Agric4Profits.com – Your Comprehensive Practical Agricultural Knowledge and Farmer’s Guide Website…
It’s All About Agriculture – The Way Forward!
Browse Our Categories
Free Consultancy for African Women (Let’s Feed Africa!)
Free Agricultural Consultation Form
Testimonials
Agric4Profits TV
Check out the latest videos from Agric4Profits TV here....

Chicken Ovulation 101: How to Maximize Chicken Egg Production
Discover the fascinating process of chicken ovulation in this step-by-step guide designed especially for chicken farmers and poultry enthusiasts! This video will help you understand how hens produce eggs naturally.… Read More

Regenerative Agriculture Explained: Profit with Soil Health
Farmers are transforming their land and boosting profits through regenerative agriculture! In this video, titled Regenerative Agriculture Explained: Profit with Soil Health, discover how soil restoration, crop rotation, and natural… Read More

5 Climate-Smart Practices to Slash Farm Costs
Climate-smart farming isn’t just eco-friendly — it’s profit-smart! In this video, discover 5 essential practices that help African farmers slash costs while boosting sustainability. Learn how mulching conserves soil moisture,… Read More

Top 5 Precision Farming Tools Every Farmer Needs
Discover the future of farming with our latest video, “Top 5 Precision Farming Tools Every Farmer Needs!” 🌾✨ These 5 smart tools will revolutionize your agricultural practices forever! From high-tech… Read More

How to Use Drones for Field Mapping and Pest Control
Discover how drones are helping farmers reduce losses and boost yields! How drones are used in agriculture for mapping, pest detection, and crop health. Include drone footage and animation to… Read More

What is Precision Agriculture? Simple Guide for African Smallholders
Welcome to Agric4Profits TV, where we turn small farms into big profits. Let’s explore how precision agriculture is transforming African farming. Discover how precision agriculture is revolutionizing farming for smallholder… Read More

The Secret Life of Tortoise Reproduction!
Discover the fascinating world of tortoise reproduction in “The Secret Life of Tortoise Reproduction!” 🐢 In this video, we explore their unique mating rituals, nest-building behaviors, and the incredible journey… Read More

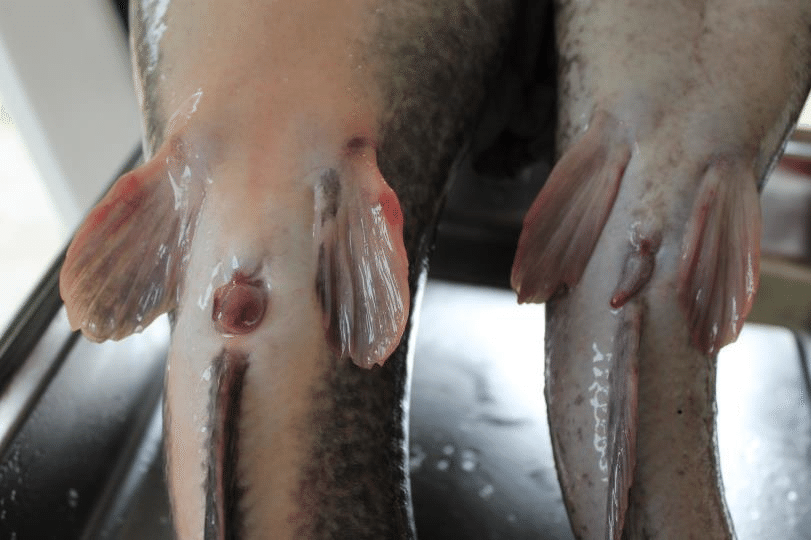
Unveiling Catfish Secrets: Anatomy and Reproduction!
Featured Image Description: Female (Left), Male (Right) Let’s dive into the fascinating world of catfish as we unveil their secrets in this in-depth exploration of catfish anatomy and reproduction! Discover… Read More
Latest Posts
What is Sustainable Development in Agriculture
What is sustainable development in agriculture? Sustainable development in agriculture aims to ensure a sustainable increase in agricultural production, improve the global supply chain, decrease food losses and wastes, and… Read More
Simple Analysis for a Successful Snail Farming Business
Snail farming business also known as Heliciculture or Heliculture or snail rearing is the process of raising edible land snails, primarily for human consumption or cosmetic use. The meat and… Read More
Uses and Economic Importance of Plantain Peels
Plantain peels contain minerals nutrient like potassium, magnesium, iron, zinc, copper and as well as many other nutrient. Most times, plantain peels are often discarded as people thought of it… Read More

Understanding Soil Composition and Its Influencing Factors
Soil serves as a critical environmental component, acting as a repository for human activities and a sink for nutrients essential for crop production. Like other natural materials, soil comprises basic… Read More

Factors Influencing Nitrogen Availability in Agricultural Soils
The availability of nitrogen, a major nutrient required in large quantities by plants, depends on several factors. This article examines the factors affecting the soil’s ability to supply nitrogen for… Read More

Factors Influencing Soil Nutrient Availability for Crop Production
Soil serves as a primary source of nutrients for crop production, expected to supply nutrients to plants in the right amounts and at the appropriate times. However, abundant soil nutrients… Read More

Fundamentals of Soil Chemistry in Agricultural Systems
Soil chemistry, fertility, and soil microbiology represent key disciplines within soil science. Knowledge gained from SLM 201 highlights soil as both a source and sink for plant nutrients and a… Read More

Interconnections Between Soil Chemistry, Water Chemistry, and Pollution Science
This article continues the exploration of soil chemistry, focusing on its relationships with other scientific disciplines, specifically water chemistry and pollution science. Read Also: CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS OF EGG GLUT IN… Read More