertilizer must be reduced.
The maturity period of this variety of European eggplant occurs between 65-75days and the plant is a vigorous plant, it also has a long tapered shape and a black purple color.
The size is usually between 300grams-450grams measuring about 20×8-10cm with tolerances and resistance to Tobacco Mosaic Virus, Cucumber Mosaic Virus, Bacterial Wilt and Anthracnose. Finally it stays a long period of harvest and can also be cultured in open field.
Below is a breakdown of other different varieties of European eggplant, their maturity period (days), the unique characteristics of the plant, the shape of the fruit, the color of the fruit, the size of the fruit and its disease tolerance and resistance remarks
| Variety | Maturity | Plant | Fruit | Remarks and tolerance/ resistances | |||
| (days) | Shape | Color | Size | ||||
| OP | |||||||
| Ravaya | 70/75 | Very vigorous | Oval | Purple | Small (50-80g) = 5x6cm | Hardy / CMV | |
| Black Beauty | 75/80 | Vigorous | Lobulous Slight fruit fascination | Dark purple | Big (300-400) = 13x15cm | Widely adapted,
it can also be cultured on bothshelter and open field. | |
| Zebrine | 75/80 | Vigorous | Lon oval | Striped purple and white | Medium
(250-300g) = 15-16cmx7-8cm | Very popular in the Caribbean area and Anthracnose/
Phomopsis vexans. It can be cultured in open field. | |
| Florida market | 85/95 | Large | Oval | Purple | Big (400 – 500g) = 16-18 x 10cm | Phomopsis vexans | |
| Long purple | 70/75 | Erected | Long | Purple | Medium
(200/300g) = 20-25 x 6-7cm | The reference for long standard variety. | |
| HYBRID F1 | |||||||
| F1 African Beauty | 70/75 | Vigorous | Regular globulous very slight fruit fasciation | Lossy black purple | Bi (350-450) =14x15cm | High yielding especially suited for tropical conditions, TMV / CMV | |
| F1 Obala | 75/80 | Medium size | Oval | Dark purple | Medium(300-400g) = 13x12cm | TMV / CMV | |
| F1 Adama | 70 | Medium size | Long cylindrical | Black purple | Medium (250-
350g)=20-22x6cm | Anthracnose Phomopsis vexans, TMV / CMV | |
| F1 Melina | 55-60 | Deep purple | 18×9.5cm/400g | Can be cultured in open field, CMV | |||
| Purple Tiger | 70-80 | green with purple strips | 20.5x10cm/450g | Can be cultured in open field, CMV, BW | |||
As a crop farmer you should be aware of the seeds you need to plant and how they are being cultured as some seeds perform better when being cultivated under shelter while some perform better in the open field therefore I will suggest that aside from knowing the season for your crops, you should also be aware how and where to plant the seeds in order to achieve an optimum result from your effort. Remember that your seed and management practices determines the rate of your success in farming.
Read Also: The Ultimate Step-by-Step Guide to Vegetable Gardening
Read Also: Hydroponics Guide 101: All You Need to Know About it
