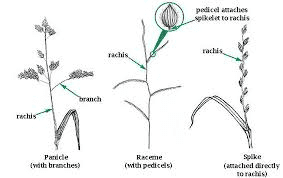
The millet rachis is a central axis in the millet plant’s inflorescence that plays a pivotal role in the structure and function of the millet panicle. It acts as the main support for the arrangement of spikelets, which are critical for the plant’s reproductive process.
In millet plants, the rachis is the elongated stem or axis of the panicle from which the spikelets emerge. It serves as the primary support for these spikelets and facilitates their distribution along the panicle. The rachis is crucial for organizing the spikelets in a manner that optimizes their exposure to pollinators and sunlight, thus enhancing the efficiency of pollination and seed development.
The rachis typically extends from the main stem of the plant and branches out to form a panicle. In different millet species, the rachis can vary in length, thickness, and texture. For instance, in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum), the rachis is usually stout and supports a cylindrical or elongated panicle with densely packed spikelets. This robust rachis helps in holding the spikelets securely and aids in the plant’s ability to withstand environmental conditions such as wind and rain.
In contrast, finger millet (Eleusine coracana) features a more compact and branching rachis. The branches of the rachis are closely spaced, supporting a dense cluster of spikelets. This arrangement helps in optimizing space and improving the plant’s resilience against adverse conditions.
The rachis is also involved in nutrient and water transport to the spikelets. As the central axis of the panicle, it facilitates the movement of essential resources from the plant’s main stem to the developing spikelets, ensuring that they receive adequate nourishment for seed development.
The development and characteristics of the rachis are influenced by various factors including genetic traits, environmental conditions, and cultivation practices. Breeding programs often focus on the rachis to improve traits such as panicle size, spikelet arrangement, and overall yield. For instance, breeders may select for a sturdier rachis to enhance the plant’s ability to support a larger number of spikelets or to better withstand environmental stresses.
The millet rachis is a vital structural component of the millet panicle. It serves as the main axis from which spikelets branch out, playing a crucial role in supporting the arrangement of spikelets and facilitating their exposure to pollinators and sunlight. Its characteristics and development are essential for the reproductive success and yield of millet crops, making it a key focus in agricultural research and breeding programs.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Millet Rachis
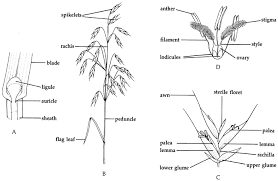
1. Structural Support: The rachis is the central stem of the millet panicle, providing structural support for the branches and spikelets where seeds develop.
2. Grain Production: The rachis plays a critical role in the distribution of nutrients to the developing seeds, affecting overall grain production and quality.
3. Seed Collection: After harvesting, the rachis helps in the easy separation and collection of millet grains from the panicle.
4. Livestock Feed: Rachis, once separated from the grains, can be used as roughage in livestock feed, providing fiber and some nutrients.
5. Mulching Material: The rachis can be used as mulch to help retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
6. Compost Ingredient: Millet rachis can be added to compost piles, where it decomposes and contributes to nutrient-rich compost for gardening and farming.
7. Biofuel Production: The rachis can be processed into biofuel, such as ethanol, contributing to renewable energy sources.
8. Erosion Control: Used in erosion control practices, millet rachis helps stabilize soil and prevent erosion by forming a protective layer on the soil surface.
9. Craft Materials: The rachis can be used in crafting, including making natural decorations, woven items, or other ornamental products.
10. Soil Amendment: Decomposed millet rachis adds organic matter and improves soil health, enhancing soil fertility and structure.
11. Animal Bedding: Dried millet rachis can be used as bedding material for livestock, providing a comfortable and absorbent surface.
12. Carbon Sequestration: Millet rachis contributes to carbon sequestration when used as biomass or incorporated into soil, helping mitigate climate change.
13. Biomass Energy: Millet rachis can be used as biomass for energy production, providing a renewable source of heat and electricity.
14. Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, millet rachis is used in traditional medicine for its purported health benefits.
15. Green Manure: The rachis can be used as green manure, adding organic matter and nutrients to the soil when decomposed.
16. Packaging Material: Millet rachis can be used as biodegradable packaging material, offering an eco-friendly alternative to plastic.
17. Soil Fertility Improvement: The decomposition of millet rachis adds valuable nutrients to the soil, enhancing its fertility and promoting healthy plant growth.
18. Educational Uses: Millet rachis can be used in educational settings to teach about plant anatomy, seed formation, and agricultural practices.
Read Also: Everything You Need To Know About Herbs for High Blood Pressure
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Millet Rachis
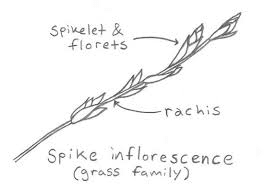
1. Livestock Feed: After separating the grain, millet rachis can be used as roughage in animal feed, providing fiber and nutrients.
2. Mulch: The rachis can be chopped and used as mulch to retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
3. Compost: Millet rachis is added to compost piles, where it decomposes and contributes to nutrient-rich compost for agricultural use.
4. Biofuel: The rachis can be processed into biofuel, such as ethanol, contributing to renewable energy sources.
5. Craft Materials: Rachis can be used in crafting for making natural decorations, woven items, and other ornamental products.
6. Soil Amendment: Decomposed rachis improves soil health by adding organic matter and enhancing soil structure and fertility.
7. Animal Bedding: Dried rachis is used as bedding material for livestock, providing a comfortable and absorbent surface.
8. Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, millet rachis is used in traditional medicine for its potential health benefits.
9. Erosion Control: The rachis helps stabilize soil in erosion control practices by forming a protective layer.
10. Carbon Sequestration: Millet rachis contributes to carbon sequestration when used as biomass or incorporated into soil.
11. Biomass Energy: The rachis is used as biomass for energy production, providing a renewable source of heat and electricity.
12. Green Manure: Rachis can be used as green manure to enrich the soil with organic matter and nutrients.
13. Packaging Material: Millet rachis can be used as biodegradable packaging material, offering an eco-friendly alternative to plastic.
14. Soil Fertility: The decomposition of rachis adds valuable nutrients to the soil, enhancing its fertility.
15. Educational Purposes: The rachis can be used in educational settings to demonstrate plant anatomy and agricultural practices.
16. Feed Supplement: Rachis can be included in feed mixes to provide additional fiber and nutrients to livestock diets.
17. Biochar Production: Millet rachis can be converted into biochar, which is used to improve soil health and retain soil moisture.
Read Also: Gray Leaf Spot (Stemphylium spp) – Symptoms and Damage Control
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Millet Rachis
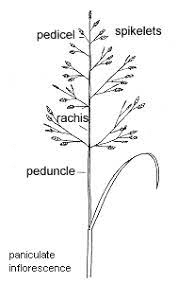
1. What is a millet rachis?
The millet rachis is the central stem of the millet panicle that provides structural support for the branches and spikelets where seeds develop.
2. How does the rachis affect grain production?
The rachis distributes nutrients to the developing seeds, influencing the overall grain production and quality.
3. Can millet rachis be used in animal feed?
Yes, after separating the grain, the rachis can be used as roughage in livestock feed, providing fiber and nutrients.
4. How is rachis used in mulching?
The rachis can be chopped and used as mulch to retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
5. Are millet rachis suitable for composting?
Yes, millet rachis can be added to compost piles, where it decomposes and contributes to nutrient-rich compost.
6. Can rachis be used for biofuel production?
Yes, millet rachis can be processed into biofuel, such as ethanol, contributing to renewable energy sources.
7. What role does millet rachis play in erosion control?
The rachis helps stabilize soil in erosion control practices by forming a protective layer on the soil surface.
8. Can millet rachis be used in crafting?
Yes, rachis can be used in crafting for natural decorations, woven items, and other ornamental products.
9. How does millet rachis benefit soil health?
Decomposed rachis adds organic matter to the soil, improving soil fertility and structure.
10. Are millet rachis used in traditional medicine?
In some cultures, millet rachis is used in traditional medicine for its potential health benefits.
Read Also: Principles of Planning in Feasibility Studies and Business Plan