Ticks, scientifically known as Ixodida, are small arachnids that belong to the class Arachnida, which also includes spiders and scorpions. These tiny creatures are ectoparasites, meaning they live on the outside of their host organisms. Ticks are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, where they await the opportunity to attach themselves to passing animals or humans.
Ticks have a distinct life cycle consisting of four stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. Each stage requires a blood meal for sustenance, and they often target mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles. The process of feeding on blood allows ticks to acquire essential nutrients and progress through their life cycle.
One remarkable feature of ticks is their specialized mouthparts, known as a hypostome, which enables them to securely attach to their hosts. This feeding structure is equipped with backward-facing barbs, making it challenging for the tick to be easily dislodged once attached.
Ticks are known vectors of various diseases, such as Lyme disease, babesiosis, and anaplasmosis. The transmission of these diseases occurs when an infected tick feeds on a host, passing the pathogens into the bloodstream. As a result, understanding and preventing tick-borne illnesses are crucial for public health.
To protect oneself from tick bites, individuals should employ preventive measures, including wearing long clothing, using tick repellents, and avoiding tall grass and wooded areas. Additionally, conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities can help remove attached ticks promptly.
Additionally, ticks play a significant role in ecosystems, but their ability to transmit diseases makes them a concern for human and animal health. Understanding their life cycle, habits, and preventive measures is essential in minimizing the risks associated with tick-borne illnesses.
Read Also: Birman Cat Breed Description and Complete Care Guide
Animals Affected by Ticks (Ixodida)

Ticks have a broad impact on various animals, affecting both domesticated and wild species. These arachnids are opportunistic parasites that feed on the blood of their hosts, leading to potential health issues. Animals affected by ticks include mammals, birds, and even reptiles.
Mammals are commonly targeted by ticks, with domestic animals such as dogs, cats, horses, and cattle being particularly vulnerable. In addition to causing discomfort and irritation, ticks can transmit diseases to these animals, posing a threat to their well-being. Wildlife, including deer, rodents, and small mammals, is also susceptible to tick infestations.
Birds are not immune to tick infestations either. Ticks can attach themselves to the feathers or skin of birds, affecting their overall health and potentially leading to the spread of diseases. Avian species that nest in areas with high tick populations may face increased challenges in maintaining their health.
Reptiles, though less commonly associated with ticks, can also be affected. Ticks may attach themselves to the skin of reptiles, especially in habitats where both ticks and reptiles coexist. While the impact on reptiles is not as extensively studied as with mammals and birds, tick infestations can still pose a threat to their health.
The consequences of ticks on animals extend beyond direct health issues. Ticks can contribute to the spread of diseases within animal populations, affecting ecosystems and potentially leading to imbalances in wildlife communities. Additionally, domestic animals suffering from tick-borne diseases may require veterinary attention and medical treatments.
However, ticks have a wide-ranging impact on animals, affecting mammals, birds, and reptiles alike. The consequences of tick infestations go beyond physical discomfort, with the potential for disease transmission and broader ecological implications. Effective tick prevention and control measures are essential to safeguard the health of both domesticated and wild animals.
Damages Caused by Ticks
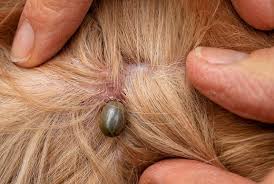
Ticks can inflict various damages, particularly through their feeding habits and potential transmission of diseases. The impacts of ticks extend to both humans and animals, contributing to health issues and economic burdens.
1. Health Issues in Humans: Ticks are notorious for transmitting diseases to humans, with Lyme disease being one of the most well-known examples. Other tick-borne illnesses include Rocky Mountain spotted fever, anaplasmosis, and babesiosis. These diseases can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe complications, affecting the overall well-being of those who are bitten by infected ticks.
2. Health Issues in Animals: Ticks pose a significant threat to the health of animals, both domesticated and wild. Diseases such as anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis, and babesiosis can be transmitted to animals through tick bites. Infestations can lead to weakened immune systems, anemia, and in severe cases, can be fatal.
3. Reduced Livestock Productivity: In agricultural settings, ticks can cause economic losses due to reduced productivity in livestock. Infested animals may experience weight loss, decreased milk production, and impaired growth, leading to financial setbacks for farmers.
4. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may develop allergic reactions to tick bites, experiencing symptoms such as itching, swelling, and redness at the bite site. Severe allergic reactions are rare but can occur in sensitive individuals.
5. Impact on Wildlife: Ticks can also affect wildlife populations by transmitting diseases and causing health issues. In some cases, these impacts may disrupt ecological balances and lead to changes in wildlife dynamics.
6. Veterinary Costs: Pet owners may face veterinary costs associated with treating tick-borne diseases in their animals. Regular preventive measures and tick checks are essential to reduce the risk and associated expenses.
7. Environmental Impact: The presence of ticks and the diseases they carry can influence ecosystems. Imbalances in wildlife populations, particularly those affected by tick-borne diseases, may have cascading effects on the environment.
The damages caused by ticks encompass health issues in humans and animals, economic losses in agriculture, and potential ecological impacts. Preventive measures, such as tick control and awareness of tick-borne diseases, are crucial to mitigate these damages and safeguard both public health and the well-being of various animal species.
Read Also: Balinese Cat Breed Description and Complete Care Guide
Control and Preventive Measures

Controlling and preventing tick infestations is crucial to minimize the associated health risks for humans and animals. Various measures can be employed to manage ticks effectively:
1. Use of Tick Repellents: Applying tick repellents on exposed skin and clothing can be an effective preventive measure. These repellents often contain active ingredients such as DEET or permethrin.
2. Wearing Protective Clothing: When venturing into tick-prone areas, wearing long sleeves, pants, and closed shoes can reduce the chances of ticks attaching to the skin.
3. Tick-Resistant Landscaping: Modifying the landscape to discourage tick habitats is important. This includes keeping lawns well-maintained, clearing tall grasses, and creating barriers like gravel or wood chips between wooded areas and recreational spaces.
4. Regular Tick Checks: Conducting thorough tick checks on the body and clothing after outdoor activities can help detect and remove ticks promptly. Paying special attention to areas like armpits, groin, and scalp is essential.
5. Tick Control Products for Pets: Using tick control products, such as collars, spot-on treatments, or oral medications, on pets can prevent tick infestations. Regular grooming and inspection of pets are also important.
6. Tick-Proofing Homes: Implementing measures to reduce ticks in and around the home is essential. This includes keeping lawns well-trimmed, using insecticides in tick-prone areas, and ensuring a tick-free environment for pets.
7. Avoiding Tick Habitats: Being aware of and avoiding areas with high tick populations, such as dense woods and tall grasses, can significantly reduce the risk of tick exposure.
8. Prompt Removal of Attached Ticks: If a tick is found attached, it should be removed promptly and properly using fine-tipped tweezers. Grasping the tick close to the skin’s surface and pulling upward with steady, even pressure can help avoid leaving mouthparts in the skin.
9. Tick-Testing Programs: Participating in tick-testing programs, where ticks can be sent to laboratories for identification and testing for pathogens, can provide valuable information on the prevalence of tick-borne diseases in specific areas.
10. Educational Outreach: Public awareness campaigns about tick prevention, identification, and the importance of early detection of tick-borne diseases can empower individuals and communities to take preventive measures.
However, a combination of personal vigilance, environmental management, and the use of preventive measures plays a crucial role in controlling and preventing tick infestations. By adopting these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of tick-borne illnesses and contribute to overall public and animal health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Ticks (Ixodida)
1. Q: What are ticks and what is their scientific name?
A: Ticks are small arachnids that belong to the class Arachnida. Their scientific name is Ixodida.
2. Q: Where do ticks live?
A: Ticks are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, where they wait for the opportunity to attach themselves to passing animals or humans.
3. Q: What is the life cycle of ticks?
A: Ticks have a four-stage life cycle: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. Each stage requires a blood meal for sustenance, and they often target mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles.
4. Q: How do ticks transmit diseases?
A: Ticks can transmit diseases by feeding on the blood of infected hosts. When an infected tick feeds on a new host, it can transfer pathogens into the bloodstream, leading to tick-borne illnesses.
5. Q: What diseases can ticks transmit to humans?
A: Ticks can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, anaplasmosis, and babesiosis to humans.
6. Q: How can I protect myself from tick bites?
A: Protective measures include wearing long clothing, using tick repellents, avoiding tick-prone areas, and conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
7. Q: Can ticks affect pets?
A: Yes, ticks can infest pets and transmit diseases to them. Using tick control products and conducting regular pet checks are important preventive measures.
8. Q: What are the symptoms of tick-borne diseases in animals?
A: Symptoms can vary but may include lethargy, fever, joint pain, and in severe cases, anemia or organ failure.
9. Q: How do I safely remove a tick?
A: Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick close to the skin’s surface and pull upward with steady, even pressure. Clean the bite area and your hands with rubbing alcohol, an antiseptic, or soap and water.
10. Q: Are there tick-borne diseases in my area?
A: It’s advisable to check local health authorities or veterinary sources for information on prevalent tick-borne diseases in your specific area.
11. Q: Can ticks be tested for diseases?
A: Yes, tick-testing programs exist where ticks can be sent to laboratories for identification and testing for pathogens.
Read Also: How to Start an Urban Farm
