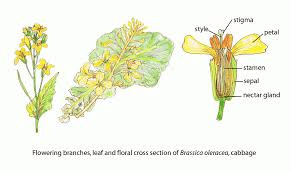
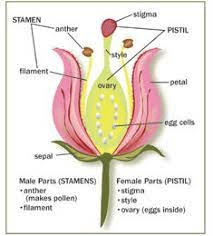
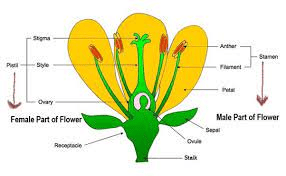
The cabbage stigma is a critical part of the reproductive anatomy of cabbage plants (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). As part of the female reproductive organs, the stigma plays a pivotal role in the process of pollination and fertilization, ultimately leading to the production of seeds and the continuation of the cabbage species.
Located at the top of the pistil, the stigma is the receptive surface where pollen grains land and germinate during pollination. In cabbage plants, the stigma is typically positioned at the tip of the pistil, which is part of the flower’s central structure. The stigma is often characterized by its sticky or moist surface, which helps to capture and retain pollen grains that come into contact with it.
The primary function of the cabbage stigma is to facilitate the pollination process by providing a suitable landing site for pollen grains. When pollen is transferred from the male reproductive organs (anthers) to the stigma, it adheres to the surface of the stigma. This triggers a series of biochemical reactions that initiate the germination of the pollen grains, leading to the growth of pollen tubes.
These pollen tubes grow down through the style, the elongated structure that connects the stigma to the ovary, where the ovules are located. The pollen tubes deliver the male gametes (sperm cells) to the ovules, allowing fertilization to occur. Once fertilized, the ovules develop into seeds, which are contained within the ovary of the flower.
The cabbage stigma, like those of many other flowering plants, may exhibit variations in color, size, and texture. These variations may influence the attraction of pollinators and the efficiency of pollination. For example, some cabbage cultivars may have stigmas with bright colors or strong scents to attract insects such as bees and butterflies, which aid in pollen transfer.
Understanding the structure and function of the cabbage stigma is essential for plant breeders and agricultural scientists involved in cabbage cultivation and breeding programs. By studying the characteristics of the stigma, researchers can gain insights into the reproductive biology of cabbage plants and develop strategies to enhance pollination, seed production, and overall crop yield.
In summary, the cabbage stigma is a specialized structure that plays a crucial role in the reproduction of cabbage plants. Through its function as a pollen receptor and initiator of pollen tube growth, the stigma facilitates the successful fertilization and development of cabbage seeds, ultimately contributing to the production of healthy and viable offspring in the cabbage population.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Cabbage Stigma
1. Plant Reproduction: The cabbage stigma plays a crucial role in the reproduction of cabbage plants by receiving pollen grains during pollination. This process is essential for seed production and the continuation of cabbage cultivation.
2. Agricultural Sustainability: Cabbage stigma contributes to agricultural sustainability by facilitating natural pollination and seed production in cabbage crops. Healthy stigmas ensure the production of viable seeds for future planting, reducing reliance on external seed sources.
3. Crop Diversity: Cabbage stigma supports crop diversity by promoting genetic variation through cross-pollination and hybridization. This leads to the development of new cabbage varieties with improved traits such as disease resistance, yield, and nutritional content.
4. Seed Production Industry: The quality and viability of cabbage stigma directly impact the seed production industry. Pollinated stigmas develop into seed pods containing cabbage seeds, which are harvested, processed, and sold to farmers and growers worldwide.
5. Horticultural Research: Cabbage stigma provides valuable research material for horticultural studies focused on cabbage plant reproduction, pollination biology, and seed development. Researchers investigate stigma morphology, physiology, and pollen-stigma interactions to enhance cabbage breeding programs.
6. Culinary Traditions: While not a direct culinary ingredient, cabbage stigma indirectly contributes to culinary traditions through seed production. Cabbage seeds harvested from pollinated stigmas are used to grow cabbage plants, which yield fresh cabbage heads for culinary use in various dishes.
7. Medicinal Uses: In herbal medicine, cabbage stigma may be used in traditional remedies or preparations for its potential health benefits. While not as commonly utilized as other parts of the cabbage plant, stigma extracts may contain bioactive compounds with medicinal properties.
8. Livestock Forage: While not a primary source of forage, cabbage stigma may be consumed by grazing animals along with other parts of the cabbage plant. In agricultural settings, cabbage residues left in fields after harvest can serve as fodder for livestock.
9. Soil Improvement: Cabbage stigma, along with other plant residues, contributes organic matter to the soil upon decomposition. This organic matter improves soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity, enhancing overall soil health and productivity.
10. Culinary Exploration: While not typically consumed directly, cabbage stigma may inspire culinary exploration through its role in seed production. Growers and culinary enthusiasts can experiment with different cabbage varieties grown from seeds produced by pollinated stigmas, leading to culinary diversity and innovation.
11. Seed Saving Tradition: Cabbage stigma is integral to seed saving traditions practiced by farmers, gardeners, and seed enthusiasts. By allowing cabbage plants to naturally pollinate and develop seeds, individuals preserve heirloom cabbage varieties and maintain seed sovereignty.
12. Agroforestry Systems: In agroforestry systems, cabbage stigma contributes to soil fertility and ecosystem health when cabbage plants are integrated into diverse cropping systems. Agroforestry practices enhance ecological resilience and sustainable food production.
13. Botanical Education: Cabbage stigma serves as educational material in botanical studies and plant science courses focused on plant reproduction and sexual development. Students learn about stigma morphology, function, and reproductive strategies in cabbage plants.
14. Seed Exchange Networks: Cabbage stigma fosters seed exchange networks among farmers, gardeners, and seed savers interested in preserving cabbage diversity. Through seed swaps and sharing, individuals access a wide range of cabbage varieties adapted to different climates and growing conditions.
15. Culinary Preservation: While not directly involved in culinary preservation, cabbage stigma indirectly contributes to food preservation by ensuring the availability of cabbage seeds for future planting. Preserving diverse cabbage varieties helps maintain culinary traditions and culinary heritage.
16. Home Gardening: Cabbage stigma is relevant to home gardeners interested in growing cabbage plants from seeds. By understanding cabbage plant reproduction and pollination, gardeners can maximize seed production and harvest quality cabbage seeds for planting in home gardens.
17. Culinary Tradition: Although not a direct culinary component, cabbage stigma indirectly supports culinary traditions by enabling seed production for cabbage cultivation. Cabbage seeds harvested from pollinated stigmas are used to grow cabbage plants for culinary use in various cuisines.
Read Also: Flowers for Honey Bees
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Cabbage Stigma
1. Cabbage Seeds: The primary product derived from cabbage stigma is cabbage seeds, which develop after successful pollination. These seeds serve as the starting point for growing new cabbage plants in agricultural, horticultural, and home garden settings.
2. Seed Pods: Cabbage stigma pollinated by pollen grains develops into seed pods containing cabbage seeds. These seed pods are harvested, processed, and sold by seed companies for use in seed production and agriculture.
3. Culinary Ingredients: While not a direct culinary ingredient, cabbage stigma indirectly contributes to culinary ingredients through seed production. Cabbage seeds harvested from pollinated stigmas are used to grow cabbage plants, yielding fresh cabbage heads for culinary use.
4. Herbal Remedies: In herbal medicine, cabbage stigma may be used in traditional remedies or preparations for its potential health benefits. Stigma extracts may contain bioactive compounds with medicinal properties, although research on their efficacy is limited.
5. Livestock Forage: Cabbage stigma, along with other parts of the cabbage plant, may be consumed by grazing animals as supplemental forage. Residues left in fields after harvest provide fodder for livestock in agricultural settings.
6. Soil Amendment: Upon decomposition, cabbage stigma contributes organic matter to the soil, improving soil fertility and structure. Organic matter enhances soil health, moisture retention, and nutrient availability, supporting plant growth in agricultural and horticultural systems.
7. Compost Material: Cabbage stigma, along with other plant residues, can be composted to create nutrient-rich compost for gardens and landscapes. Composted stigma contributes organic matter, beneficial microorganisms, and essential nutrients to the soil, promoting soil health and fertility.
8. Biodegradable Packaging: While not directly derived from cabbage stigma, biodegradable packaging materials may be produced from plant-based sources, including cabbage residues. These eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics offer sustainable packaging solutions for various industries.
9. Botanical Education Materials: Cabbage stigma serves as educational material in botanical studies and plant science courses focused on plant reproduction and sexual development. Students learn about stigma morphology, function, and reproductive strategies in cabbage plants.
10. Seed Saving Tradition: Cabbage stigma is integral to seed saving traditions practiced by farmers, gardeners, and seed enthusiasts. By allowing cabbage plants to naturally pollinate and develop seeds, individuals preserve heirloom cabbage varieties and maintain seed sovereignty.
Read Also: Black Honey Bees: A Closer Look
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cabbage Stigma
1. What is cabbage stigma?
Cabbage stigma is the receptive tip of the female reproductive organ (pistil) in cabbage plants. It plays a crucial role in plant reproduction by receiving pollen grains during pollination.
2. How does cabbage stigma contribute to seed production?
Cabbage stigma facilitates natural pollination by receiving pollen grains from male reproductive organs (stamens) of other cabbage plants or pollinators. Pollinated stigmas develop into seed pods containing cabbage seeds.
3. Are cabbage seeds harvested directly from stigma?
No, cabbage seeds are not harvested directly from stigma. After successful pollination, cabbage stigma develops into seed pods containing seeds. These seed pods are harvested, processed, and sold for seed production.
4. Can cabbage stigma be used in cooking or culinary applications?
No, cabbage stigma is not typically used in cooking or culinary applications. Its primary function is in plant reproduction and seed production rather than culinary use.
5. How does cabbage stigma contribute to agricultural sustainability?
Cabbage stigma promotes agricultural sustainability by facilitating natural pollination and seed production in cabbage crops. Healthy stigmas ensure the availability of viable seeds for future planting, reducing dependence on external seed sources.
6. What is the role of pollinators in cabbage stigma function?
Pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other insects play a crucial role in cabbage stigma function by transferring pollen grains from stamens to stigma during pollination. This process is essential for seed production and crop yield.
7. Can cabbage stigma be preserved or stored for future use?
Cabbage stigma itself is not typically preserved or stored for future use. Its primary function is in plant reproduction, and once pollination occurs, stigma senescence and seed development follow.
8. Are there any health benefits associated with cabbage stigma?
While cabbage stigma is not commonly consumed for its health benefits, cabbage seeds produced from pollinated stigma are used to grow cabbage plants rich in nutrients and phytochemicals beneficial for human health.
9. How does cabbage stigma contribute to biodiversity?
Cabbage stigma promotes biodiversity by supporting natural pollination and genetic variation in cabbage crops. Cross-pollination between different cabbage plants leads to the development of diverse cabbage varieties with unique traits.
10. Can cabbage stigma be used in research or educational settings?
Yes, cabbage stigma is used in research and educational settings to study plant reproduction, pollination biology, and seed development. It serves as valuable material for botanical studies and plant science courses focused on reproductive processes in plants.
Read Also: The Impact of Waste to Compost Business
