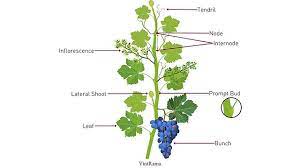
Grape internodes refer to the sections or segments between two successive nodes on the stem of a grapevine plant. Nodes are the points where leaves, tendrils, and clusters of grapes emerge from the stem, while internodes are the spaces or lengths of stem between these nodes.
The length and characteristics of grapevine internodes can vary depending on various factors, including the grapevine variety, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Generally, internodes are relatively elongated segments that allow for the growth and expansion of the grapevine.
In terms of physical appearance, grapevine internodes typically have a cylindrical or elongated shape. The diameter of the internodes can vary depending on the age and vigor of the plant. When young, the internodes tend to be shorter, thinner, and more succulent, while in older, more mature vines, the internodes become longer and thicker.
Internodes play a vital role in the overall growth and development of the grapevine. They serve as conduits for the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars between different parts of the plant. They also provide structural support, allowing the plant to maintain an upright posture. Additionally, internodes are involved in the process of photosynthesis, contributing to the production of energy for the grapevine.
Understanding the characteristics and dynamics of grapevine internodes is crucial in viticulture and grapevine management. It helps growers determine the appropriate training and trellising systems, as well as the timing and methods for pruning, canopy management, and overall vineyard maintenance.
Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Grape Internodes
Grapevine internodes, which are the segments of stem between two adjacent nodes, have several economic importance and uses. Here are some of the key ones:
1. Propagation: Grapevine internodes are commonly used for propagation, allowing the production of new grapevine plants. By taking stem cuttings that include one or more internodes, growers can root and establish new vines. This method is known as vegetative propagation. For example, a grapevine internode with a dormant bud can be planted in a suitable growing medium, and with proper care, it can develop roots and eventually grow into a new grapevine plant.
2. Grafting: Grapevine internodes are also utilized in grafting, a technique used to combine the desired characteristics of different grapevine varieties onto a single plant. In grafting, a scion (the upper part of a grapevine that contains the desired variety) is attached to a rootstock (a different grapevine variety with specific root characteristics) using an internode as the connection point. This allows for the production of disease-resistant or adapted grapevines by utilizing the advantageous traits of both scion and rootstock.
3. Research and breeding: Grapevine internodes are valuable for scientific research and breeding programs. They can be used to study various aspects of grapevine physiology, genetics, and disease resistance. Researchers can collect internodes to analyze the expression of specific genes, study the effects of environmental conditions on vine growth, or assess the impact of pathogens on grapevine health.
4. Production of secondary metabolites: Grapevines contain several secondary metabolites, such as resveratrol and polyphenols, which have significant economic value. The internodes of grapevines are a rich source of these compounds. Extracts from grapevine internodes can be used in the production of dietary supplements, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals due to their antioxidant and potential health benefits.
5. Wood and biomass: Grapevine internodes can be used as a source of wood and biomass. The woody parts of the internodes can be processed for furniture making, flooring, or other woodworking applications. Additionally, grapevine prunings, including internodes, can be used as a source of biomass for energy production or composting.
6. Craft and decorative purposes: The twisted and interesting shapes of grapevine internodes make them popular for decorative purposes. They are often used in wreaths, floral arrangements, and other craft projects due to their natural beauty and flexibility.
7. Wine production: Grapevine internodes play a crucial role in the production of wine. The internodes contain the buds that give rise to grape clusters, which are harvested and used for winemaking. The quality and characteristics of the internodes, such as their size, shape, and sugar content, can impact the flavor, aroma, and overall quality of the resulting wine.
8. Culinary uses: Grapevine internodes, particularly young and tender ones, can be utilized in culinary applications. They are sometimes used in traditional recipes, pickling, or added to salads and stir-fries. The internodes can provide a unique flavor and texture to dishes.
9. Vinegar production: Grapevine internodes can be used in the production of vinegar. Vinegar is made through a fermentation process, and grapevine internodes can serve as a source of sugar and nutrients for the bacteria that convert alcohol into acetic acid. The internodes are crushed or macerated to release the sugars, which are then fermented to produce vinegar.
10. Traditional and medicinal uses: In some cultures, grapevine internodes have been used in traditional medicine for various purposes. They may be brewed into teas or used as an ingredient in herbal remedies, believed to have beneficial effects on digestion, circulation, or as an anti-inflammatory agent.
11. Erosion control: Grapevine internodes can be used for erosion control and soil stabilization purposes. The long, flexible stems of grapevines can be woven into fences, trellises, or barriers to prevent soil erosion on slopes or in areas susceptible to erosion. The intertwined internodes create a natural barrier that helps retain soil and prevent water runoff.
12. Landscaping and ornamental purposes: Due to their attractive foliage, grapevines are often used for landscaping and ornamental purposes. The internodes, with their twisted and vine-like appearance, can be trained along fences, pergolas, or arbors to create beautiful and functional elements in gardens or outdoor spaces.
Read Also : Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Grape Berries
13. Fiber production: Grapevine internodes can be processed to extract fibers that can be used in the textile industry. The fibers are typically obtained from the inner bark or phloem layer of the internodes. Once extracted, they can be spun into yarns or woven into fabrics. Grapevine fibers are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for applications such as rope-making, twine, and even fabric blends.
14. Animal feed and forage: Grapevine internodes, especially the prunings, can be used as a source of feed and forage for livestock. They are rich in fiber and can provide nutritional value to animals. They can be chopped, dried, and incorporated into feed mixes or used as bedding material for animals.
15. Environmental uses: Grapevine internodes can have environmental uses, such as in landscaping to provide shade, windbreaks, or privacy screens. They can also be used in ecological restoration projects to stabilize soil, create habitat structures, or support the growth of other plant species.
16. Traditional crafts and products: Grapevine internodes have been used for centuries in traditional crafts. They can be crafted into baskets, furniture, small decorative items, or even musical instruments. These traditional crafts can have cultural and artistic significance and contribute to local heritage industries.
17. Tannin extraction: Grapevine internodes contain tannins, which are a type of polyphenolic compound. Tannins have various industrial applications, including in the leather tanning industry, where they are used in the process of preserving and treating animal hides to produce leather products. Grapevine internodes can be a source of tannin extraction for these purposes.
18. Bioactive compounds: Grapevine internodes contain bioactive compounds that have potential health benefits. Extracts from grapevine internodes can be used in the production of dietary supplements, functional foods, or nutraceuticals. These compounds may have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, or other bioactive properties.
It’s important to note that the economic importance and uses of grapevine internodes can vary based on factors such as regional practices, market demand, and technological advancements. Additionally, some uses may be more commercially significant than others, depending on the specific context and industry requirements.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Grape Internodes

Grapevine internodes are the sections of the grapevine stem or shoot between two consecutive nodes. These internodes can be utilized to produce various products and by-products. Here are some examples along with their processes:
1. Grapevine Canes: Internodes can be used to produce grapevine canes, which are commonly employed for vine propagation. The process involves selecting healthy internodes and cutting them into suitable lengths, typically 15-20 cm. These canes are then planted in the ground or used for grafting onto rootstock.
2. Grapevine Cuttings: Internodes can also be used to create grapevine cuttings, which are primarily used for grapevine propagation. The process involves selecting internodes with multiple buds and cutting them into shorter lengths, typically 20-30 cm. These cuttings are planted in the ground or used for grafting.
3. Grapevine Extracts: Internodes contain various compounds that can be extracted and utilized for various purposes. For example, resveratrol, a polyphenol found in grapevine internodes, has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It can be extracted and used in dietary supplements, skincare products, or functional foods.
4. Mulch: Dried and ground grapevine internodes can be used as mulch in gardening and horticulture. Mulching with grapevine internodes can help retain soil moisture, regulate temperature, suppress weed growth, and improve soil fertility as it breaks down.
5. Decorative Crafts: Grapevine internodes can be used in crafts and decorative items due to their unique shape and texture. They can be cleaned, dried, and varnished to enhance their appearance. Examples include wreaths, baskets, and rustic furniture.
6. Biomass: Grapevine internodes can be utilized as biomass for energy production. They can be processed into pellets, chips, or briquettes and used as a renewable energy source in biomass power plants or heating systems.
7. Animal Bedding: Dried grapevine internodes can be used as bedding material for animals. They provide a comfortable and absorbent bedding option for livestock, poultry, or small pets like rabbits or guinea pigs.
Read Also : Economic Importance, Uses, and By-Products of Grape Skin
8. Compost: Grapevine internodes can be composted along with other organic materials. As they decompose, they contribute to the nutrient content of the compost, improving soil fertility and structure.
9. Animal Feed: While less common, grapevine internodes can be used as feed for certain livestock, such as goats or sheep. However, it’s important to note that some grapevine parts contain tannins and other compounds that may be harmful to certain animals. Proper processing and analysis of nutritional content are necessary to ensure safe use as animal feed.
10. Vinegar: Grapevine internodes can be used to produce vinegar. The process involves fermenting the internodes with the help of acetic acid bacteria, which convert the alcohol present in the internodes into acetic acid. This acetic acid fermentation results in grapevine vinegar, which can be used for culinary purposes or as a natural cleaning agent.
11. Essential Oils: Grapevine internodes can be steam-distilled to extract essential oils. These oils contain aromatic compounds and can be used in perfumes, aromatherapy, or as natural fragrances in various cosmetic and personal care products.
12. Natural Dyes: The pigments present in grapevine internodes can be used as natural dyes for fabrics, yarns, or other materials. The process involves extracting the pigments from the internodes and then dyeing the desired material using traditional dyeing techniques.
13. Bioactive Compounds: Grapevine internodes contain bioactive compounds with potential health benefits. For example, grapevine internodes are a rich source of polyphenols, flavonoids, and other antioxidants. These compounds have been studied for their potential anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and cardiovascular health benefits.
14. Medicinal Extracts: Grapevine internodes can be processed to create medicinal extracts, such as herbal tinctures or liquid extracts. These extracts can be used in traditional medicine or as ingredients in pharmaceutical preparations.
15. Vinegaroons: Vinegaroons are fermented products made from grapevine internodes that have undergone an extended fermentation process. The internodes are soaked in water for an extended period, allowing fermentation to occur. The resulting vinegaroons can be consumed as a unique culinary condiment or used as a flavoring agent.
16. Craft Materials: Grapevine internodes can be used as raw materials in various craft projects. They can be carved, shaped, or combined with other materials to create artwork, sculptures, or decorative items.
17. Vineyard Trellis: Grapevine internodes can be utilized in the construction of trellises or support structures in vineyards. They can be cut and shaped to create sturdy posts or beams that help support grapevines and maintain their growth.

It’s important to note that the processing methods and specific applications of grapevine internodes may vary depending on local traditions, industry practices, and regulations. Additionally, sustainability and responsible sourcing should be considered when utilizing grapevine internodes to ensure the preservation of vineyards and ecosystems.
Read Also : What Kind Of Plastics Can Be Recycled?
