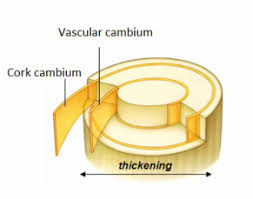
In this article, we shall be looking at the vascular cambium and the cork cambium. The xylem tissue is responsible for the transportation of water and mineral nutrients, while the phloem tissue is concerned with the translocation of foods (Organic Nutrients or Photosynthates) in plants.
Vascular Cambium
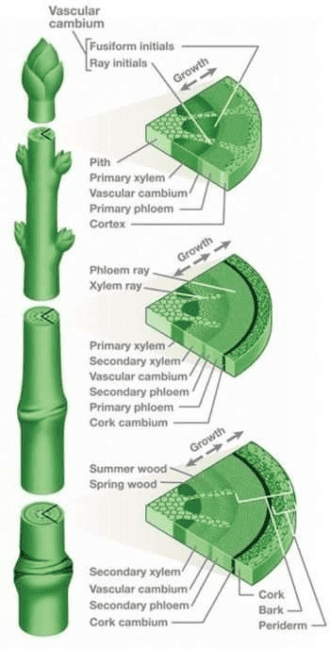
The vascular cambium is a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. The vascular cambium is the source of both the secondary xylem (inwards, towards the pith) and the secondary phloem (outwards), and is located between these tissues in the stem and root. A few leaves even have a vascular cambium (Ewers, 1982).
 Fig 4.5a Multiple cross sections of a stem showing vascular cambium and companion cells (Winterborne, 2005).
Fig 4.5a Multiple cross sections of a stem showing vascular cambium and companion cells (Winterborne, 2005).
The vascular cambium usually consists of two types of cells:
Fusiform initials (tall cells, axially oriented).
Ray initials (almost isodiametric cells – smaller and round to angular in shape).
Vascular cambium is a type of meristem – a tissue consisting of embryonic (incompletely differentiated) cells from which other (and more differentiated) plant tissues originate.
Primary meristems are the apical meristems on root tips and shoot tips. Another lateral meristem is the cork cambium, which produces cork, part of the bark.
Vascular cambia are found in dicots and gymnosperms but not monocots, which usually lack secondary growth.
For successful grafting, the vascular cambia of the stock and scion must be aligned so they can grow together.
Read Also: Methods of Sampling Plant Tissue
Cork Cambium
Cork cambium is a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth that replaces the epidermis in roots and stems.
It is found in woody and many herbaceous dicots, gymnosperms and some monocots, which usually lack secondary growth.
b. Multiple cross sections of a stem showing cork cambium.
Cork cambium is one of the plant’s meristems – the series of tissues consisting of embryonic (incompletely differentiated) cells from which the plant grows.
It is one of the many layers of bark, between the cork and primary phloem. The function of cork cambium is to produce the cork, a tough protective material.
Synonyms for cork cambium are bark cambium, pericambium or phellogen. Phellogen is defined as the meristematic cell layer responsible for the development of the periderm.
Cells that grow inwards from the phellogen are termed phelloderm, and cells that develop outwards are termed phellemor cork (note similarity with vascular cambium). The periderm thus consists of three different layers:
Phelloderm, Phellogen (cork cambium) and Phellem.
Growth and development of cork cambium is very variable between different species, and also highly dependent on age, growth conditions etc. as can be observed from the different surfaces of bark; smooth, fissured, tessellated, scaly, flaking off, etc.
Economic importance of Cork Cambium
Commercial cork is derived from the bark of the cork oak (Quercussuber). Cork has many uses including wine bottle stoppers, bulletin boards, coasters, hot pads to protect tables from hot pans, insulation, sealing for lids, flooring, gaskets for engines, fishing bobbers, handles for fishing rods and tennis rackets, etc.
It is also a high strength-to-weight/cost ablative material for aerodynamic prototypes in wind tunnels, as well as satellite launch vehicle payload fairings, reentry surfaces, and compression joints in thrust-vectored solid rocket motor nozzles.
Many types of bark are used as mulch in the farm. The vascular cambium and cork cambium are both lateral meristem in the vascular tissues of plants.
In summary, the vascular cambium is a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. The vascular cambium is the source of both the secondary xylem and the secondary phloem.
The vascular cambium consists of two types of cells which are Fusiform initials and Ray initials. Vascular cambia are found in dicots and gymnosperms but not monocots
Cork cambium is found in woody and many herbaceous dicots, gymnosperm and some monocots. The function of the cork cambium is to produce the cork, a tough protective material.
Read Also : Definition, Types and Importance of a Business
Frequently Asked Questions
We will update this section soon.