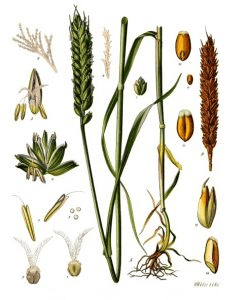
The wheat filament refers to the slender, thread-like structure found within the wheat flower. Specifically, it is part of the male reproductive organ known as the stamen. The stamen typically consists of two main parts: the filament and the anther. The filament is the thin stalk-like structure that supports the anther, which contains the pollen grains.
In the context of wheat, the filament serves as a supportive structure for the anther, holding it aloft within the flower where it can release pollen. The elongated shape of the filament helps position the anther so that it can efficiently shed pollen onto the stigma of the female reproductive organ, facilitating pollination.
During the flowering stage of wheat plants, the filaments extend from the central axis of the flower, each supporting an anther at its tip. As the anther matures, it releases pollen grains onto the surface of the filament. These pollen grains are then transported by wind or pollinators to nearby wheat flowers, where they may come into contact with the stigma, initiating the pollination process.
The length and structure of the wheat filament are important factors that influence the efficiency of pollen dispersal and successful pollination. A well-developed filament ensures that the anther is properly positioned within the flower, maximizing the chances of pollen transfer to receptive stigmas.
The wheat filament is a slender structure within the wheat flower that supports the anther, facilitating the release of pollen during the pollination process. Its role is crucial in ensuring the successful fertilization and subsequent formation of wheat grains, ultimately contributing to the yield and quality of wheat crops.
Economic Importance and Uses of Wheat Filament

1. Agricultural Applications: Wheat filaments play a vital role in agriculture, particularly in the production of wheat grains. These filaments are essential for pollination, facilitating the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organs to the female reproductive organs of the wheat plant, leading to fertilization and grain formation.
2. Food Production: Wheat filaments contribute to food production by ensuring successful pollination and grain development in wheat crops. This process is crucial for the production of wheat-based food products such as bread, pasta, and breakfast cereals, which are staple foods consumed worldwide.
3. Crop Yield: The presence of healthy wheat filaments is essential for maximizing crop yield, as they enable efficient pollination and fertilization, leading to the production of a higher number of grains per plant. This, in turn, contributes to increased agricultural productivity and food security.
4. Genetic Diversity: Wheat filaments play a role in maintaining genetic diversity within wheat populations, as they facilitate cross-pollination between different wheat plants. This genetic diversity is essential for breeding programs aimed at developing new wheat varieties with desirable traits such as disease resistance, yield potential, and environmental adaptability.
5. Biodiversity: Wheat filaments support biodiversity by providing a habitat and food source for various pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and other insects. These pollinators play a crucial role in ecosystem functioning and the pollination of other plant species, contributing to overall environmental health and sustainability.
6. Commercial Value: Wheat filaments have commercial value in industries such as agriculture, food production, and biotechnology. Companies involved in seed production, crop protection, and agricultural research rely on healthy wheat filaments to ensure the success of their operations and the development of new agricultural technologies.
7. Research and Innovation: Wheat filaments are the subject of scientific research aimed at understanding their structure, function, and role in wheat reproduction. This research contributes to advancements in crop science, genetics, and biotechnology, leading to the development of improved agricultural practices and technologies.
8. Environmental Benefits: Healthy wheat filaments contribute to environmental sustainability by supporting natural pollination processes and reducing the reliance on artificial pollination methods. This, in turn, helps conserve resources, minimize environmental pollution, and preserve biodiversity in agricultural landscapes.
9. Cultural Significance: Wheat filaments hold cultural significance in many societies, symbolizing fertility, abundance, and prosperity. They are often featured in cultural rituals, traditions, and celebrations associated with agriculture, harvest festivals, and religious ceremonies.
10. Educational Purposes: Wheat filaments are used for educational purposes in schools, universities, and agricultural extension programs to teach students and farmers about plant reproduction, pollination mechanisms, and the importance of biodiversity conservation in agricultural ecosystems.
Read Also: Apple Maggot: Description, Damages Caused, Control and Preventive Measures
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Wheat Filament

1. Wheat Grains: Wheat filaments contribute to the production of wheat grains, which are harvested and processed into various food products such as flour, bread, pasta, and breakfast cereals.
2. Wheat Straw: After harvesting wheat grains, the remaining wheat straw, which includes wheat filaments, can be used as livestock feed, bedding material, and in the production of biofuels, paper, and building materials.
3. Wheat Pollen: Wheat filaments produce pollen, which is essential for pollination and fertilization in wheat plants. Pollen grains contain male gametes that fertilize the female reproductive organs, leading to grain formation.
4. Wheat Flour: Wheat filaments indirectly contribute to the production of wheat flour, a versatile ingredient used in baking, cooking, and food processing to make a wide range of food products.
5. Wheat Germ: Wheat filaments contain wheat germ, the embryo of the wheat grain, which is a concentrated source of nutrients and is used in food manufacturing and dietary supplements.
6. Wheat Bran: Wheat filaments contain bran, the outer layer of the wheat grain, which is rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals and is used in food processing and animal feed.
7. Wheat Straw Board: Wheat filaments are utilized in the production of wheat straw board, a sustainable alternative to traditional wood-based fiberboard for construction and packaging.
8. Wheat Biomass: After harvesting wheat grains, the remaining wheat straw, which includes wheat filaments, contributes to biomass production, with the stems and leaves being used as feedstock for bioenergy production, composting, and soil improvement.
9. Wheat Aleurone: Wheat filaments contain aleurone, a protein-rich layer of the wheat grain, which is used in food processing to enhance the nutritional value of wheat products.
10. Wheat Protein Concentrate: Wheat filaments are processed to extract wheat protein concentrate, a high-protein ingredient used in food manufacturing to improve texture, moisture retention, and nutritional profile.
Read Also: 17 Medicinal Health Benefits Of Aquilegia canadensis (Eastern Red Columbine)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Wheat Filament
1. What Are Wheat Filaments?
Wheat filaments are the thread-like structures that emerge from the male reproductive organs of the wheat plant, carrying pollen grains essential for pollination and fertilization.
2. What Is the Role of Wheat Filaments in Plant Reproduction?
Wheat filaments play a crucial role in plant reproduction by producing pollen grains that contain male gametes, which fertilize the female reproductive organs of the wheat plant, leading to grain formation.
3. How Do Wheat Filaments Facilitate Pollination?
Wheat filaments release pollen grains into the air or attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and other insects, which transfer pollen from the male reproductive organs to the female reproductive organs of the wheat plant, enabling pollination to occur.
4. What Factors Can Affect Wheat Filament Development?
Several factors can affect wheat filament development, including environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light intensity, as well as genetic factors and agricultural practices such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest management.
5. Are Wheat Filaments Edible?
While wheat filaments themselves are not typically consumed directly as food, they play a crucial role in the production of wheat grains, which are harvested and processed into various food products consumed by humans and animals.
6. How Can Farmers Improve Wheat Filament Development in Their Crops?
Farmers can improve wheat filament development in their crops by selecting high-quality seed varieties, implementing proper crop management practices, and creating favorable growing conditions such as adequate soil fertility, moisture, and sunlight.
7. What Are Some Common Challenges Associated with Wheat Filament Development?
Common challenges associated with wheat filament development include adverse weather conditions such as drought, excessive heat, or frost, as well as pest and disease pressure, nutrient deficiencies, and genetic factors affecting plant growth and development.
8. How Do Wheat Filaments Contribute to Agricultural Productivity?
Wheat filaments contribute to agricultural productivity by ensuring successful pollination and fertilization, leading to the production of a higher number of grains per plant, which ultimately increases crop yield and farmer income.
9. Are There Any Environmental Benefits Associated with Healthy Wheat Filament Development?
Yes, healthy wheat filament development supports environmental sustainability by promoting natural pollination processes, reducing the need for artificial pollination methods, and supporting biodiversity in agricultural landscapes by providing habitat and food sources for pollinators.
10. What Research is Being Conducted on Wheat Filaments?
Research on wheat filaments encompasses various areas such as plant physiology,genetics, pollination biology, and crop improvement, with the aim of understanding their structure, function, and role in wheat reproduction to develop strategies for improving crop yield, quality, and resilience to environmental stressors.
Read Also: Potato Farming Guide – 7 Tips to Grow Sacks Full of Potatoes
