Antarctic krill scientifically known as Euphausia superba is a tiny, shrimp-like creature that lives in the cold waters surrounding Antarctica. These small crustaceans play a crucial role in the Southern Ocean’s ecosystem, serving as a primary food source for various marine animals, including whales, seals, and penguins.
These remarkable creatures are fascinating due to their unique characteristics and important place in the food web. Antarctic krill are known for their distinctive appearance, with a transparent body that allows them to blend into the ocean’s icy waters. Despite their small size, usually around 2 to 6 centimeters in length, they form massive swarms, sometimes containing millions of individuals.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Antarctic krill is their feeding behavior. These tiny creatures consume phytoplankton, microscopic plants that thrive in the nutrient-rich Southern Ocean. Krill use specialized limbs called thoracopods to filter these tiny plants from the water. This feeding process not only sustains the krill population but also contributes to the transfer of energy through the entire Antarctic marine ecosystem.
The life cycle of Antarctic krill involves various stages, including egg, larval, juvenile, and adult phases. Krill reproduce in the cold, nutrient-rich waters of the Southern Ocean, and their life cycle is closely tied to the seasonal changes in sea ice. Female krill lay eggs under the sea ice during the winter months, and these eggs hatch into larvae, marking the beginning of a new generation.
As they grow, krill undergo a molting process, shedding their exoskeleton to accommodate their increasing size. This molting is essential for their development and allows them to adapt to changing environmental conditions. The survival of krill is crucial not only for their own species but also for the diverse array of marine life that depends on them for sustenance.
One of the most significant consumers of Antarctic krill is the baleen whale. Species like the blue whale and the minke whale rely heavily on krill as a primary food source. Penguins, seals, and various fish species also form part of the intricate web of Antarctic marine life that depends on these tiny crustaceans.
In recent years, scientists have been closely monitoring the Antarctic krill population due to concerns about the impact of climate change on their habitat. Changes in sea ice extent and ocean temperatures can influence the distribution and abundance of krill, affecting the entire ecosystem that relies on them.
In addition, Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) may be small, but their significance in the Southern Ocean’s ecosystem is immense. From their transparent bodies to their vital role in the food web, these tiny crustaceans contribute to the delicate balance of life in Antarctica. Understanding and preserving the habitat of Antarctic krill is essential for the well-being of numerous marine species that depend on them for survival.
Read Also: 15 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Wikstroemia
Selecting the Right Antarctic krill Species for Your Farm
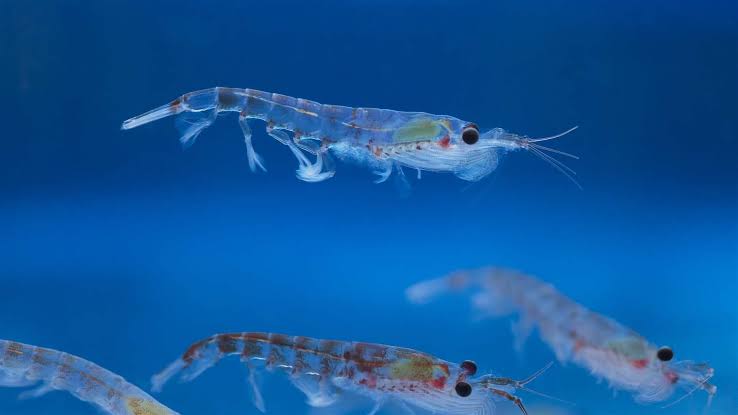

Selecting the right Antarctic krill fish species for your farm is a crucial decision that involves various considerations to ensure the success and sustainability of your aquaculture venture. Among the numerous species of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba stands out as a primary candidate for cultivation due to its ecological significance, nutritional value, and adaptability to controlled farming environments.
Euphausia superba, commonly known as Antarctic krill, has gained attention not only for its role in the natural marine ecosystem but also for its potential as a valuable resource in aquaculture. As you embark on the journey of selecting the appropriate krill species for your farm, it’s essential to understand the unique characteristics of Euphausia superba that make it a preferred choice.
First and foremost, Euphausia superba is a key link in the Antarctic food chain, serving as a primary food source for a variety of marine organisms, including whales, seals, and penguins.
This indicates its nutritional richness, which can be advantageous for cultivating a species that holds such ecological importance. The high nutritional content of Antarctic krill makes it a desirable candidate for aquaculture, especially as a feed source for various farmed fish species.
Furthermore, Euphausia superba exhibits adaptability to a range of environmental conditions, mirroring the diverse habitats found in the Southern Ocean. This adaptability can simplify the process of establishing and maintaining a controlled farming environment, as the krill species is accustomed to the variable conditions of its natural habitat.
Understanding the ecological preferences of Antarctic krill can guide the design and management of your farm to ensure optimal growth and reproduction. When considering the selection of Antarctic krill species, it’s also important to assess the economic viability of cultivation.
Euphausia superba’s prominence in the marine ecosystem translates into potential market demand for its by-products, such as krill oil and meal. These by-products have gained attention for their nutritional benefits and are used in aquafeed for enhancing the health and growth of farmed fish.
In addition to economic considerations, sustainability should be a key factor in your decision-making process. Sustainable aquaculture practices aim to minimize environmental impact and ensure the long-term viability of the chosen species. Euphausia superba’s natural role in the Antarctic ecosystem highlights the importance of responsible farming practices to preserve the delicate balance of the Southern Ocean.
However, selecting the right Antarctic krill fish species for your farm involves a comprehensive understanding of the ecological, nutritional, and economic aspects associated with cultivation.
Euphausia superba, with its ecological significance, adaptability, and potential for valuable by-products, emerges as a promising choice. As you embark on this endeavor, consider the interplay of these factors to establish a sustainable and successful Antarctic krill farming operation.
Setting Up Your Antarctic krill Farm: A Step-by-Step Guide
Establishing your Antarctic krill farm involves a series of essential steps to ensure the success and sustainability of your aquaculture venture. From selecting a suitable location to implementing responsible farming practices, each step plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of a thriving krill farming operation.
1. Site Selection: Choosing the right location is paramount for the success of your Antarctic krill fish farm. Opt for a site with access to cold, nutrient-rich waters, resembling the natural habitat of Antarctic krill. Consider environmental factors, such as water temperature, salinity, and currents, to create an optimal setting for krill growth and reproduction.
2. Infrastructure Development: Invest in the necessary infrastructure to support your krill farm. This includes the construction of floating platforms or pens that mimic the conditions of the Southern Ocean. Ensure proper water circulation and aeration systems to maintain the desired environmental parameters for krill cultivation.
3. Water Quality Management: Maintain strict control over water quality to promote the health and well-being of Antarctic krill. Regularly monitor parameters such as temperature, pH, and nutrient levels. Implement filtration systems to remove impurities and ensure a clean and conducive environment for krill growth.
4. Feeding and Nutrition: Develop a comprehensive feeding strategy for your krill farm. Antarctic krill are filter feeders, so provide a suitable diet rich in phytoplankton and other microorganisms. Consider the nutritional needs of krill at different life stages, adjusting feeding practices accordingly to support optimal growth and reproduction.
5. Monitoring and Surveillance: Implement a robust monitoring system to track the health and behavior of your krill population. Utilize technology and sensors to collect data on factors like population density, molting patterns, and reproductive activity. Regular surveillance is essential for early detection of any issues and prompt intervention.
6. Disease Prevention and Management: Establish biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction and spread of diseases in your krill farm. Quarantine new individuals before introducing them to the main population, and implement sanitation protocols to maintain a disease-free environment. Swift action is crucial in the event of disease outbreaks.
7. Reproduction and Molting: Understand the reproductive cycle of Antarctic krill and create conditions that encourage successful reproduction. Provide suitable substrate for egg attachment and ensure proper temperature and nutrient availability for larval development. Consider molting patterns and support this natural process through appropriate environmental conditions.
8. Harvesting and Processing: Develop efficient harvesting techniques to collect mature krill for processing. Consider sustainable harvesting practices to maintain a balanced ecosystem. Once harvested, process the krill into valuable products such as krill oil and meal. Ensure compliance with regulations and standards for product quality.
9. Environmental Impact Assessment: Regularly assess the environmental impact of your krill farm. Collaborate with environmental experts to minimize any potential negative effects on the surrounding ecosystem. Implement measures to reduce waste, energy consumption, and other ecological footprints associated with aquaculture activities.
10. Research and Innovation: Stay informed about the latest research and innovations in Antarctic krill farming. Collaborate with scientists, researchers, and industry experts to continually improve your farming practices. Embrace sustainable and innovative technologies that enhance the efficiency and environmental sustainability of your krill farm.
In addition, setting up your Antarctic krill fish farm requires a comprehensive and systematic approach. By carefully considering each step, from site selection to ongoing monitoring and innovation, you can establish a successful and sustainable krill farming operation that contributes positively to the aquaculture industry.
Nutrition Essentials: Feeding Your Antarctic krill for Optimal Growth
Feeding your Antarctic krill is a critical aspect of ensuring optimal growth and overall health within your aquaculture system. Understanding the nutritional requirements of Euphausia superba, the Antarctic krill species, is fundamental to developing a feeding strategy that supports their well-being and contributes to the success of your fish farming endeavor.
Antarctic krill are filter feeders, relying on phytoplankton and other microorganisms present in the water for their nutritional needs. Replicating this natural diet in a controlled environment is key to fostering the growth and development of your krill population. Phytoplankton, rich in essential nutrients and fatty acids, serves as a primary food source for krill and is integral to their overall health.
To meet the nutritional demands of your krill, consider incorporating a diverse range of microorganisms into their diet. This can include small zooplankton and other marine particles that contribute to a balanced and nutritionally rich feeding regimen. Understanding the specific nutritional composition of these food sources is crucial in formulating a well-rounded diet for your krill.
Given the importance of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet of many marine species, including Antarctic krill, it’s essential to ensure that your feeding strategy provides an adequate supply of these essential nutrients. Omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in krill growth, reproduction, and overall physiological well-being. Consider supplementing their diet with sources rich in these fatty acids, such as algae or fish oil, to enhance their nutritional profile.
Moreover, recognizing the different life stages of Antarctic krill is crucial when developing a feeding plan. Larval krill, for instance, may have distinct nutritional requirements compared to adults. Adjusting the particle size and nutrient composition of the feed to accommodate these variations in developmental stages is essential for promoting optimal growth and survival rates.
Maintaining water quality is intricately linked to the effectiveness of your feeding program. Regularly monitor parameters such as temperature, pH, and nutrient levels to ensure an environment conducive to nutrient absorption and utilization by the krill. A well-managed water quality system not only enhances the effectiveness of your feeding efforts but also contributes to the overall health and resilience of your krill population.
Consider implementing feeding regimes that mimic the natural feeding behavior of Antarctic krill. Since they exhibit diel vertical migration, moving closer to the surface at night to feed on phytoplankton, adjusting your feeding schedule to align with these natural behaviors can enhance the efficiency of nutrient intake and utilization by your krill.
In addition, feeding your Antarctic krill fish for optimal growth requires a nuanced understanding of their nutritional requirements, natural behaviors, and the environmental conditions within your aquaculture system.
Developing a comprehensive feeding strategy that incorporates diverse and nutrient-rich sources, aligns with their life stages, and considers water quality parameters is essential for fostering a healthy and thriving krill population in your farm.
Read Also: 9 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Wikstroemia indica (Sweet Indrajao)
Disease Prevention and Control in Antarctic krill Farming

Disease prevention and control are paramount considerations in Antarctic krill fish farming, as maintaining a healthy population is essential for the success and sustainability of aquaculture operations. Implementing effective disease management strategies involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing various aspects of farm design, biosecurity measures, and vigilant monitoring to mitigate the risk of diseases that could impact the Antarctic krill population.
Firstly, it is crucial to establish a robust biosecurity framework to prevent the introduction and spread of diseases within the krill farm. This involves implementing strict quarantine measures for new individuals entering the farm, including proper screening and isolation procedures. By minimizing the risk of introducing pathogens or contaminants, biosecurity measures act as a frontline defense against potential disease outbreaks.
Regular health checks and monitoring are integral components of disease prevention in Antarctic krill farming. Observing the behavior, growth rates, and overall condition of the krill population allows for early detection of any abnormalities that may indicate the presence of diseases. Utilizing advanced technologies such as underwater cameras and sensors facilitates continuous surveillance, enabling prompt intervention in case of disease-related issues.
Water quality management plays a significant role in disease prevention and control. Maintaining optimal water conditions, including temperature, salinity, and oxygen levels, supports the overall health and immune function of the krill. Poor water quality can stress the krill population, making them more susceptible to diseases. Regular water testing and treatment interventions, if necessary, are essential components of a proactive disease management strategy.
Implementing a vaccination program, although less common in invertebrates like krill, is an area of ongoing research and development. Identifying specific pathogens and developing preventive measures, such as immunization or selective breeding for disease resistance, could contribute to enhancing the resilience of Antarctic krill populations against potential diseases.
In the event of a disease outbreak, swift and targeted responses are critical. Isolating affected individuals or groups can help contain the spread of the disease within the population. Quarantine protocols may be implemented to prevent the further transmission of the pathogen, and affected krill may be treated with appropriate medications or antimicrobial agents under the guidance of veterinary experts.
Collaboration with researchers, veterinarians, and industry experts is essential for staying informed about emerging diseases and implementing best practices for disease prevention and control. Continuous education and training for farm personnel regarding disease recognition, reporting, and response protocols contribute to a vigilant and well-prepared team capable of addressing potential health challenges.
Furthermore, engaging in responsible farming practices is inherently tied to disease prevention in Antarctic krill fish farming. Sustainable aquaculture practices that prioritize environmental health, water conservation, and ethical treatment of the krill population contribute to overall disease resilience. Minimizing stressors and providing optimal conditions for krill growth and reproduction are foundational principles in preventing diseases from taking hold within the farm.
In addition, disease prevention and control in Antarctic krill fish farming require a comprehensive and proactive approach. From stringent biosecurity measures to vigilant monitoring, water quality management, and collaborative research efforts, a well-rounded strategy is essential for maintaining a healthy and resilient krill population in aquaculture operations.
Antarctic krill Breeding Techniques: Guide to Successful Reproduction
Successfully breeding Antarctic krill in a controlled environment involves a nuanced understanding of their natural reproductive behaviors and the implementation of specific techniques to support optimal reproduction. As Euphausia superba, or Antarctic krill, plays a vital role in the Southern Ocean ecosystem, reproducing them in captivity is not only beneficial for aquaculture but also for research and conservation efforts.
Understanding the reproductive cycle of Antarctic krill is fundamental to implementing successful breeding techniques. In their natural habitat, krill typically undergo reproductive processes in response to environmental cues, such as changes in day length and temperature. To replicate these conditions in captivity, carefully manipulating environmental factors becomes crucial.
Creating conditions conducive to successful reproduction involves controlling water temperature, light cycles, and nutrient availability. Mimicking the seasonal changes in the Southern Ocean can trigger the onset of the krill’s reproductive cycle. This might involve adjusting temperature regimes to simulate seasonal variations and providing specific substrates for egg attachment, allowing the krill to express their natural reproductive behaviors.
Carefully monitoring the reproductive stages of Antarctic krill is essential for successful breeding. Female krill lay eggs, usually in the form of gelatinous egg sacs, in the water column. Recognizing these egg sacs and understanding the timing of egg deposition is critical for managing the breeding process. Once eggs are laid, providing optimal conditions for their development into larvae becomes the next focus.
Supporting the larval stages of Antarctic krill requires attention to nutritional needs and environmental conditions. Larvae are particularly sensitive to changes in water quality and food availability. Developing a suitable larval diet, often consisting of small-sized phytoplankton and other microorganisms, is essential for their growth and development. Additionally, maintaining stable water parameters, including temperature and salinity, is crucial during the vulnerable larval stages.
Molting is a natural process in the life cycle of Antarctic krill, and understanding and supporting this process is integral to successful breeding. Providing appropriate substrates for molting and ensuring that the krill have access to a well-balanced diet that supports the molting process contribute to the overall reproductive success.
As with any breeding program, careful management of population density is crucial. Overcrowding can lead to stress, affecting the reproductive success of Antarctic krill. Monitoring population density, especially during peak reproductive periods, allows for adjustments in housing and feeding strategies to maintain optimal conditions for successful breeding.
In addition to environmental and nutritional considerations, incorporating technological advancements into breeding techniques can enhance the efficiency of reproduction. Continuous monitoring using underwater cameras and sensors enables real-time observation of reproductive behaviors, allowing for timely adjustments in husbandry practices.
Collaboration with researchers and experts in krill biology is instrumental in refining and advancing breeding techniques. Ongoing research contributes to a deeper understanding of the factors influencing reproductive success, leading to continuous improvements in captive breeding programs.
Successfully breeding Antarctic krill in a controlled environment requires a holistic approach that considers the intricate details of their natural reproductive cycle. By mimicking environmental conditions, closely monitoring reproductive stages, providing optimal nutrition, and incorporating technological advancements, aquaculturists can contribute to the conservation and sustainable use of this crucial species in the Southern Ocean ecosystem.
Harvesting and Processing Your Antarctic krill Farm Yield
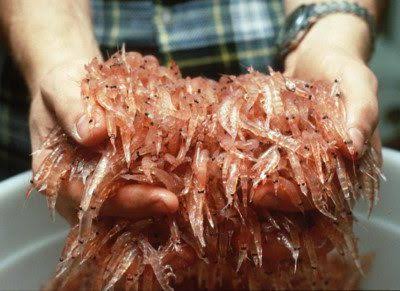
Harvesting and processing the yield from your Antarctic krill farm is a culmination of careful planning, efficient techniques, and a commitment to sustainability. As you approach this critical stage in your aquaculture venture, a comprehensive understanding of the harvesting process and subsequent processing steps is essential to maximize the value of your krill yield.
The timing of the harvest is a crucial consideration in Antarctic krill fish farming. Monitoring the growth and developmental stages of the krill population is key to determining the optimal time for harvest. Harvesting too early may result in smaller-sized krill with lower nutritional content, while delaying the harvest might lead to overpopulation and increased competition for resources within the farm.
Various harvesting techniques can be employed, ranging from simple net-based methods to more advanced technologies. The choice of method depends on factors such as farm design, population density, and the intended use of the krill yield. Gentle harvesting techniques are often preferred to minimize stress on the krill and preserve the quality of the final product.
Once harvested, the processing phase begins, transforming the raw krill yield into valuable products. Immediate processing is crucial to maintain the freshness and nutritional quality of the krill. Technological advancements have introduced methods like flash freezing on-site, preserving the integrity of the krill and preventing degradation of its valuable components.
Processing options for krill yield are diverse and can include the extraction of krill oil, which is rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. Krill oil has gained popularity for its potential health benefits, including cardiovascular support and anti-inflammatory properties. The extraction process involves separating the oil from the krill biomass, often using advanced techniques like cold pressing or solvent extraction.
In addition to krill oil, krill meal is another valuable by-product derived from the processing of the yield. Krill meal is a protein-rich substance that can be utilized as a key ingredient in aquafeed for various farmed fish species. Its nutritional composition, including amino acids and essential fatty acids, makes it a sought-after supplement in aquaculture diets.
Quality control measures during processing are imperative to ensure that the final products meet industry standards. Rigorous testing for purity, nutritional content, and absence of contaminants is essential to produce high-quality krill oil and meal. Compliance with regulatory standards and certification processes adds credibility to the products, facilitating their entry into the market.
Sustainability remains a central theme in the harvesting and processing of krill yield. Responsible practices, such as implementing selective harvesting techniques and adhering to catch limits, contribute to maintaining the delicate balance of the Southern Ocean ecosystem. Continuous research and monitoring of the environmental impact of harvesting operations are essential components of a sustainable krill fish farming enterprise.
Market considerations also play a crucial role in determining the success of your harvesting and processing efforts. Understanding consumer demands, market trends, and potential applications of krill products enables you to position your yield effectively. Establishing partnerships with distributors, retailers, and research institutions further strengthens the market presence of your krill-derived products.
However, the harvesting and processing of your Antarctic krill fish farm yield mark the culmination of a meticulous and sustainable aquaculture journey. From selecting the right time for harvest to employing advanced processing techniques and ensuring product quality, each step contributes to the success of your venture. With a commitment to responsible practices and a focus on market dynamics, your krill farming operation can thrive and make a positive contribution to both the aquaculture industry and the broader ecological landscape.
Market Strategies for Selling Your Antarctic krill Products
Developing effective market strategies for selling your Antarctic krill fish products is a multifaceted endeavor that involves understanding consumer preferences, industry trends, and the unique qualities of your krill-derived offerings. In navigating the market landscape, consider factors such as product positioning, target demographics, sustainability messaging, and strategic partnerships to optimize the market presence and success of your krill fish products.
One crucial aspect of market strategy is identifying and understanding your target audience. Analyze consumer demographics, preferences, and purchasing behaviors to tailor your marketing efforts. Highlight the nutritional benefits of krill oil and meal, emphasizing their omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and protein content. Position your products in a way that resonates with health-conscious consumers and those seeking sustainable and environmentally friendly choices.
Effective branding is essential in differentiating your krill fish products in a competitive market. Develop a brand identity that communicates the unique qualities of your products, emphasizing factors such as purity, quality, and sustainability. Utilize creative and informative packaging that highlights the nutritional benefits and versatile applications of krill-derived products, capturing the attention of potential consumers.
Educational marketing campaigns can play a pivotal role in informing consumers about the health benefits of krill oil and meal. Emphasize the omega-3 fatty acids, astaxanthin, and other bioactive compounds present in your products. Consider collaborating with healthcare professionals, nutritionists, and influencers to amplify your educational messaging and build credibility within the market.
Engaging in sustainability initiatives and transparent sourcing practices can further enhance the market appeal of your krill fish products. Emphasize your commitment to responsible aquaculture, ethical harvesting methods, and environmental stewardship. Certification from reputable sustainability organizations can provide third-party validation of your environmentally conscious practices, appealing to consumers who prioritize eco-friendly choices.
Market diversification is another strategic approach to consider. Explore various distribution channels, including online platforms, retail outlets, and specialty health stores. Establishing partnerships with retailers and distributors can expand the reach of your krill products, making them accessible to a broader audience. Participate in trade shows and industry events to showcase your products and network with potential partners.
Strategic pricing is a critical component of market strategy. Consider market research to determine competitive pricing while ensuring that your products offer perceived value. Highlight the unique selling points of your krill fish products to justify premium pricing, such as superior nutritional content, sustainable sourcing, or innovative processing methods.
Utilize digital marketing channels to create a strong online presence for your krill products. Develop a user-friendly website that provides comprehensive product information, educational resources, and an easy purchasing experience. Leverage social media platforms to engage with your audience, share success stories, and showcase the versatility of krill-derived products in various culinary applications.
Customer feedback and reviews can be powerful tools in shaping your market strategy. Encourage satisfied customers to share their experiences and testimonials. Address any concerns promptly and transparently, demonstrating your commitment to customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
Incorporate flexibility into your market strategy, staying agile to adapt to evolving consumer trends and industry dynamics. Regularly monitor market trends, consumer preferences, and competitor activities. Innovate your product offerings, explore new applications, and embrace emerging technologies to stay ahead in a dynamic and competitive market.
In addition, developing effective market strategies for selling your Antarctic krill fish products involves a comprehensive and dynamic approach. By understanding your target audience, establishing a strong brand identity, emphasizing sustainability, diversifying distribution channels, and staying attuned to market trends, you can position your krill-derived products for success in the evolving landscape of the food and health industry.
Sustainability Practices in Antarctic krill Farming: A Green Approach
Implementing sustainability practices in Antarctic krill fish farming is a fundamental commitment to preserving the delicate balance of the Southern Ocean ecosystem while ensuring the long-term viability of aquaculture operations. A green approach in krill farming involves integrating environmentally conscious strategies across various facets of the farming process, from site selection and farm design to harvesting methods and waste management.
One of the first considerations in a sustainable approach to krill fish farming is the careful selection of farm sites. Choosing locations with minimal environmental impact and suitable conditions for krill growth is crucial. This includes assessing factors such as water quality, temperature, and proximity to marine protected areas. By avoiding ecologically sensitive regions and adhering to site-specific environmental guidelines, farmers can minimize the potential impact of their operations.
Innovative farm design can contribute significantly to sustainability in krill farming. Floating platforms and pens, equipped with efficient water circulation and aeration systems, can optimize environmental conditions for krill growth while minimizing the use of resources. Additionally, incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, into farm infrastructure can reduce the carbon footprint associated with energy consumption.
Sustainable harvesting methods are paramount in minimizing the ecological impact of krill fish farming. Implementing selective harvesting techniques that target mature individuals while avoiding the overexploitation of the population helps maintain a balanced ecosystem. Monitoring population density and adhering to established catch limits are essential practices to prevent overharvesting and ensure the sustainability of the krill population.
The use of technology in monitoring and data collection plays a pivotal role in sustainable krill farming. Underwater cameras, sensors, and automated monitoring systems enable real-time observation of krill behavior, population dynamics, and environmental conditions. This data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making, facilitating adjustments in farming practices to minimize environmental impact and optimize resource utilization.
Waste management is a critical aspect of a green approach in krill fish farming. Responsibly handling and disposing of waste products, such as uneaten feed and by-products, prevents water pollution and supports a healthier ecosystem. Developing efficient waste recycling systems or exploring alternative uses for waste, such as converting it into organic fertilizers, contributes to the circular economy principles of sustainability.
Furthermore, a sustainable krill farming operation should prioritize the reduction of by-catch and unintended environmental consequences. By employing careful harvesting techniques and employing escape devices in fishing gear, farmers can minimize the impact on non-target species and protect the biodiversity of the Southern Ocean.
Collaboration with environmental organizations, research institutions, and regulatory bodies is instrumental in fostering sustainability in krill farming. Participating in research initiatives, sharing data, and staying informed about best practices contribute to the development of industry standards that prioritize ecological health.
Educational outreach is a key component of a green approach in krill fish farming. By raising awareness about the importance of sustainable practices, both within the industry and among consumers, farmers can foster a culture of responsibility and stewardship. Transparent communication about farming practices, environmental impact assessments, and ongoing sustainability efforts enhances public trust and engagement.
However, adopting a green approach in Antarctic krill fish farming is a holistic commitment to environmental stewardship. From site selection and farm design to harvesting methods, waste management, and community engagement, sustainable practices safeguard the Southern Ocean ecosystem while ensuring the viability of krill farming for generations to come.
Common Issues and their Solutions in Antarctic krill Farming
In Antarctic krill fish farming, various challenges may arise, requiring careful consideration and proactive solutions to ensure the success and sustainability of aquaculture operations. Addressing these common issues is essential for maintaining the health of the krill population and optimizing farming practices.
1. Environmental Variability:
Issue: The dynamic and harsh conditions of the Southern Ocean can pose challenges in maintaining stable environmental parameters for krill farming.
Solution: Implement advanced monitoring systems to continuously assess water quality, temperature, and other environmental factors. Develop adaptive farm designs that can withstand variability and fluctuations in the natural environment.
2. Disease Outbreaks:
Issue: Diseases can impact krill populations in confined farming environments, leading to increased mortality and decreased overall productivity.
Solution: Establish stringent biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction of diseases. Regularly monitor the health of the krill population, and implement timely interventions in case of disease outbreaks. Collaborate with veterinary experts to develop disease prevention and management strategies.
3. Overpopulation and Density-related Stress:
Issue: Overcrowding in farm environments can lead to stress among krill, affecting growth rates, reproduction, and overall well-being.
Solution: Monitor population density closely and adjust farming practices to maintain optimal conditions. Implement responsible harvesting techniques to prevent overpopulation. Consider farm expansion or reconfiguration based on population dynamics.
4. Nutritional Imbalances:
Issue: Inadequate nutrition can lead to health issues and slower growth in krill populations.
Solution: Develop a well-balanced and species-appropriate diet, considering the nutritional needs at different life stages. Incorporate a diverse range of microorganisms and phytoplankton into the feed. Regularly assess and adjust the nutritional content of the diet based on population requirements.
5. Reproductive Challenges:
Issue: Reproductive success may be impacted by environmental factors or inadequate conditions for egg attachment and larval development.
Solution: Create optimal conditions for reproduction by manipulating environmental cues. Provide suitable substrates for egg attachment and support larval development through proper nutrition and environmental management.
6. Environmental Impact Assessment:
Issue: The potential environmental impact of krill farming on the surrounding ecosystem is a growing concern.
Solution: Conduct regular environmental impact assessments in collaboration with environmental experts. Implement sustainable farming practices, such as responsible harvesting, waste management, and habitat protection, to minimize the ecological footprint.
7. Technological Challenges:
Issue: Dependence on technology for monitoring and data collection can pose challenges, including technical failures or data interpretation issues.
Solution: Invest in robust and redundant technological systems. Provide training for farm personnel to handle and troubleshoot technological equipment. Collaborate with technology experts to stay updated on the latest advancements.
8. Market Demand and Product Positioning:
Issue: Fluctuations in market demand and ineffective product positioning can impact the success of krill-derived products.
Solution: Conduct market research to understand consumer preferences and industry trends. Develop effective marketing strategies that highlight the unique selling points of krill-derived products, such as nutritional benefits and sustainability. Establish partnerships with retailers and distributors to enhance market reach.
In summary, addressing common issues in Antarctic krill fish farming involves a comprehensive and proactive approach. By incorporating advanced monitoring systems, implementing sustainable practices, and adapting farming strategies to environmental conditions, farmers can navigate challenges effectively and contribute to the success of this unique aquaculture industry

