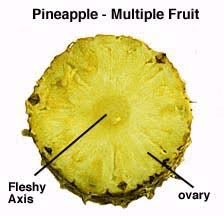
The pineapple ovary is a crucial component in the plant’s reproductive system, playing a significant role in the development of the fruit. Understanding the structure and function of the pineapple ovary provides insight into the intricate processes involved in fruit formation.
The pineapple plant belongs to the Bromeliaceae family and thrives in tropical and subtropical regions. It is characterized by a rosette of long, stiff, spiny leaves, from which a central flowering stalk, or peduncle, emerges. This peduncle supports the inflorescence, a dense cluster of individual flowers arranged in a spiral pattern. Each flower within the inflorescence is small, tubular, and varies in color from pale lavender to deep purple.
The ovary of a pineapple flower is part of the pistil, the female reproductive organ of the plant. The pistil consists of three main parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the top part that receives pollen, the style is the slender stalk that connects the stigma to the ovary, and the ovary is the swollen base that contains the ovules.
In the case of the pineapple, the ovary is inferior, meaning it is located below the attachment point of the other flower parts. This positioning is significant because it influences how the fruit develops. Inside the ovary are ovules, which, if fertilized, can develop into seeds. However, in commercial pineapple cultivation, natural pollination is typically discouraged to prevent seed formation, as seeds are considered undesirable in the fruit.
After the flowering process, the individual flowers begin to fuse together in a process called coalescence. This fusion involves the ovaries of each flower merging to form the central core of the pineapple fruit. Each hexagonal segment, or “eye,” on the surface of the pineapple represents an individual flower’s ovary that has fused with others.
As the ovary and other floral parts develop and mature, they contribute to the formation of the pineapple’s flesh. The tissue surrounding the ovary expands and becomes juicy and sweet, giving the pineapple its distinctive taste and texture. The development of the fruit from the ovary stage to maturity takes several months, during which the fruit changes in size, color, and composition.
Initially, the developing pineapple fruit is green and firm. As it matures, it undergoes significant changes, turning golden-yellow and becoming softer and juicier. The sugar content increases, making the fruit sweeter. Pineapples are typically harvested when they reach full ripeness, as they do not continue to ripen significantly after being picked.
The ovary of a pineapple flower is an essential structure in the plant’s reproductive system, playing a pivotal role in the development of the fruit. Located at the base of the pistil, the ovary contains ovules that, in commercial cultivation, are prevented from developing into seeds.
The fusion of the ovaries from individual flowers leads to the formation of the pineapple fruit, a process that results in the characteristic appearance and flavor of this beloved tropical fruit. Understanding the function and development of the pineapple ovary provides valuable insights into the complex processes of plant reproduction and fruit formation.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Pineapple Ovary
1. Fruit Development: The pineapple ovary is essential for the development of the pineapple fruit, which is a significant economic product in the agricultural industry.
2. Horticultural Research: Pineapple ovary studies help in improving fruit quality, yield, and resistance to pests and diseases through genetic research.
3. Nutrient Source: The pineapple fruit, developed from the ovary, is a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, contributing to human nutrition.
4. Export Commodity: Pineapple fruits, derived from the ovary, are a major export commodity for tropical countries, boosting their economies.
5. Fresh Consumption: Pineapple fruits are consumed fresh, providing a healthy and delicious food option.
6. Processed Foods: Pineapples are processed into products like canned pineapple, pineapple juice, and dried pineapple, expanding their market value.
7. Culinary Uses: Pineapple fruits are used in a variety of culinary dishes, including desserts, salads, and beverages, enhancing the culinary arts.
8. Beverage Industry: Pineapple juice and other beverages made from the fruit are popular, creating a significant market.
9. Confectionery: Pineapples are used in making candies, jellies, and other sweets, adding variety to the confectionery industry.
10. Nutritional Supplements: Extracts from pineapple fruits are used in dietary supplements for their health benefits, such as aiding digestion and reducing inflammation.
11. Traditional Medicine: Pineapples are used in traditional medicine for their anti-inflammatory and digestive properties.
12. Cosmetics: Pineapple extracts are used in skincare products for their hydrating and anti-aging properties.
13. Animal Feed: The by-products of pineapple processing, including parts of the ovary, are used as animal feed.
14. Enzyme Production: The pineapple ovary contains bromelain, an enzyme used in various industrial and medical applications.
15. Natural Sweetener: Pineapple extracts are used as natural sweeteners in food and beverages.
16. Biodegradable Packaging: Fibrous material from the pineapple plant, including the ovary, can be used to create eco-friendly packaging.
17. Biofuel: Organic matter from pineapple plants, including the ovary, can be processed into biofuel.
18. Cultural Significance: Pineapples, including their ovaries, hold cultural significance in various tropical regions and are used in festivals and rituals.
Read Also: Recommended Number of Ruminant Animals per Housing Unit for Fattening
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Pineapple Ovary
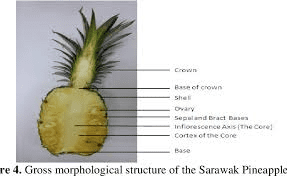
1. Pineapple Fruit: The primary product developed from the ovary, consumed fresh or processed.
2. Pineapple Juice: Extracted from the fruit for use as a beverage or in culinary dishes.
3. Canned Pineapple: Processed pineapple fruit used in various culinary applications.
4. Dried Pineapple: The fruit is dried and used as a snack or ingredient in recipes.
5. Pineapple Jams and Preserves: Made from the fruit and used as spreads and in baking.
6. Pineapple Vinegar: Produced through fermentation of pineapple juice.
7. Pineapple Wine: An alcoholic beverage made from fermented pineapple juice.
8. Pineapple Extract: Used in food flavoring, nutritional supplements, and cosmetics.
9. Bromelain Enzyme: Extracted from the ovary for use in meat tenderizers and medical applications.
10. Pineapple Essential Oil: Used in aromatherapy and cosmetics for its fragrance.
11. Animal Feed: By-products from pineapple processing used as feed for livestock.
12. Pineapple Candy: Made from the fruit and used in confectionery.
13. Pineapple Tea: Made from dried pineapple fruit or extracts.
14. Pineapple Skincare Products: Extracts used in cosmetics for their hydrating properties.
15. Pineapple Natural Dye: Used in textiles for coloring fabrics.
16. Biodegradable Packaging: Made from the fibrous material of the pineapple plant.
17. Pineapple Beverages: Non-alcoholic drinks such as smoothies and flavored water.
Read Also: Gray Leaf Spot (Stemphylium spp) – Symptoms and Damage Control
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Pineapple Ovary
1. What is the pineapple ovary? The pineapple ovary is the part of the plant that develops into the fruit.
2. How is the pineapple ovary important for fruit development? It contains the reproductive organs that, when fertilized, grow into the pineapple fruit.
3. What are the main products derived from the pineapple ovary? Products include fresh fruit, juice, canned pineapple, and dried pineapple.
4. Can pineapple ovary be used in traditional medicine? Yes, the fruit derived from the ovary is used for its anti-inflammatory and digestive properties.
5. How does the pineapple ovary contribute to the economy? It is essential for fruit production, which is a major export commodity and a source of income for many tropical countries.
6. What are the nutritional benefits of pineapple fruit? Pineapple fruit is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, beneficial for health.
7. Are there any non-food uses for the pineapple ovary? Yes, it is used in cosmetics, animal feed, and biodegradable packaging.
8. How is bromelain enzyme extracted from the pineapple ovary? Bromelain is extracted from the fruit and stem of the plant for use in various applications.
9. What are the cosmetic uses of pineapple ovary extracts? Extracts are used in skincare products for their hydrating and anti-aging properties.
10. Can pineapple ovary be used in biofuel production? Yes, organic matter from the ovary can be processed into biofuel.
Read Also: 4 Steps to help an Orange Tree Produce Sweet Oranges