Cayenne (Capsicum annuum), also known as red pepper, is a spicy chili pepper widely used in culinary and traditional medicine. This plant, native to Central and South America, belongs to the nightshade family and is known for its hot flavor due to the presence of capsaicin, a bioactive compound with various health benefits.
One of the primary uses of cayenne is in culinary applications. It is a popular spice that adds heat and flavor to a wide range of dishes, from savory to sweet. Cayenne pepper is also a source of essential nutrients, including vitamins A and C, as well as capsaicin, which gives it its characteristic spiciness.
In traditional medicine, cayenne has been employed for its potential medicinal properties. One notable benefit is its role in promoting cardiovascular health. Capsaicin has been found to support heart health by helping to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. It may also improve circulation by dilating blood vessels and reducing the risk of blood clots.
Cayenne is also recognized for its digestive benefits. The spice can stimulate saliva production and gastric juices, aiding in digestion. It may be used to alleviate symptoms of indigestion and bloating. Additionally, cayenne has been included in traditional remedies for its potential to boost metabolism and promote weight loss.
Topically, cayenne has been used for its analgesic properties. Capsaicin can act as a natural pain reliever by desensitizing nerve receptors responsible for transmitting pain signals. This has led to the use of cayenne-containing creams and patches for the relief of conditions such as arthritis pain and muscle soreness.
While cayenne offers various health benefits, it’s important to use it in moderation, especially for individuals sensitive to spicy foods. Excessive consumption of cayenne may lead to digestive discomfort in some individuals.
The Botanical Description of Cayenne
1. Plant Structure: Cayenne, scientifically known as Capsicum annuum, is a perennial shrub that belongs to the Solanaceae family. It is characterized by a branching structure with multiple stems and a bushy appearance.
2. Leaves: The leaves of the cayenne plant are simple, elongated, and alternately arranged along the stems. They are dark green and can vary in size, with smooth margins.
3. Flowers: Cayenne produces small, white to pale green flowers that are typically star-shaped. These flowers grow individually or in clusters and have a characteristic five-petal structure.
4. Fruits: The most distinctive feature of cayenne is its elongated, tapered fruits, commonly referred to as peppers. These peppers can range in color from green to red, depending on their maturity. They are known for their pungent taste.
5. Size: The size of the cayenne plant can vary, with mature plants reaching heights between 2 to 4 feet. The overall size is influenced by factors such as growing conditions and pruning practices.
6. Root System: Cayenne has a well-developed root system that aids in nutrient absorption and provides stability to the plant. The roots are typically fibrous and spread horizontally.
7. Growth Habit: Cayenne exhibits an upright growth habit, with stems that may require support as the plant matures and produces an abundance of peppers.
8. Foliage: The foliage of cayenne is dense and contributes to the plant’s overall bushy appearance. The leaves, stems, and fruits contain capsaicin, the compound responsible for the plant’s spiciness.
9. Reproduction: Cayenne reproduces primarily through its seeds, which are contained within the peppers. The peppers serve as both the plant’s reproductive organs and a means of dispersing seeds.
The Geographic Distribution of Cayenne
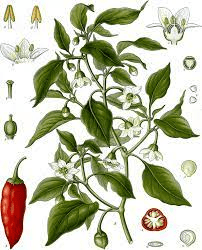
1. Origin: Cayenne is native to the tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas. It is believed to have originated in South America and has been cultivated for centuries.
2. Global Cultivation: Due to its popularity and versatility, cayenne is now cultivated worldwide in regions with suitable climates. It thrives in warm temperatures and well-drained soils.
3. Growing Conditions: Cayenne peppers are commonly grown in countries with tropical, subtropical, and Mediterranean climates. They are cultivated in home gardens, commercial farms, and greenhouses.
4. Key Producers: Major producers of cayenne peppers include countries in Central and South America, such as Mexico, Peru, and Brazil. Additionally, India, China, and some African nations contribute significantly to global cayenne production.
5. Adaptability: Cayenne has proven adaptable to various growing conditions, allowing it to flourish in both humid and arid climates. This adaptability contributes to its widespread distribution.
6. Culinary Use: In addition to being grown for commercial production, cayenne is often cultivated in home gardens around the world for culinary use, adding spice to a variety of dishes.
7. Global Cuisine Influence: Cayenne’s influence extends to diverse cuisines, and its peppers are used in the preparation of sauces, condiments, and spice blends in many regions.
8. Climate Specifics: While cayenne is resilient and can tolerate different climates, it thrives in warm temperatures between 70°F to 80°F (21°C to 27°C) and requires a frost-free environment for optimal growth.
The Chemical Composition of Cayenne
1. Capsaicin: The primary bioactive compound in cayenne peppers is capsaicin, responsible for the characteristic spiciness. Capsaicin has been studied for its various health benefits.
2. Capsaicinoids: Cayenne peppers contain a group of compounds collectively known as capsaicinoids, which contribute to the heat intensity of the peppers. Other capsaicinoids include dihydrocapsaicin and nordihydrocapsaicin.
3. Vitamins: Cayenne is a rich source of vitamins, including vitamin C, vitamin A, and several B vitamins. These vitamins contribute to the overall nutritional value of the peppers.
4. Minerals: Essential minerals such as potassium, manganese, and iron are present in cayenne peppers, supporting various bodily functions.
5. Flavonoids: Cayenne contains flavonoids with antioxidant properties, which play a role in neutralizing free radicals in the body.
6. Carotenoids: The red color of mature cayenne peppers is attributed to carotenoids, including beta-carotene. Carotenoids are antioxidants that promote eye health.
7. Alkaloids: In addition to capsaicinoids, cayenne peppers may contain alkaloids, natural compounds with potential pharmacological effects.
8. Fiber: Cayenne peppers provide dietary fiber, contributing to digestive health and promoting a feeling of fullness.
9. Essential Oils: Some varieties of cayenne peppers produce essential oils with aromatic compounds that add to the overall flavor profile.
10. Fatty Acids: Cayenne peppers may contain trace amounts of fatty acids, contributing to their nutritional content.
11. Proteins and Amino Acids: While not a significant source, cayenne peppers contain proteins and amino acids that contribute to their overall nutritional profile.
12. Water Content: Like many fruits, cayenne peppers have a high water content, providing hydration and aiding in digestion.
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Saffron (Crocus sativus)
The Medicinal Health Benefits Of Cayenne (Capsicum annuum)

1. Pain Relief: Capsaicin in cayenne peppers has analgesic properties, making it a natural pain reliever. Topical capsaicin creams are used for conditions such as arthritis and muscle pain.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Cayenne may help reduce inflammation due to its capsaicin content, potentially benefiting conditions like osteoarthritis.
3. Cardiovascular Health: Capsaicin has been linked to cardiovascular benefits, including improved blood circulation and lower blood pressure.
4. Weight Management: The heat generated by capsaicin may increase metabolism and promote weight loss by aiding in the breakdown of fats.
5. Digestive Aid: Cayenne may support digestion by stimulating salivary glands and promoting the production of digestive enzymes.
6. Respiratory Health: The spiciness of cayenne may help alleviate nasal congestion and promote respiratory health by thinning mucus.
7. Immune System Support: The vitamins and antioxidants in cayenne contribute to overall immune system health, helping the body defend against infections.
8. Painful Conditions: Capsaicin creams are used for conditions like shingles and diabetic neuropathy to alleviate pain and discomfort.
9. Detoxification: Cayenne peppers may have detoxifying effects, stimulating circulation and aiding in the elimination of toxins from the body.
10. Skin Health: Topical applications of cayenne may benefit skin health, promoting circulation and potentially improving conditions like psoriasis.
11. Regulation of Blood Sugar: Some studies suggest that cayenne may help regulate blood sugar levels, benefiting individuals with diabetes.
12. Anti-Cancer Properties: Capsaicin has shown promise in laboratory studies for its potential anti-cancer effects, though more research is needed.
13. Headache Relief: The spiciness of cayenne may help relieve headaches by inhibiting substance P, a neuropeptide associated with pain.
14. Anti-Bacterial Effects: Cayenne peppers may exhibit antibacterial properties, helping to combat certain bacterial infections.
15. Joint Pain Relief: Topical capsaicin creams may be effective in reducing joint pain associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
16. Enhanced Circulation: The heat generated by cayenne consumption may promote blood circulation, benefiting overall cardiovascular health.
17. Anti-Allergic Effects: Capsaicin’s anti-inflammatory properties may contribute to reducing allergic symptoms.
18. Gastrointestinal Health: Cayenne may support gastrointestinal health by promoting the production of stomach acids and reducing symptoms of indigestion.
19. Antioxidant Support: The flavonoids and carotenoids in cayenne peppers provide antioxidant support, protecting cells from oxidative stress.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits Of Cayenne (Capsicum annuum)
1. Culinary Use: Incorporate cayenne peppers into your diet by adding them to various dishes, sauces, soups, or stews. The spiciness can be adjusted based on personal preference.
2. Capsaicin Creams: Topical capsaicin creams are available for pain relief. Apply a small amount to the affected area, following the product’s instructions.
3. Cayenne Supplements: Capsaicin supplements are available in various forms, including capsules. Follow recommended dosage guidelines, and consult with a healthcare professional.
4. Herbal Teas: Some individuals enjoy the benefits of cayenne by consuming it in the form of herbal teas. These teas may be purchased or prepared by steeping dried cayenne peppers.
5. Tinctures: Cayenne tinctures can be taken orally by diluting them in water. Follow the recommended dosage on the product label.
6. Culinary Spices: Use ground cayenne pepper as a spice to add heat to your favorite dishes. Start with small amounts and adjust according to taste.
7. Cayenne-Infused Oils: Infuse olive oil with cayenne to create a spicy oil for cooking. Use it to add flavor to salads or drizzle over dishes.
8. Capsaicin Patches: Medicated patches containing capsaicin can be applied to the skin for localized pain relief. Follow the instructions provided with the patches.
9. Cayenne-Containing Balms: Some topical balms and salves contain cayenne for muscle and joint pain relief. Apply a small amount to the affected area.
10. Cayenne Detox Drinks: Create detox drinks by combining cayenne with lemon juice and water. This may help boost metabolism and support detoxification.
The Side Effects Of Using Cayenne Medicinal Plant
1. Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Excessive consumption of cayenne may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including heartburn or stomach irritation. Start with small amounts and monitor your body’s response.
2. Skin Irritation: Topical applications of capsaicin creams may cause skin irritation, redness, or a burning sensation. Perform a patch test and discontinue use if irritation occurs.
3. Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, individuals may be allergic to cayenne peppers, leading to allergic reactions. Monitor for symptoms such as itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
4. Interaction with Medications: Cayenne supplements may interact with certain medications, including blood-thinning drugs. Consult with a healthcare professional if you are on medication.
5. Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnant or lactating individuals should exercise caution when using cayenne, especially in medicinal doses. Consult with a healthcare professional.
6. Sensitivity to Spiciness: Some individuals may be more sensitive to the spiciness of cayenne. Start with milder forms and gradually increase consumption if desired.
7. Capsaicin Burns: Handling fresh cayenne peppers without protection may lead to skin irritation or burns due to the capsaicin content. Use gloves when handling.
8. Potential Exacerbation of GERD: Individuals with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may experience worsened symptoms with excessive consumption of spicy foods like cayenne.
9. Increased Bleeding Risk: Cayenne may have blood-thinning effects due to capsaicin. Individuals on blood-thinning medications should consult with healthcare professionals.
10. Interaction with Hypertension Medications: Cayenne may affect blood pressure. Individuals on hypertension medications should monitor their blood pressure regularly and consult with healthcare professionals.
11. Interference with Sleep: Some individuals may experience difficulty sleeping or increased heart rate after consuming cayenne, especially in the evening.
12. Interference with Iron Absorption: Cayenne may hinder the absorption of non-heme iron from plant-based foods. Consider spacing out the consumption of cayenne and iron-rich foods.
13. Potential for Drug Interactions: Cayenne may interact with certain medications. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using cayenne supplements.
Read Also: Pixie Bob Cat Breed Description and Complete Care Guide
The Scientific Research and Studies of Cayenne

1. Pain Management: Scientific studies have explored the use of capsaicin for pain management, including conditions like neuropathy and arthritis.
2. Cardiovascular Effects: Research has investigated the impact of cayenne on cardiovascular health, including its potential to improve blood circulation and lower blood pressure.
3. Weight Loss: Some studies suggest that capsaicin may aid in weight loss by increasing metabolism and promoting fat breakdown.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Cayenne’s anti-inflammatory effects, attributed to capsaicin, have been studied for their potential in reducing inflammation, particularly in conditions such as osteoarthritis.
5. Respiratory Health: Research has explored the use of cayenne in promoting respiratory health by alleviating nasal congestion and thinning mucus.
6. Immune System Modulation: Studies have investigated the role of cayenne in modulating the immune system, contributing to overall immune function and defense against infections.
7. Gastrointestinal Benefits: Cayenne’s impact on gastrointestinal health, including its ability to stimulate salivary glands and aid in digestion, has been a subject of scientific interest.
8. Antioxidant Effects: The antioxidants found in cayenne, such as flavonoids and carotenoids, have been studied for their ability to combat oxidative stress and protect cells from damage.
9. Blood Sugar Regulation: Preliminary research suggests that cayenne may play a role in regulating blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
10. Anti-Cancer Properties: Some laboratory studies have explored the anti-cancer properties of capsaicin, indicating potential effects on inhibiting the growth of cancer cells. However, more research is needed in clinical settings.
11. Headache Relief: Capsaicin’s ability to inhibit substance P, a neuropeptide associated with pain, has been investigated for its potential in relieving headaches.
12. Anti-Bacterial Effects: Research has examined the antibacterial properties of cayenne peppers, suggesting potential benefits in combating certain bacterial infections.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations In Using Cayenne Medicinal Plant
1. Gradual Introduction: Introduce cayenne gradually into your diet or health regimen, especially if you are not accustomed to spicy foods, to monitor your body’s response.
2. Moderation is Key: Consume cayenne in moderation. Excessive intake may lead to discomfort and potential side effects.
3. Patch Test for Topical Use: Before applying capsaicin creams or balms, perform a patch test on a small area of skin to check for any adverse reactions.
4. Consult Healthcare Professionals: If you are pregnant, lactating, on medication, or have pre-existing health conditions, consult with healthcare professionals before using cayenne supplements or incorporating it into your diet.
5. Personal Sensitivity: Be aware of your personal sensitivity to spiciness. Start with milder forms of cayenne and adjust according to your tolerance.
6. Handling Fresh Peppers: When handling fresh cayenne peppers, wear gloves to avoid skin irritation or burns from the capsaicin content.
7. Blood Pressure Monitoring: Individuals with hypertension should monitor their blood pressure regularly when consuming cayenne, as it may affect blood pressure levels.
8. Iron Absorption: If you are concerned about iron absorption, consider spacing out the consumption of cayenne and iron-rich foods.
9. Bedtime Consumption: Some individuals may experience difficulty sleeping or increased heart rate after consuming cayenne, especially in the evening. Consider adjusting the timing of consumption.
10. Allergic Reactions: Monitor for allergic reactions, especially if you have a history of allergies. Discontinue use and seek medical attention if symptoms arise.
11. Consultation for Capsaicin Patches: If using medicated patches containing capsaicin, follow the instructions provided and consult with healthcare professionals if needed.
12. Interaction with Medications: Cayenne supplements may interact with certain medications, including blood-thinning drugs. Consult with healthcare professionals if you are on medication.
FAQs About Cayenne Medicinal Plant
1. Is Cayenne Safe for Daily Consumption?
Yes, cayenne is generally safe for daily consumption in moderate amounts. However, individual tolerance may vary, and those with specific health conditions should consult with healthcare professionals.
2. Can Cayenne Interact with Blood-Thinning Medications?
Cayenne, particularly in supplement form, may have blood-thinning effects. Individuals on blood-thinning medications should monitor their blood clotting regularly and consult with healthcare professionals.
3. Can Pregnant Individuals Consume Cayenne?
Pregnant individuals should exercise caution when consuming cayenne, especially in medicinal doses. It’s advisable to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating it into the diet.
4. How Long Does It Take to Experience the Health Benefits of Cayenne?
The timeline for experiencing health benefits from cayenne can vary. Some individuals may notice effects sooner, while others may take longer. Consistent and moderate consumption is key.
5. Can Cayenne Help with Weight Loss?
Capsaicin in cayenne peppers may contribute to weight loss by increasing metabolism and promoting fat breakdown. However, it’s important to maintain a balanced diet and exercise.
6. Are There Different Varieties of Cayenne Peppers?
Yes, there are different varieties of cayenne peppers, each with its own level of spiciness and flavor profile. Common varieties include the Long Slim Cayenne and the Thai Bird’s Eye.
7. Can Cayenne Help with Digestive Issues?
Cayenne may support digestion by stimulating salivary glands and promoting the production of digestive enzymes. However, individuals with gastrointestinal conditions should consult with healthcare professionals.
8. Can Cayenne Help with Respiratory Issues?
The spiciness of cayenne may help alleviate nasal congestion and promote respiratory health by thinning mucus. Inhaling steam from cayenne tea may provide relief.
9. Are Cayenne Supplements Recommended?
Cayenne supplements, including capsules, are available. It’s advisable to follow recommended dosage guidelines and consult with healthcare professionals before using supplements.
10. Can Cayenne Help Alleviate Joint Pain?
Topical capsaicin creams containing cayenne may be effective in reducing joint pain associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Follow product instructions and consult with healthcare professionals.
11. Is Cayenne Safe for Individuals with Allergies?
While cayenne allergies are not common, it’s advisable to perform a patch test before using cayenne topically or consuming it, especially if you have a history of allergies.
12. Can Cayenne Contribute to Digestive Health?
Cayenne’s ability to stimulate digestion may contribute to overall digestive health. However, individuals with digestive conditions should seek guidance from healthcare professionals.
13. Can Cayenne be Used Topically for Headache Relief?
Topical applications of capsaicin creams containing cayenne may be effective in relieving headaches by inhibiting substance P. Follow product instructions and avoid contact with eyes.
14. Are There Different Culinary Uses for Cayenne?
Cayenne can be used in various culinary applications, including adding heat to dishes, preparing spicy sauces, and infusing oils for cooking.
15. Can Cayenne Help Boost the Immune System?
The vitamins and antioxidants in cayenne may contribute to immune system support. However, maintaining overall health through a balanced diet is essential for immune function.
16. Can Cayenne Help with Detoxification?
Cayenne’s potential detoxifying effects are attributed to its ability to stimulate circulation and aid in the elimination of toxins. Consider incorporating it into detox drinks with other beneficial ingredients.
17. Can Cayenne Aid in Skin Health?
Topical applications of cayenne may benefit skin health by promoting circulation and potentially improving conditions like psoriasis. Perform a patch test and follow product instructions.
Read Also: Operation and Maintenance for Comminutor and Grinder

