The plantain ovary is a crucial part of the plant’s reproductive system. Located within the flower, the ovary plays a key role in the development of the plantain fruit. Understanding the structure, function, and significance of the plantain ovary provides valuable insights into the biology and cultivation of plantains.
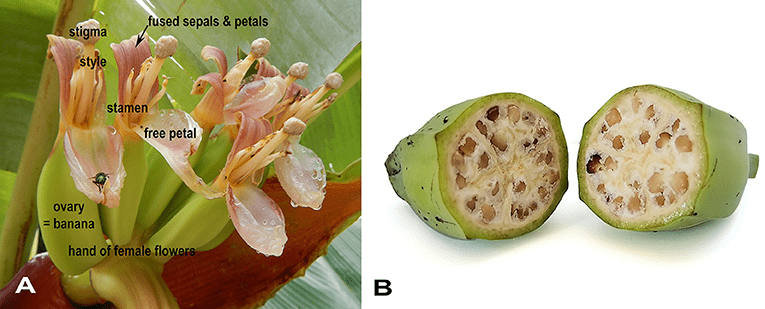
The plantain ovary is found at the base of the flower, positioned beneath the petals and sepals. It is part of the female reproductive organ, known as the pistil, which also includes the stigma and style. The ovary is typically a swollen structure that houses the ovules, which are the potential seeds.
In plantains, the ovary is inferior, meaning it is located below the other floral parts. This positioning helps protect the developing ovules and later the seeds from environmental stress and physical damage. The ovary is generally divided into several compartments, or locules, each containing one or more ovules. The number of locules can vary, but this compartmentalization is essential for the orderly development of the seeds.
The primary function of the plantain ovary is to facilitate the development of seeds and, subsequently, the fruit. When pollination occurs, pollen grains land on the stigma and travel down the style to reach the ovary. Here, the pollen fertilizes the ovules, initiating the process of seed formation. Each fertilized ovule develops into a seed, while the ovary itself transforms into the fruit.
The ovary also plays a role in the protection and nourishment of the developing seeds. Its structure shields the ovules from physical harm and provides a controlled environment for their growth. Additionally, the ovary supplies the necessary nutrients and hormones that support seed development and maturation.
As the ovary matures into the fruit, it undergoes significant changes. The tissues surrounding the ovules expand and thicken, forming the flesh of the plantain. This process involves the accumulation of starches, sugars, and other compounds that contribute to the fruit’s nutritional value and taste. The mature fruit serves as a vessel for seed dispersal, ensuring the continuation of the plant species.
The plantain ovary is of great significance both biologically and economically. Biologically, it is essential for the reproduction and genetic diversity of plantains. By producing viable seeds, the ovary ensures that plantains can propagate and adapt to different environmental conditions. This genetic diversity is vital for the resilience and long-term survival of the species.
Economically, the ovary is the origin of the plantain fruit, which is a staple food in many parts of the world. Plantains are a significant source of carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, making them a crucial component of the diet in various cultures. The successful development of the ovary into fruit directly impacts the yield and quality of the plantain crop, influencing both local food security and international trade.
The ovary’s role in seed formation also has implications for plantain breeding and cultivation. Understanding the processes involved in ovary development and fertilization can help in the creation of improved plantain varieties. These varieties may exhibit desirable traits such as increased yield, disease resistance, and better nutritional content, benefiting farmers and consumers alike.
The plantain ovary is a vital part of the plantain’s reproductive system, responsible for seed development and fruit formation. Its structure and functions are essential for the propagation and genetic diversity of plantains, as well as for the production of a valuable food resource. Understanding the plantain ovary’s role in the plant’s life cycle provides important insights into the biology, cultivation, and economic significance of this key crop.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Plantain Ovary
1. Food Production: The plantain ovary develops into the fruit, which is a staple food in many tropical regions. Plantains are consumed in various forms, such as fried, boiled, or baked.
2. Nutritional Value: Plantains are rich in carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, providing essential nutrients to many populations.
3. Flour Production: Dried and ground plantain ovaries are used to produce plantain flour, a gluten-free alternative for baking and cooking.
4. Animal Feed: Plantain fruit and peels, derived from the ovary, are used as feed for livestock and poultry.
5. Export Commodity: Plantains are a significant export commodity for many tropical countries, contributing to their economies.
6. Ethanol Production: The starchy content of plantains can be fermented to produce ethanol, which is used as a biofuel.
7. Pharmaceutical Uses: Plantain extracts are used in traditional medicine to treat various ailments, including digestive issues and inflammation.
8. Dietary Fiber: Plantain ovaries, when processed, provide dietary fiber that is beneficial for digestive health.
9. Snack Industry: Plantains are processed into various snacks, such as chips and crisps, which are popular worldwide.
10. Baby Food: Plantain puree is used in baby food products due to its high nutritional value and digestibility.
11. Vinegar Production: Plantains can be fermented to produce vinegar, which is used in cooking and as a preservative.
12. Alcoholic Beverages: In some cultures, plantains are used to produce alcoholic beverages through fermentation.
13. Natural Sweeteners: Extracts from ripe plantain ovaries are used as natural sweeteners in food products.
14. Cosmetics: Plantain extracts are used in skincare products for their moisturizing and antioxidant properties.
15. Composting: Plantain waste, including the ovary, is composted to produce organic fertilizer.
16. Culinary Uses: Plantains are used in a variety of culinary dishes, adding flavor and nutritional value.
17. Traditional Dishes: Plantain ovaries are essential ingredients in many traditional dishes across different cultures.
18. Green Plantain Products: Unripe plantain ovaries are used to make products like tostones, which are popular in Latin American cuisine.
Read Also: Importance of a Sick Bay in a Ruminant House
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Plantain Ovary

1. Plantain Fruit: The primary product from the ovary, consumed in various forms.
2. Plantain Flour: Made from dried and ground plantains, used in baking and cooking.
3. Animal Feed: Plantain peels and fruit are used as feed for livestock and poultry.
4. Ethanol: Produced through the fermentation of plantains.
5. Plantain Extracts: Used in traditional medicine and pharmaceuticals.
6. Dietary Fiber: Extracted from processed plantains for digestive health.
7. Plantain Chips: A popular snack made from sliced and fried plantains.
8. Plantain Puree: Used in baby food products.
9. Vinegar: Produced by fermenting plantains.
10. Alcoholic Beverages: Made from fermented plantains in some cultures.
11. Natural Sweeteners: Extracts from ripe plantains used in food products.
12. Skincare Products: Containing plantain extracts for moisturizing and antioxidant benefits.
13. Organic Fertilizer: Compost made from plantain waste.
14. Culinary Dishes: Plantains are used in a variety of dishes for their flavor and nutrition.
15. Traditional Foods: Plantain ovaries are integral to many traditional recipes.
16. Green Plantain Products: Items like tostones made from unripe plantains.
17. Snack Foods: Various snack products made from plantains.
Read Also: Stocking Management for Ruminant Animals
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Plantain Ovary

1. What is a plantain ovary? The plantain ovary is the part of the flower that develops into the plantain fruit.
2. How are plantains used in cooking? Plantains can be fried, boiled, baked, or mashed and are used in a variety of dishes.
3. What are the nutritional benefits of plantains? Plantains are rich in carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, providing essential nutrients.
4. Can plantains be used as animal feed? Yes, plantain fruit and peels are used as feed for livestock and poultry.
5. How is plantain flour made? Plantain flour is made by drying and grinding plantains into a fine powder.
6. What are the medicinal uses of plantains? Plantain extracts are used to treat digestive issues, inflammation, and other ailments in traditional medicine.
7. How do plantains contribute to the economy? Plantains are a significant export commodity for many tropical countries, boosting their economies.
8. Can plantains be used to produce ethanol? Yes, the starchy content of plantains can be fermented to produce ethanol.
9. What are some popular plantain snacks? Plantain chips and tostones are popular snacks made from plantains.
10. How are plantains used in skincare products? Extracts from plantains are used in skincare products for their moisturizing and antioxidant properties.
Read Also: The Impact of Inefficient Waste Management on Oceans

