Strawberry receptacle, also known as the strawberry’s “core,” is the central part of the strawberry where the stem attaches to the fruit. It is often referred to as the “stem end” of the strawberry. The receptacle is the area from which the strawberry’s seeds protrude and is surrounded by the fleshy part of the fruit that is typically consumed.
In technical terms, the strawberry receptacle is a specialized part of the flower’s anatomy. It holds the ovaries of the flower, which develop into the tiny seeds that cover the outer surface of the strawberry. These seeds are the small, edible specks that give the strawberry its characteristic texture.
When consuming a strawberry, the receptacle and its attached seeds are usually eaten along with the surrounding flesh, contributing to the berry’s flavor and overall eating experience. The receptacle is typically tender and not as firm as the rest of the fruit, making it easy to bite into and enjoy.
Strawberries are popular fruits that can be eaten fresh, used in various culinary creations such as desserts, jams, sauces, and more. The receptacle plays a role in the overall appearance and taste of the strawberry, and its texture can vary slightly between different strawberry varieties.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Strawberry Receptacle
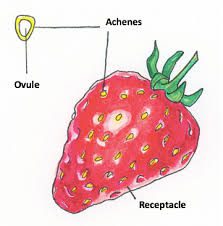
The strawberry receptacle, also known as the “fruit base” or “stem end,” is the area of the strawberry fruit where the stem attaches. While it might not be the most commonly discussed part of the strawberry, it does have some economic importance and uses:
1. Culinary and Food Industry: The receptacle is typically removed when preparing strawberries for consumption, as it can be tough and less palatable compared to the fleshy fruit. It is essential to remove the receptacle to enhance the eating experience and make the strawberries more versatile for various culinary applications. The culinary industry benefits from the fact that removing the receptacle improves the taste and texture of strawberry-based dishes, such as desserts, jams, jellies, sauces, and beverages.
2. Food Processing and Packaging: In the food processing sector, strawberries are often processed to create products like frozen strawberries, strawberry puree, and dried strawberries. The receptacle is generally removed during these processes to maintain product quality, consistency, and appearance. Additionally, the removal of the receptacle can help enhance the shelf life of processed strawberry products by reducing potential moisture and nutrient loss.
3. Marketing and Aesthetics: The appearance of strawberries is a significant factor in consumer purchasing decisions. Removing the receptacle enhances the visual appeal of strawberries, making them look more attractive and uniform. This can lead to better marketability and higher demand for strawberries in supermarkets, grocery stores, and farmers’ markets.
4. Preservation and Quality: The receptacle can be a source of moisture and vulnerability to microbial growth. Removing it reduces the chances of spoilage, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of strawberries during transportation, storage, and distribution. Better preservation ultimately extends the marketable lifespan of the fruit.
5. Value-Added Products: The receptacle is typically not used as a primary ingredient in most food products due to its texture and taste. However, innovative food companies might explore ways to utilize the receptacle in value-added products, such as creating extracts, flavorings, or functional ingredients from its components.
Read Also: Strawberry Leaves: Economic Importance, Uses and By-Products
6. Waste Reduction and Processing: While the receptacle is often discarded, some agricultural and food processing operations might explore ways to repurpose or process it into animal feed, compost, or biofuels. This could contribute to waste reduction and sustainable practices within the industry.
7. Research and Development: Research into the composition and properties of the strawberry receptacle can lead to the discovery of potential bioactive compounds, flavors, or aromas that could have commercial applications in the food, cosmetic, or pharmaceutical industries. This can open up opportunities for new product development and market expansion.
8. Biotechnological Applications: The receptacle, like other plant tissues, contains cellular materials that could potentially be used in biotechnological processes. For instance, enzymes or compounds derived from the receptacle could have applications in enzymatic reactions, biofuel production, or other industrial processes.
9. Organic Farming and Sustainability: In organic farming practices, utilizing various parts of the strawberry plant, including the receptacle, for compost or natural fertilizers can contribute to sustainability by reducing waste and promoting soil health. Incorporating plant residues back into the soil as organic matter can enhance soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability.
10. Cultural and Traditional Uses: In some cultures, certain parts of plants, including the receptacle, may have traditional or folk uses. While not as common, there might be cultural practices that involve using the strawberry receptacle for specific purposes, such as in herbal remedies or natural dyes.
11. Educational and Outreach Activities: The study of plant anatomy and fruit structure often includes the examination of various plant parts, including the receptacle. Educational institutions, botanical gardens, and science centers might use strawberries as a tool for teaching about plant biology and the anatomy of fruits.
12. Genetic Studies and Crop Improvement: Understanding the genetics and characteristics of the receptacle can have implications for crop breeding and improvement. Researchers can study the receptacle to identify traits related to taste, texture, and nutritional content, which can guide breeding efforts to develop strawberries with enhanced qualities.
13. Cultural and Culinary Heritage: In some regions, the culinary heritage might include recipes or traditional dishes that use strawberries with the receptacle intact. While this is less common, such practices can provide insights into local food culture and history.
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Strawberry Receptacle
The strawberry receptacle, also known as the “stem end” or “core” of the strawberry, is the small, conical section at the top of the fruit where the stem attaches. While it’s not commonly thought of as a primary source of valuable products, there are a few things that can be derived from strawberry receptacles:
1. Food Additives: The strawberry receptacle contains some amount of dietary fiber, natural sugars, and phytochemicals. Extracts from the receptacle could potentially be used as natural flavor enhancers or sweeteners in various food products.
2. Phytochemical Extracts: Phytochemicals are bioactive compounds found in plants that have potential health benefits. The receptacle may contain certain phytochemicals like anthocyanins, flavonoids, and antioxidants, which have been associated with various health-promoting effects.
3. Cosmetic Ingredients: Phytochemical extracts from the receptacle might be used in cosmetic products due to their potential antioxidant and skin-soothing properties. These extracts could be incorporated into skincare formulations like creams, lotions, and serums.
4. Natural Dyes: The pigments present in strawberry receptacles, particularly the anthocyanins responsible for the red color of the fruit, could potentially be used as natural dyes for textiles, food products, or cosmetics.
5. Biodegradable Packaging Material: Researchers are investigating the potential use of plant-based materials for creating biodegradable and eco-friendly packaging. Components from the receptacle, being plant-based, might find use in this context.
6. Animal Feed: While not a direct human product, the receptacle could be used as a supplementary feed source for certain livestock animals due to its fiber content and potential nutritional value.
7. Compost and Organic Fertilizer: The receptacle, along with other fruit and vegetable scraps, can be composted to create nutrient-rich organic fertilizer for gardening and agriculture.
8. Nutritional Supplements: If the receptacle contains significant amounts of vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients, it could potentially be processed into dietary supplements. These supplements might be marketed for their potential health benefits, such as supporting immune function or providing antioxidants.
9. Bioactive Compounds for Pharmaceutical Use: If the phytochemicals present in the receptacle exhibit specific bioactive properties, they could be investigated for potential use in pharmaceutical products. This could include research into their anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, or other medicinal properties.
10. Flavorings and Aromas: If the receptacle contains aromatic compounds, they could be extracted and used as natural flavorings or aromas in the food and beverage industry. These could enhance the taste and aroma of various products.
11. Plant Extracts for Agricultural Use: Extracts from the receptacle might have pesticidal or growth-promoting properties when used in agriculture. This could involve developing organic or natural alternatives to conventional chemical pesticides and fertilizers.
12. Essential Oils: If the receptacle contains volatile compounds, it might be a source of essential oils. Essential oils have various applications, including aromatherapy, perfumery, and even potential therapeutic uses.
13. Biofuel Production: In a more experimental context, some plant materials can be used as feedstocks for biofuel production. If the receptacle contains suitable carbohydrates or cellulose, it might be considered for bioenergy applications.
14. Research and Biotechnology: The study of the phytochemical composition of strawberry receptacles could lead to insights into plant biology, genetics, and metabolism. This research might have broader implications for biotechnology and crop improvement.
15. Culinary Uses: While less common, some culinary experimentation might involve using strawberry receptacles as a unique ingredient in dishes, beverages, or preserves.
In conclusion, while the economic importance of the strawberry receptacle might not be as pronounced as other parts of the fruit, it still has a range of potential uses and implications across various industries, from agriculture and food processing to research and sustainability initiatives. Its role in enhancing the overall value of strawberries and contributing to different aspects of the economy and society should not be overlooked.
Read Also: How to Start a Banana Farm
