Barley internodes are the segments of the barley plant’s stem located between adjacent nodes. Internodes play a crucial role in the structural support and growth of the barley plant, facilitating the transport of water, nutrients, and photosynthetic products throughout the plant.
Economically, barley internodes contribute to the overall productivity and profitability of barley cultivation. They provide the structural framework for the plant, supporting the development of leaves, flowers, and ultimately, grain heads. Strong and healthy internodes are essential for maintaining upright growth and preventing lodging, which occurs when plants bend or break under the weight of grain or adverse weather conditions.
Furthermore, barley internodes influence crop management practices such as planting density, fertilization, and irrigation. Optimal internode length and spacing promote efficient light interception, photosynthesis, and grain filling, leading to higher yields and better grain quality.
Moreover, the length and arrangement of internodes can affect the barley plant’s resilience to environmental stressors such as drought, heat, and wind. Breeding efforts aimed at improving barley varieties often target internode characteristics to enhance stress tolerance and adaptability to diverse growing conditions.
The Economic Importance and Uses of Barley Internodes
1. Structural Support: Barley internodes provide structural support for the plant, facilitating upright growth and stability. This is crucial for maximizing sunlight capture and optimizing photosynthetic efficiency, leading to increased biomass production and yield.
2. Grain Production: Barley internodes contribute to grain production by supporting the development and arrangement of spikelets along the stem. Each internode accommodates multiple spikelets, which ultimately mature into grains, the primary economic product of barley cultivation.
3. Crop Improvement: Studying barley internodes aids in crop improvement efforts to enhance yield, quality, and resilience. Research on internode elongation, distribution, and architecture informs breeding programs aimed at developing varieties with superior agronomic traits and performance.
4. Nutrient Transport: Barley internodes serve as conduits for nutrient transport within the plant. They facilitate the movement of water, minerals, and photosynthates between the roots, leaves, and developing grains, ensuring optimal nutrient uptake and allocation for growth and development.
5. Disease Resistance: Barley internodes play a role in disease resistance mechanisms, particularly against fungal pathogens. Understanding internode physiology and biochemistry informs strategies for breeding disease-resistant barley varieties, reducing yield losses due to diseases.
6. Carbon Sequestration: Barley internodes contribute to carbon sequestration by incorporating atmospheric carbon dioxide into plant biomass through photosynthesis. This process helps mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
7. Biomass Production: Barley internodes are a source of biomass for various applications, including bioenergy, animal feed, and industrial processes. Maximizing internode growth and density enhances biomass yield, supporting sustainable bio-based industries and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
8. Crop Rotation: Barley internodes influence crop rotation strategies to manage soil health and fertility. Rotating barley with other crops helps break pest and disease cycles, improve soil structure, and maintain overall field productivity over successive growing seasons.
9. Phytoremediation: Barley internodes contribute to phytoremediation efforts by absorbing and sequestering contaminants from soil and water. Their extensive root system and vascular network facilitate the uptake and accumulation of pollutants, improving environmental quality in contaminated sites.
10. Research and Education: Barley internodes are subjects of research and education in plant biology, agronomy, and crop physiology. Investigating internode development, anatomy, and function advances scientific knowledge and informs agricultural practices for sustainable crop production.
Read Also: Reasons why Feeding Fishes is very Important
The Products and By-products That Can Be Derived From Barley Internodes
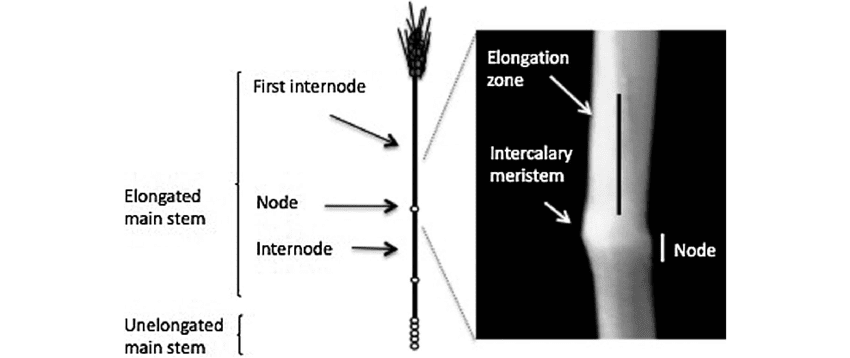
1. Grain: Barley internodes produce grain-bearing spikes, the primary economic product of barley cultivation. Barley grain is used for human consumption, animal feed, brewing, distilling, and various food and beverage applications.
2. Straw: Barley internodes contribute to the formation of straw, a by-product of grain harvest. Barley straw has multiple uses, including animal bedding, mulching, soil amendment, and biomass feedstock for bioenergy production.
3. Bioethanol: Barley internodes, along with other biomass components, can be processed into bioethanol through biochemical or thermochemical conversion processes. Bioethanol serves as a renewable fuel additive or substitute, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel dependence.
4. Silage: Barley internodes, along with other plant parts, can be ensiled to produce silage for animal feed. Silage making preserves the nutritional value of barley biomass, providing a source of forage during periods of feed scarcity or for livestock production.
5. Bioplastics: Barley internodes contain polymers that can be extracted and processed into biodegradable plastics and biopolymers. These materials offer eco-friendly alternatives to conventional petroleum-based plastics, reducing environmental impact and plastic pollution.
6. Green Manure: Barley internodes can be incorporated into the soil as green manure to improve soil fertility and structure. Green manure practices enhance soil organic matter content, nutrient availability, and microbial activity for healthy plant growth.
7. Pharmaceuticals: Barley internodes contain bioactive compounds with potential pharmaceutical applications. Extracts from internodes are investigated for their medicinal properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities.
8. Textiles: Barley internodes fibers can be processed into textiles for various applications, including clothing, upholstery, and industrial materials. Barley fiber textiles offer natural, renewable alternatives to synthetic fibers, reducing environmental impact.
9. Animal Feed: Barley internodes, along with other barley residues, are used as animal feed due to their nutritional value and palatability. Barley forage supports livestock production by providing essential nutrients and dietary fiber for growth and maintenance.
10. Soil Erosion Control: Barley internodes residues contribute to soil erosion control when used as crop residues or incorporated into the soil after harvest. Their presence helps stabilize soil structure, reduce water runoff, and prevent erosion, preserving soil fertility and productivity.
Read Also: Sudangrass (Sorghum × drummondii) Complete Guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s) About Barley Internodes
1. How do barley internodes contribute to grain production?
Barley internodes support the development and arrangement of spikelets along the stem, which ultimately mature into grains, the primary economic product of barley cultivation.
2. Are barley internodes important for crop improvement efforts?
Yes, barley internodes are studied for their role in enhancing yield, quality, and resilience in breeding programs aimed at developing improved barley varieties.
3. Do barley internodes influence disease resistance?
Yes, barley internodes play a role in disease resistance mechanisms, particularly against fungal pathogens. Research on internode physiology informs strategies for breeding disease-resistant barley varieties.
4. How do barley internodes contribute to carbon sequestration?
Barley internodes incorporate atmospheric carbon dioxide into plant biomass through photosynthesis, contributing to carbon sequestration and mitigating climate change.
5. Can barley internodes be used for biomass production?
Yes, barley internodes are a source of biomass for various applications, including bioenergy, animal feed, and industrial processes.
6. Are barley internodes considered in crop rotation strategies?
Yes, barley internodes influence crop rotation strategies to manage soil health and fertility, improve overall field productivity, and break pest and disease cycles.
7. Do barley internodes contribute to phytoremediation efforts?
Yes, barley internodes absorb and sequester contaminants from soil and water, contributing to phytoremediation and improving environmental quality in contaminated sites.
8. What is the significance of barley internodes in research and education?
Barley internodes are subjects of research and education in plant biology, agronomy, and crop physiology, advancing scientific knowledge and informing agricultural practices for sustainable crop production.
9. Are barley internodes used in the production of bioplastics?
Yes, barley internodes contain polymers that can be extracted and processed into biodegradable plastics and biopolymers, offering eco-friendly alternatives to conventional plastics.
10. How are barley internodes incorporated into animal feed production?
Barley internodes, along with other barley residues, are used as animal feed due to their nutritional value and palatability, supporting livestock production and providing essential nutrients for growth and maintenance.
Read Also: The Impact Of Hazardous Waste Disposal in Los Angeles
