Melilotus, known by its common name Sweet clover, holds a wealth of medicinal health benefits that have been cherished for centuries.
This remarkable plant has a long history of traditional use, and modern research continues to uncover its diverse therapeutic properties.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the botanical description, geographic distribution, chemical composition, harvesting and processing methods, as well as the extensive medicinal health benefits of Melilotus.
Additionally, we will discuss its usage methods, potential side effects, scientific research, and essential safety precautions and recommendations. By the end of this article, you will have a deep understanding of the incredible healing potential of Melilotus.
Melilotus, commonly referred to as sweet clover, is a flowering plant that belongs to the legume family, Fabaceae. This genus comprises various species, with Melilotus officinalis and Melilotus albus being among the most well-known. Historically, Melilotus has been used for its medicinal properties, culinary uses, and even as a forage crop for livestock. The name “Melilotus” is derived from the Greek words “mel,” meaning honey, and “lotus,” referring to the lotus plant, alluding to its sweet fragrance.
The Botanical Description of Melilotus
Melilotus is a plant with distinctive characteristics that make it easily recognizable. Understanding its botanical features is essential for identification and appreciation of its medicinal properties.
1. Life: Melilotus is a herbaceous plant, characterized by its non-woody stems and soft, green foliage.
2. Leaves: The leaves are pinnately compound, meaning that they are divided into leaflets arranged in pairs along the stem. The leaflets are typically lance-shaped with serrated edges.
3. Flowers: Melilotus produces small, fragrant flowers that are usually arranged in elongated clusters. The flowers are typically yellow or white, adding to the plant’s aesthetic appeal.
4. Height: The height of Melilotus plants can vary, but they generally reach heights of 30 to 90 centimeters, or approximately 1 to 3 feet.
5. Growth Habit: Melilotus grows in an upright and bushy manner, with multiple stems branching from the base.
6. Root System: The plant features a fibrous root system that helps it anchor in various soil types.
7. Aroma: One of the distinctive characteristics of Melilotus is its sweet aroma, which is particularly noticeable when the flowers are crushed or bruised.
8. Blooming Period: Melilotus typically blooms from late spring to early summer, depending on the species and local climate conditions.
9. Seed Pods: After flowering, Melilotus forms seed pods that contain small, oval-shaped seeds.
10. Foliage Color: The foliage of Melilotus is typically bright green, adding to its visual appeal.
11. Biennial or Perennial: Melilotus species can be either biennial or perennial, depending on the specific variety. Biennial species complete their life cycle in two years, while perennial species live for more extended periods.
Understanding the botanical description of Melilotus is crucial for proper identification and utilization in various applications, including traditional medicine and herbal remedies.
The Geographic Distribution of Melilotus
Melilotus is a plant that exhibits a wide geographic distribution, thriving in diverse climates and regions around the world. To harness its medicinal benefits, it’s essential to understand where it can be found and cultivated.
1. Native Regions: Melilotus species are native to various parts of Europe, Asia, and North Africa. Melilotus officinalis, in particular, is native to Eurasia.
2. Naturalization: Over time, Melilotus has naturalized in regions beyond its native range. It has adapted to North and South America, as well as other continents.
3. Climate Tolerance: Melilotus is known for its adaptability to different climates. It can grow in temperate, subtropical, and even arid regions.
4. Soil Preferences: These plants thrive in well-drained soils and can tolerate a wide range of soil types, from sandy to loamy.
5. Sunlight Requirements: Melilotus typically prefers full sun or partial shade for optimal growth.
6. Agricultural Use: In addition to its wild growth, Melilotus is cultivated for various purposes, including as a forage crop for livestock.
7. Invasive Species: In some regions, Melilotus species have become invasive, posing challenges to local ecosystems. This highlights the plant’s ability to adapt and thrive in various environments.
8. Medicinal Plant: The adaptability and wide distribution of Melilotus have contributed to its use in traditional medicine across diverse cultures.
9. Conservation: Given its invasive tendencies, the cultivation and management of Melilotus in some regions are subject to conservation efforts to protect native plant species.
10. Horticultural Interest: The sweet fragrance and attractive flowers of Melilotus have also made it of interest to horticulturists and garden enthusiasts.
11. Potential for Cultivation: Individuals interested in harnessing the medicinal benefits of Melilotus can consider cultivating it in their gardens, provided that the local climate and soil conditions are suitable.
Understanding the geographic distribution of Melilotus helps individuals make informed decisions regarding its cultivation and utilization in traditional and modern applications.
The Chemical Composition of Melilotus
The chemical composition of Melilotus is a key factor in understanding its medicinal properties. This plant contains various compounds that contribute to its fragrance and therapeutic effects.
1. Coumarins: Melilotus is rich in coumarins, which are responsible for its sweet scent. Coumarins also have anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory properties.
2. Flavonoids: Flavonoids, including rutin and quercetin, are present in Melilotus and contribute to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
3. Essential Oils: The plant contains essential oils, which are responsible for its fragrant aroma. These oils are often used in perfumes and aromatherapy.
4. Tannins: Tannins found in Melilotus have astringent properties and are often used in traditional remedies for wound healing.
5. Vitamins and Minerals: Melilotus may contain essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to its overall nutritional value.
6. Alkaloids: Some Melilotus species contain alkaloids, which have been of interest in pharmacological research.
7. Saponins: Saponins, present in some varieties, have potential cholesterol-lowering effects.
8. Phenolic Compounds: Phenolic compounds, such as caffeic acid, are found in Melilotus and have antioxidant properties.
9. Isoflavones: Certain Melilotus species contain isoflavones, which have phytoestrogenic properties.
10. Amino Acids: Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and are essential for various biological processes.
11. Flavonoid Glycosides: Melilotus contains flavonoid glycosides, which are compounds known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
12. Fatty Acids: Some Melilotus species may contain fatty acids, which are important for various physiological functions.
13. Cumarinolignans: These compounds are unique to Melilotus and have potential health benefits.
Understanding the chemical composition of Melilotus provides insights into its potential health effects and its applications in traditional and modern medicine.
The Harvesting and Processing of Melilotus
The harvesting and processing of Melilotus are essential steps in making the plant’s medicinal properties accessible. Proper techniques ensure the preservation of its active compounds.
1. Harvesting Time: The optimal time for harvesting Melilotus depends on the intended use. For medicinal purposes, it’s often best to harvest when the plant is in full bloom, as this is when the concentration of active compounds is highest.
2. Harvesting Method: Melilotus can be harvested by cutting the above-ground parts of the plant, including the flowers and leaves. Care should be taken to avoid damaging the roots, allowing the plant to regrow.
3. Drying: After harvesting, the plant material is typically dried to reduce moisture content. Proper drying methods help preserve the plant’s active compounds. Drying can be done in the sun or using specialized drying equipment.
4. Storage: Dried Melilotus should be stored in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption. This helps maintain the quality and potency of the plant.
5. Powdering: Some applications may require Melilotus to be ground into a powder, which can be used in various formulations, such as herbal teas or capsules.
6. Extraction: The extraction of active compounds from Melilotus can be done using different solvents, depending on the target compounds. Ethanol and water are common choices for extraction.
7. Formulation: Melilotus extracts and powders can be used to formulate various herbal products, including teas, tinctures, ointments, and supplements.
8. Quality Control: To ensure the safety and efficacy of Melilotus products, quality control measures should be in place. This includes testing for contaminants and verifying the concentration of active compounds.
The proper harvesting and processing of Melilotus are crucial to obtaining high-quality plant material that can be used in traditional and modern herbal applications.
Read Also: The Different Breeds of Rabbits
The Medicinal Health Benefits of Melilotus (Sweet clover)
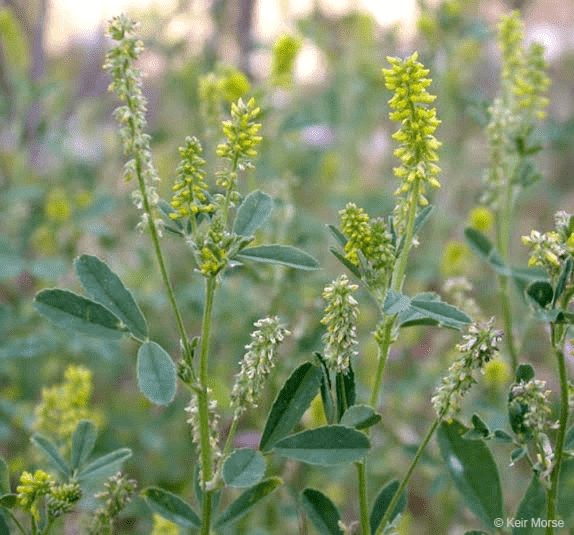

Melilotus offers a wide range of medicinal health benefits that have been recognized for centuries. These benefits encompass various aspects of well-being and health, making Melilotus a valuable plant in traditional and modern medicine.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Melilotus has anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in reducing inflammation and associated symptoms.
2. Anticoagulant Properties: The coumarins in Melilotus have anticoagulant effects, making it useful for improving blood circulation and preventing blood clots.
3. Analgesic Effects: Melilotus can help relieve pain, making it valuable for individuals experiencing discomfort or mild pain.
4. Digestive Aid: Traditional remedies often use Melilotus to support digestion and alleviate digestive discomfort.
5. Wound Healing: The plant’s tannins contribute to its wound-healing properties, helping to stop bleeding and promote the healing of minor cuts and wounds.
6. Cardiovascular Support: Melilotus can have a positive impact on heart health by promoting healthy blood flow and reducing the risk of cardiovascular issues.
7. Respiratory Health: It has been used to address respiratory problems like coughs and congestion.
8. Antioxidant Effects: The flavonoids in Melilotus have antioxidant properties, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
9. Relaxant and Sedative: Melilotus has calming properties, making it valuable for promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety.
10. Aromatherapy: The sweet fragrance of Melilotus is used in aromatherapy for its calming and mood-enhancing effects.
11. Skin Care: Melilotus extracts are used in skincare products for their potential to improve skin texture and reduce inflammation.
12. Menstrual Support: Some women use Melilotus to alleviate menstrual discomfort and cramps.
13. Cholesterol Management: Certain varieties of Melilotus may assist in managing cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
14. Diuretic Effects: It can aid in promoting healthy kidney function and reducing water retention.
15. Lymphatic Support: Melilotus may help stimulate the lymphatic system, aiding in the removal of toxins from the body.
16. Relaxation and Sleep: The plant’s calming properties can help improve sleep quality and relaxation.
17. Skin Irritations: Melilotus ointments and creams are used to soothe skin irritations and mild skin conditions.
18. Anti-Edema Effects: It has been employed for managing edema and swelling, particularly in the legs.
19. Digestive Health: Traditional uses of Melilotus include improving digestive health and reducing symptoms like bloating.
20. Joint Discomfort: Melilotus ointments and poultices are applied topically to alleviate joint discomfort.
21. Liver Health: The plant’s compounds may support liver health and function.
22. Astringent Effects: Melilotus can be used as an astringent for skin and mucous membrane conditions.
23. Culinary Uses: In some regions, Melilotus is incorporated into culinary dishes, adding a unique flavor and potential health benefits to meals.
These diverse medicinal health benefits highlight the versatile nature of Melilotus and its potential applications in different areas of health and wellness.
The Methods of Usage to Achieve the Provided Health Benefits of Melilotus (Sweet clover)
To harness the health benefits of Melilotus, it’s essential to explore the various methods of usage and preparation. This section delves into how the plant is traditionally used and the different forms in which it can be consumed.
1. Herbal Infusions: One of the most common ways to use Melilotus is by preparing herbal infusions or teas. The dried leaves and flowers are steeped in hot water, creating an infusion that can be consumed for its health benefits.
2. Tinctures: Tinctures are alcoholic extracts of Melilotus, offering a concentrated form of the plant’s active compounds. They are typically taken in small, diluted doses.
3. Poultices and Compresses: Melilotus can be prepared as poultices or compresses and applied topically to the skin to address issues like wounds, skin irritations, or joint discomfort.
4. Culinary Uses: In some regions, Melilotus is used in culinary preparations, such as salads, desserts, and condiments, adding a unique flavor to dishes.
5. Aromatherapy: The sweet scent of Melilotus is harnessed in aromatherapy to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and enhance mood.
6. Capsules and Supplements: Melilotus is available in the
form of capsules and supplements for those who prefer a convenient and standardized dosage.
7. Ointments and Creams: Topical ointments and creams containing Melilotus extracts are used for skin-related issues and discomfort.
8. Inhalations: Melilotus can be used in steam inhalations to address respiratory issues or promote relaxation.
9. Bath Additives: Adding Melilotus extracts or dried plant material to baths can have a soothing effect on the skin and the senses.
Understanding the various methods of usage allows individuals to choose the most suitable approach based on their health needs and preferences.
The Side Effects of Using Melilotus Medicinal Plant
While Melilotus offers numerous health benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and exercise caution in its usage. Understanding the possible adverse reactions is crucial for responsible and safe consumption.
1. Anticoagulant Effects: Melilotus contains coumarins, which have anticoagulant properties. While this can be beneficial for circulation, it may increase the risk of bleeding, particularly for individuals already taking blood-thinning medications.
2. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be sensitive or allergic to Melilotus. It’s important to perform a patch test before applying it topically to check for skin sensitivity.
3. Photosensitivity: Melilotus may make the skin more sensitive to sunlight, potentially leading to sunburn. Adequate sun protection is advised during its use.
4. Gastrointestinal Distress: In some cases, the consumption of Melilotus teas or infusions may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including bloating or indigestion.
5. Drug Interactions: Melilotus may interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect blood clotting. Individuals on medication should consult a healthcare provider before use.
6. Avoid During Pregnancy: Due to the potential anticoagulant effects, pregnant individuals should avoid using Melilotus, as it may increase the risk of bleeding complications during childbirth.
7. Not for Children: Melilotus should not be administered to children or infants without consulting a healthcare provider.
8. Overconsumption: Excessive consumption of Melilotus can lead to nausea and dizziness. Adhere to recommended dosages and usage guidelines.
9. Not a Substitute for Medical Treatment: While Melilotus has various health benefits, it is not a replacement for professional medical treatment. Seek medical advice for serious health issues.
Understanding the potential side effects and exercising caution ensures that Melilotus is used responsibly and safely.
Read Also: How to prevent Soldier Ants from invading your Poultry House
The Scientific Research and Studies of Melilotus
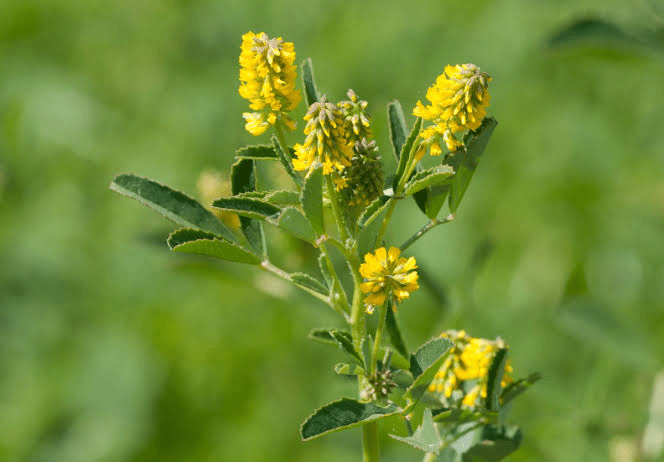
Scientific research has played a significant role in validating the traditional uses of Melilotus and uncovering its potential health benefits. This section explores some of the key studies and findings related to this remarkable plant.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Research has demonstrated the anti-inflammatory effects of Melilotus, which can be valuable in managing inflammatory conditions.
2. Anticoagulant Effects: Studies have confirmed the anticoagulant properties of Melilotus, supporting its use in improving blood circulation.
3. Analgesic Activity: Scientific investigations have shown the analgesic properties of Melilotus, providing a basis for its use in pain management.
4. Wound Healing: Studies have highlighted the wound-healing properties of Melilotus, suggesting its effectiveness in promoting the healing of minor wounds.
5. Cardiovascular Health: Research has explored the potential of Melilotus in supporting heart health by improving blood flow and reducing risk factors for heart disease.
6. Respiratory Applications: Scientific studies have investigated the use of Melilotus for respiratory issues, including its potential in managing coughs and congestion.
7. Antioxidant Effects: Research has confirmed the antioxidant properties of Melilotus, which protect cells from oxidative damage.
8. Sedative and Relaxant Properties: Scientific studies have supported the plant’s use as a sedative, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety.
9. Skin Benefits: Investigations have demonstrated the potential of Melilotus in improving skin health, making it a valuable ingredient in skincare products.
10. Menstrual Comfort: Studies have explored the use of Melilotus for menstrual discomfort and cramps, providing relief to many women.
11. Cholesterol Management: Some research suggests that Melilotus may help manage cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
12. Diuretic Effects: Scientific studies have investigated the diuretic properties of Melilotus, making it useful for promoting healthy kidney function.
13. Lymphatic Stimulation: Research has explored how Melilotus may stimulate the lymphatic system, aiding in the removal of toxins from the body.
14. Traditional Knowledge Validation: Scientific research has contributed to validating the traditional uses of Melilotus and uncovering the mechanisms behind its health benefits.
The scientific research and studies surrounding Melilotus have shed light on its potential health applications and have provided valuable insights into its mechanisms of action.
The Safety Precautions and Recommendations in Using Melilotus Medicinal Plant
Ensuring the safe and responsible use of Melilotus is essential. This section provides important safety precautions and recommendations to guide individuals in their utilization of this medicinal plant.
1. Consultation with Healthcare Providers: Before using Melilotus for medicinal purposes, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking medications.
2. Dosage and Duration: Adhere to recommended dosages and usage durations to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
3. Patch Test for Allergic Reactions: When using Melilotus topically, perform a patch test on a small area of skin to check for allergic reactions or skin sensitivity.
4. Quality Products: Ensure that the Melilotus products you use are of high quality and purity. Choose reputable brands and suppliers.
5. Awareness of Contraindications: Be aware of any contraindications for the use of Melilotus, especially if you have specific health conditions or are taking medications.
6. Monitoring for Side Effects: Pay close attention to how your body responds to the plant. If you experience unusual or severe side effects, discontinue use and seek medical advice.
7. Not a Substitute for Medical Treatment: While Melilotus offers medicinal properties, it is not a replacement for professional medical treatment. Seek medical advice for serious health issues.
8. Children and Infants: Exercise caution when using the plant in children and infants and seek guidance from a healthcare provider.
9. Pregnant and Breastfeeding Individuals: If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, it’s best to avoid the use of Melilotus due to the potential risks.
10. Reporting Adverse Effects: In the event of adverse effects, especially those that may be related to product quality, report them to relevant regulatory authorities and healthcare providers.
11. Sustainable Harvesting: If you are involved in the harvesting of Melilotus, follow sustainable practices to protect wild populations and ecosystems.
12. Support Conservation Efforts: Contribute to conservation initiatives and efforts to protect Melilotus and its natural habitat.
By following these safety precautions and recommendations, individuals can maximize the benefits of Melilotus while minimizing potential risks and adverse effects.
FAQs About Melilotus Medicinal Plant
This section addresses frequently asked questions about Melilotus, providing informative answers to common queries.
1. What are the common names of Melilotus?
Melilotus is commonly known by names such as sweet clover, yellow sweet clover, and white sweet clover.
2. Can Melilotus be grown in home gardens?
Yes, Melilotus can be cultivated in home gardens, provided that the local climate and soil conditions are suitable.
3. Are all Melilotus species used for medicinal purposes?
While several Melilotus species have traditional uses, the specific species and their parts used may vary.
4. Can Melilotus be used in culinary dishes?
In some regions, Melilotus is incorporated into salads, desserts, and condiments, adding a unique flavor to dishes.
5. Is Melilotus safe for aromatherapy use?
Melilotus is considered safe for aromatherapy, and its sweet scent can promote relaxation and mood enhancement.
6. Are there age restrictions for Melilotus usage?
It is advisable not to administer Melilotus to children or infants without consulting a healthcare provider.
7. Can Melilotus be used during pregnancy?
Due to potential anticoagulant effects, pregnant individuals should avoid using Melilotus, as it may increase the risk of bleeding complications during childbirth.
8. Does Melilotus have any drug interactions?
Melilotus may interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect blood clotting. Individuals on medication should consult a healthcare provider before use.
9. How should Melilotus products be stored?
Dried Melilotus should be stored in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and maintain quality.
10. Can Melilotus be used for skincare?
Yes, Melilotus extracts are used in skincare products for their potential to improve skin texture and reduce inflammation.
11. Can Melilotus help with anxiety and stress?
Melilotus has calming properties and can be used to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.
12. Are there any contraindications for Melilotus usage?
Individuals with specific health conditions or taking medications should be aware of potential contraindications and consult healthcare providers.
13. Is Melilotus used for pain relief?
Melilotus has analgesic properties and can be used for pain relief, particularly mild pain.
14. What are the potential adverse effects of using Melilotus?
Adverse effects may include allergic reactions, photosensitivity, gastrointestinal distress, and drug interactions, among others.
15. Can Melilotus be used for respiratory issues?
Melilotus has been traditionally used for addressing respiratory problems, including coughs and congestion.
16. Is Melilotus effective for wound healing?
The tannins in Melilotus contribute to its wound-healing properties, making it useful for minor cuts and wounds.
17. Can Melilotus help with menstrual discomfort?
Some women use Melilotus to alleviate menstrual discomfort and cramps.
18. Is Melilotus used for cardiovascular health?
Melilotus has the potential to support cardiovascular health by promoting healthy blood flow and reducing risk factors for heart disease.
19. Does Melilotus have antioxidant effects?
Yes, the flavonoids in Melilotus have antioxidant properties, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
20. Is Melilotus used for relaxation and sleep improvement?
The plant’s calming properties make it valuable for relaxation and improving sleep quality.
21. Can Melilotus be used for joint discomfort?
Melilotus ointments and poultices are applied topically to alleviate joint discomfort.
22. What is the traditional use of Melilotus in different cultures?
Melilotus has a history of traditional use in various cultures, often for its medicinal properties and pleasant fragrance.
These frequently asked questions provide valuable information about Melilotus and its applications in health and wellness.
In conclusion, Melilotus, commonly known as sweet clover, is a versatile plant with a rich history of traditional use and modern scientific exploration. Its remarkable medicinal health benefits encompass anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, analgesic, and wound-healing properties, among others. Melilotus can be used in various forms, including herbal infusions, tinctures, poultices, and even culinary dishes.
Scientific research has contributed to validating the traditional uses of Melilotus and uncovering its mechanisms of action, highlighting its potential in areas such as cardiovascular health, skin care, and respiratory support.
Responsible usage, consultation with healthcare providers, and adherence to dosage guidelines are crucial to maximizing the benefits of Melilotus while minimizing risks.
By understanding the diverse applications and safety considerations associated with Melilotus, individuals can make informed choices about its utilization for their health and well-being.
Whether in traditional remedies, aromatherapy, or skincare, Melilotus offers a wealth of potential for enhancing overall quality of life.
Read Also: Feeding the World: The Importance of Sustainable Crop Farming
